We have looked at the installation of Cockpit in Ubuntu Server and how to create & manage KVM virtual machines in Cockpit. There is another popular virtual machine management solution that is free and open source called Virt-Manager.
Let’s look at Virt-Manager and see how we can get it installed and what capabilities and features it provides in managing Kernel Virtual Machine VMs and configuration.
Overview of Virt-Manager
Virt-Manager is short for Virtual Machine Manager. It is a fairly simple tool that is designed to help with managing KVM virtualization environments, including hosts and virtual machines. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) which is usually preferred when managing multiple VMs.
The application itself is built on top of Libvirt. Libvirt is a toolkit that enables an API interface for managing the underlying environment. It provides the ability to have more detailed configuration of your KVM virtual machines than Cockpit. However, Cockpit requires no client installation of software and can accept connections over a simple web browser connection. Whereas, Virt-Manager is software that must be installed.
Features of Virt-Manager
Note the following features of Virt-Manager and the tasks it allows admins to accomplish:
- Intuitive interface – Virt-Manager enables an intuitive GUI for managing the environment
- Good VM management capabilities – With Virt-Manager, you can create, delete, and configure virtual machines. Most of the operations that you need to perform can be accomplished in just a few clicks
- Monitor Resources – In Virt-Manager you can see real-time statistics of CPU, memory, and disk usage for VMs
- Manage storage – You can manage virtual disks for your virtual machines. These capabilities include creating, resizing, and attaching storage
- Manage networking – You can configure and manage virtual networks and network interfaces
- Remote management – It also allows managing remote KVM hosts which allows admins to have management capabilities over multiple hosts using a single interface
How to install Virt-Manager
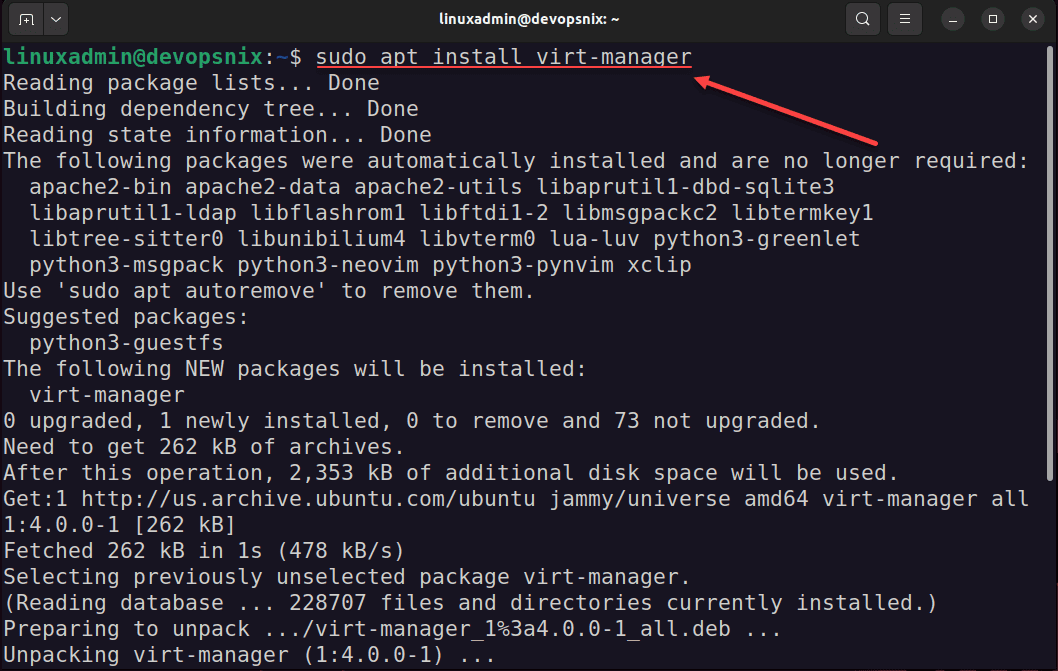
The process of installing Virt-Manager is straightforward. For Debian-based Linux distributions like Ubuntu, you can use the command:
sudo apt install virt-manager
Fedora and RHEL-based distributions:
sudo dnf install virt-manager
Once you have Virt-Manager installed, you can launch Virt-Manager using the following command:
virt-manager
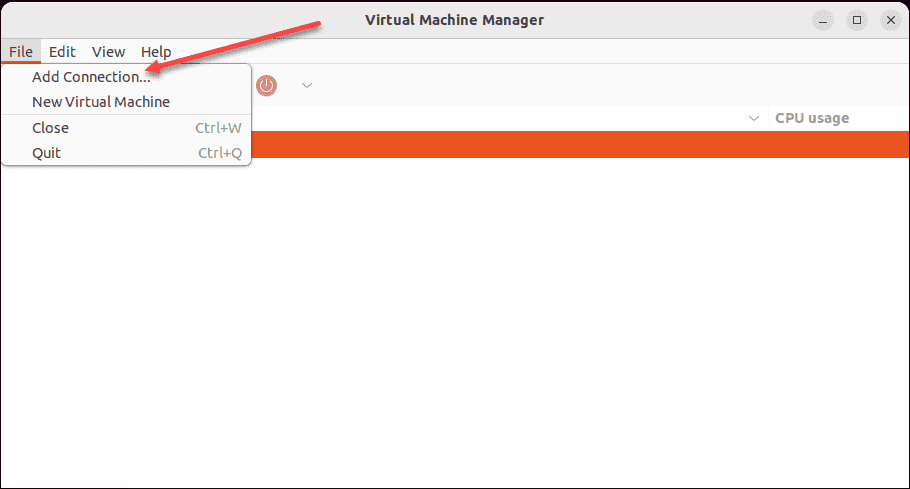
You can easily add a connection to an existing KVM server by clicking File > Add Connection.
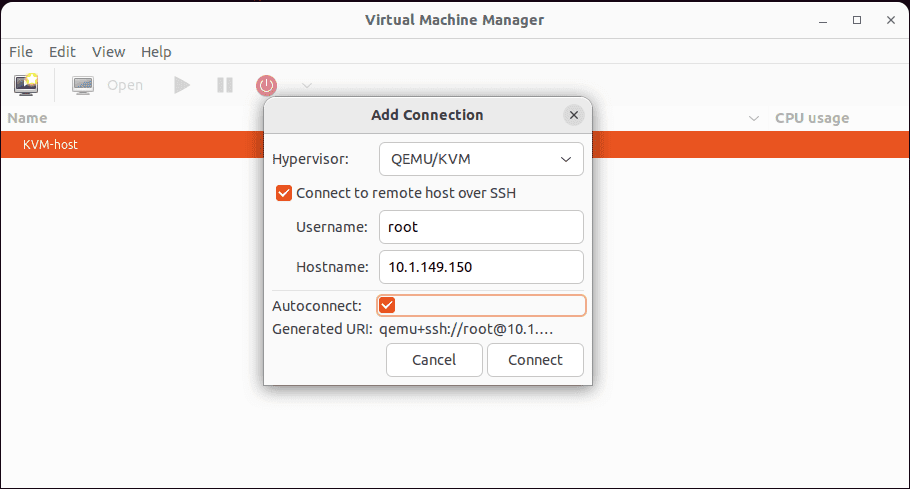
This will launch the Add Connection dialog box. Here we can define the connection to the KVM server host. For the server connection properties, note the following:
- Hypervisor
- Connect to remote host over SSH
- Username
- Password
- Hostname
- Autoconnect
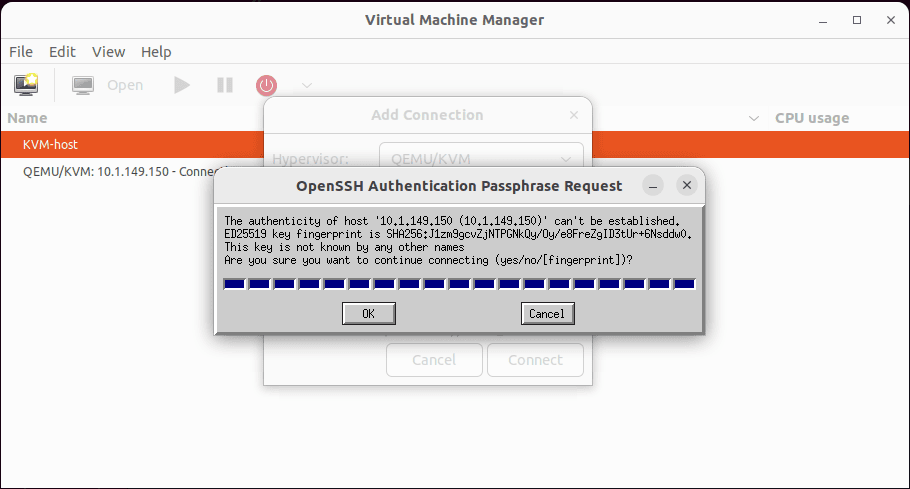
Accept the OpenSSH authentication passphrase request to continue connecting.
