There is an additional layer of control you can take advantage of with your SAS token, the storage access policy. Storage access policies help admins refine the shared access signature tokens on their storage accounts. You need to be familiar with the storage access policies and how these can be used for the AZ-104 exam.
What are Azure Stored Access Policies?
The storage access policies are an additional layer of security you can place on your shared access signatures SAS tokens deployments on the server side for the storage account. It is part of the overall Secure Access Strategies for Azure Storage. It allows for the grouping of shared access signatures and provides additional restrictions for signatures. By extension, the SAS tokens work in tandem with stored access policies.
These policies also have several capabilities to make the SAS deployment very granular and fine-tuned for your specific environment, including locking down Azure File Sync and Azure Files. Using the storage access policy configuration on your Azure storage account, you can configure the following:
- Start time
- Expiry time
- Permissions for a signature
- Revoke a signature after it has been issued
On what types of storage resources can you apply a stored access policy?
- Blob containers
- File shares
- Queues
- Tables
Use Stored Access Policies
Let’s look at creating Azure Storage Access Policies in the Azure Portal and see how these are configured to manage storage and manage data access.
in the following screenshot, we have navigated to our storage account > containers > containername > settings > access policy > add policy.
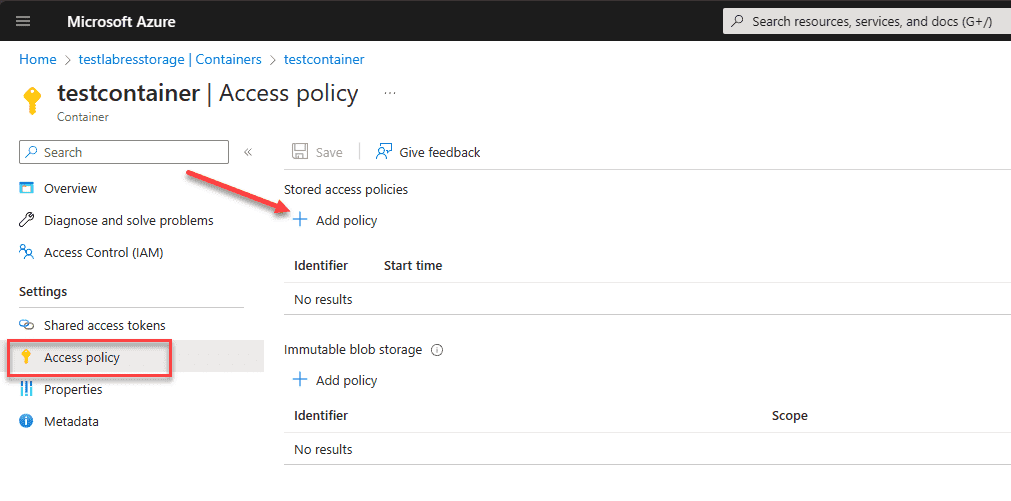
You can choose between Read, Add, Create, Delete, List, and Write permissions.