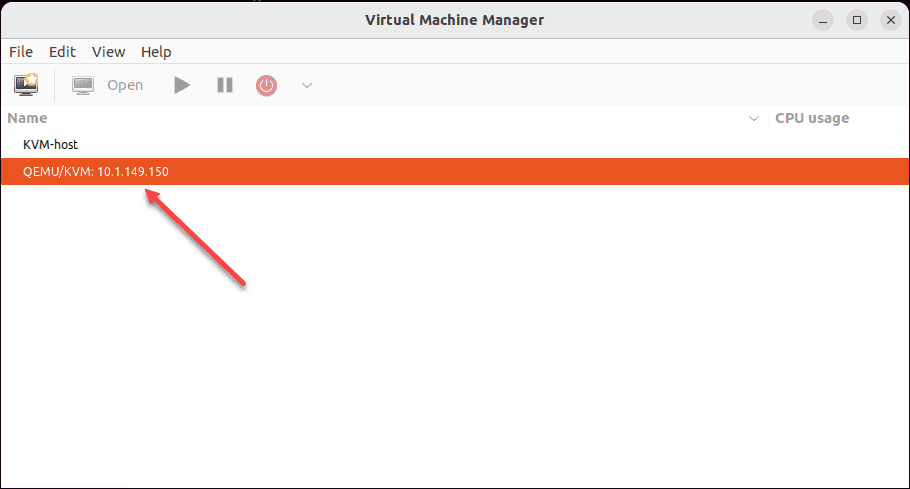
Connection to KVM server host is established in Virtual Machine Manager.
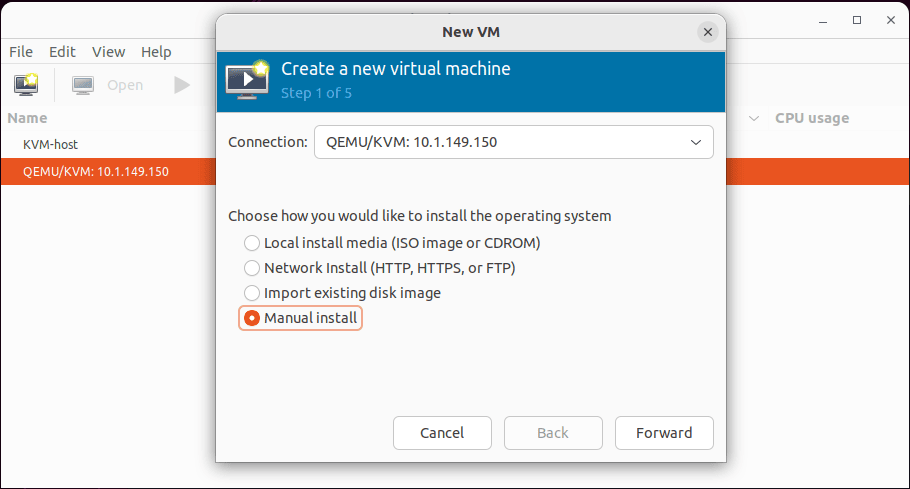
Create a new virtual machine
Let’s take a look at creating a new virtual machine. Select the connection you want to use. You have the following options on how you want to install the operating system:
- Local install media (ISO image or CDROM)
- Network install (HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP)
- Import existing disk image
- Manual install
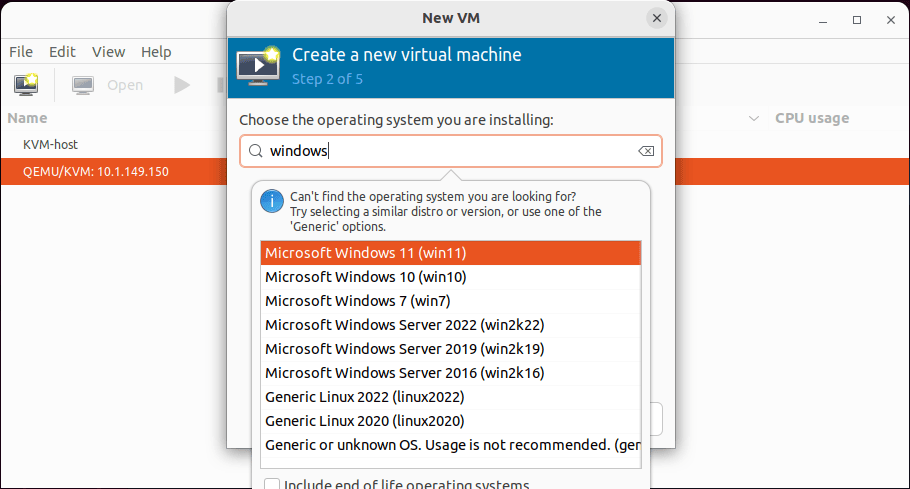
Choose the operating system you are installing in the KVM virtual machine. Start typing in the operating system you want to install like “Windows” and you should start to see the options popping up.
Choose memory and CPU settings.
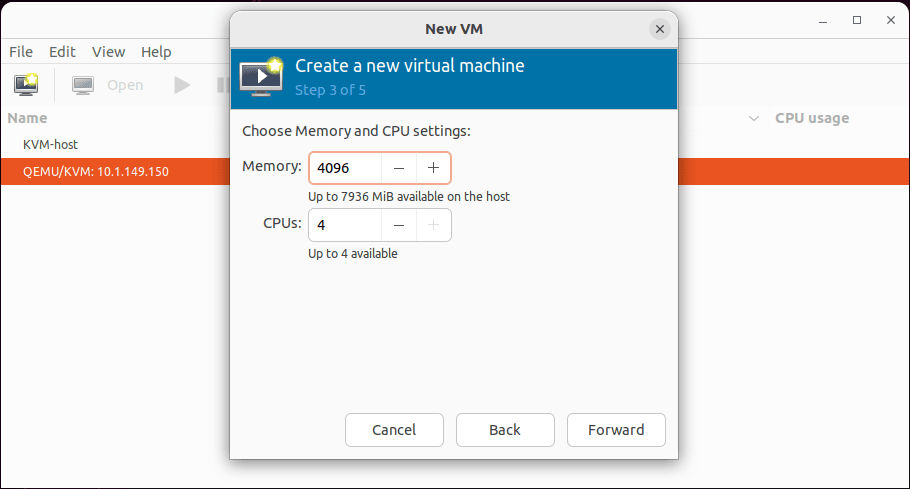
Enable and configure storage for the disk image the KVM virtual machine will use.
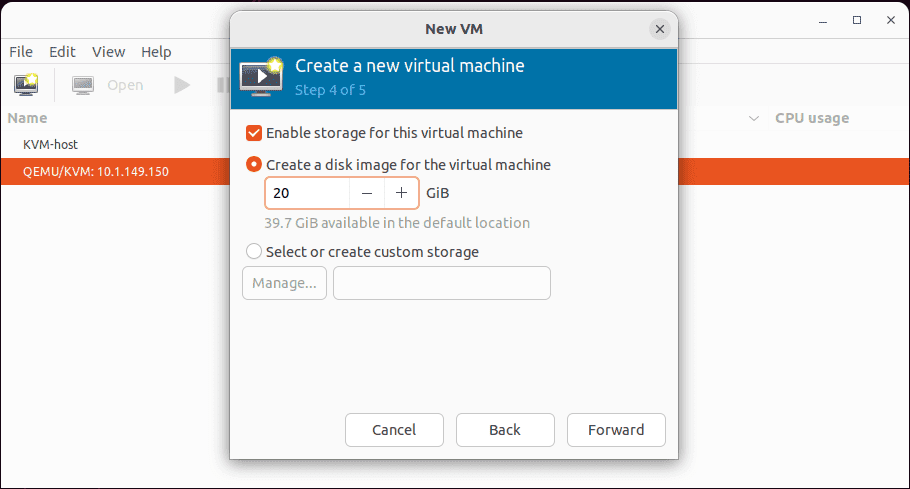
Now, we are ready to create the new virtual machine. Also, select the network you want to connect the VM to. Click Finish.