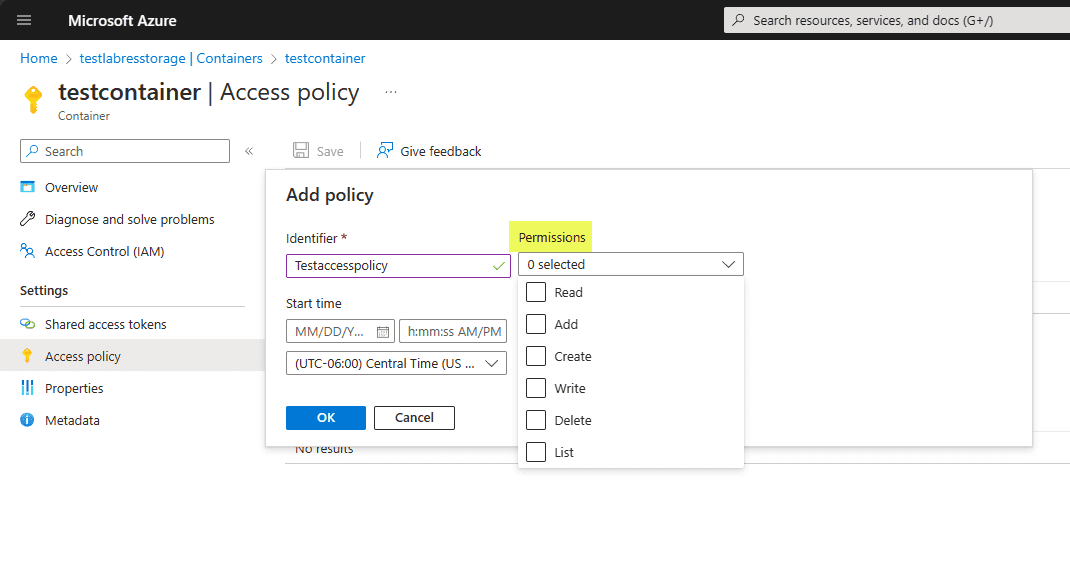
Assigning the Stored Access Policies to Shared Access Signature configurations
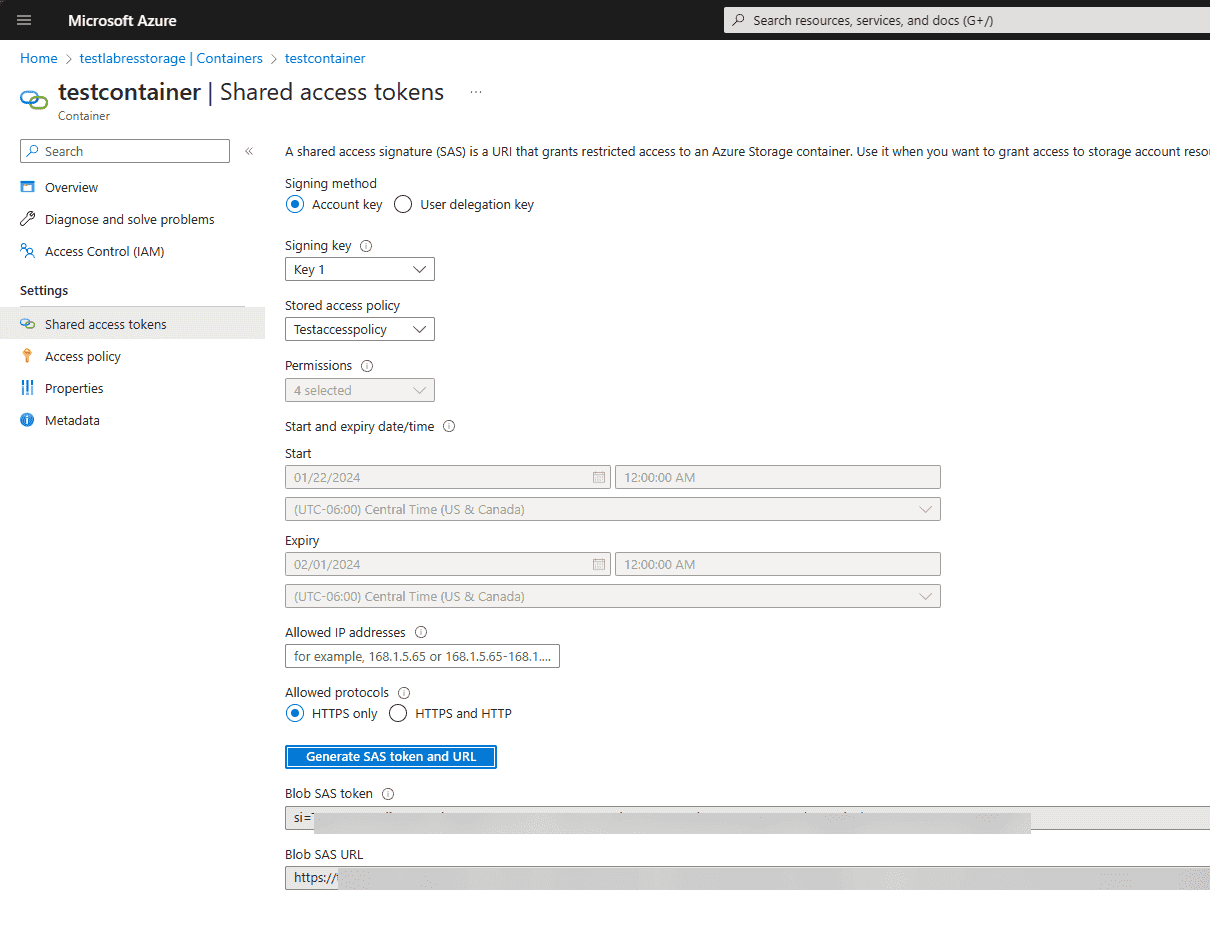
Navigate to Settings > Stored access tokens. Under the Stored access policy dropdown, select your new stored access policy to assign it to the Shared access tokens configuration.
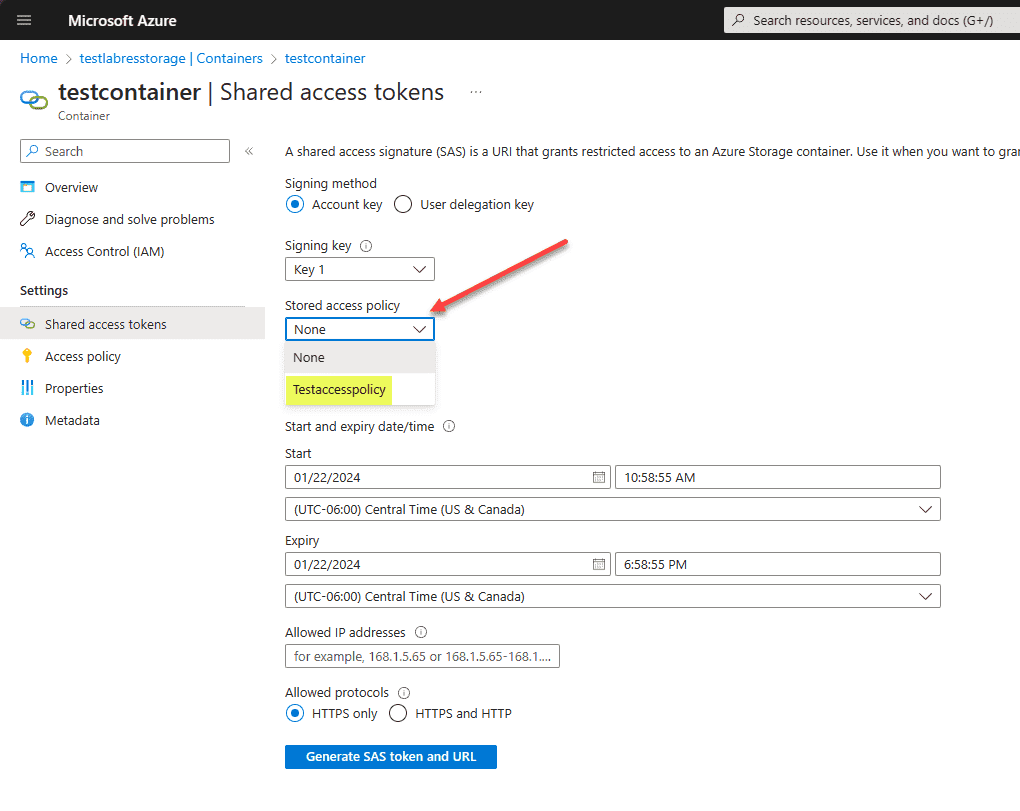
Click the Generate SAS token and URL button.