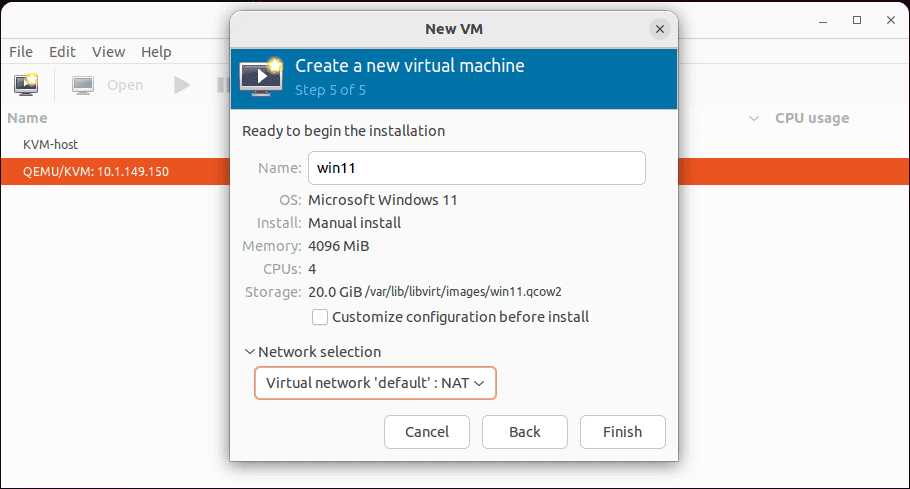
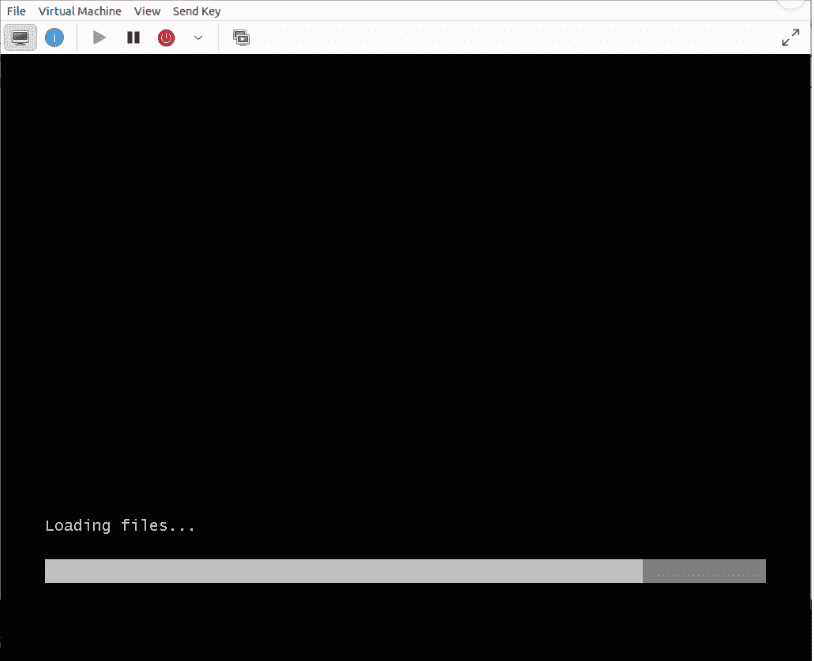
Power on the virtual machine and connect to the Virt-Manager console for the virtual machine.
Troubleshooting
There are a few things to note with Virt-Manager and troubleshooting points.
- Permissions issues – If you run into any permissions-related issues running Virt-Manager or creating virtual machines, make sure you are running the operations using a user in the sudo users group
- You can’t connect Virt-Manager to your KVM host – Make sure you don’t have a firewall filtering traffic between your workstation and the KVM server. Also, validate your connection information (IP or FQDN) and credentials
- The installation fails to install Virt-Manager: Make sure your Linux host is up to date where you attempt to install Virt-Manager. Note the specific error messages
Wrapping up
Virt-Manager is a great way to interact with your Kernel Virtual Machine hosts. It allows you to connect to the host, create and configure virtual machines, and install operating systems in your KVM VMs. The installation process is straightforward and provides more detailed configurations than what you get in Cockpit and other GUI tools. The interface of Virt-Manager looks a little more archaic than Cockpit and other newer tools. However, it is a great way to administer KVM environments and is free to download and install.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment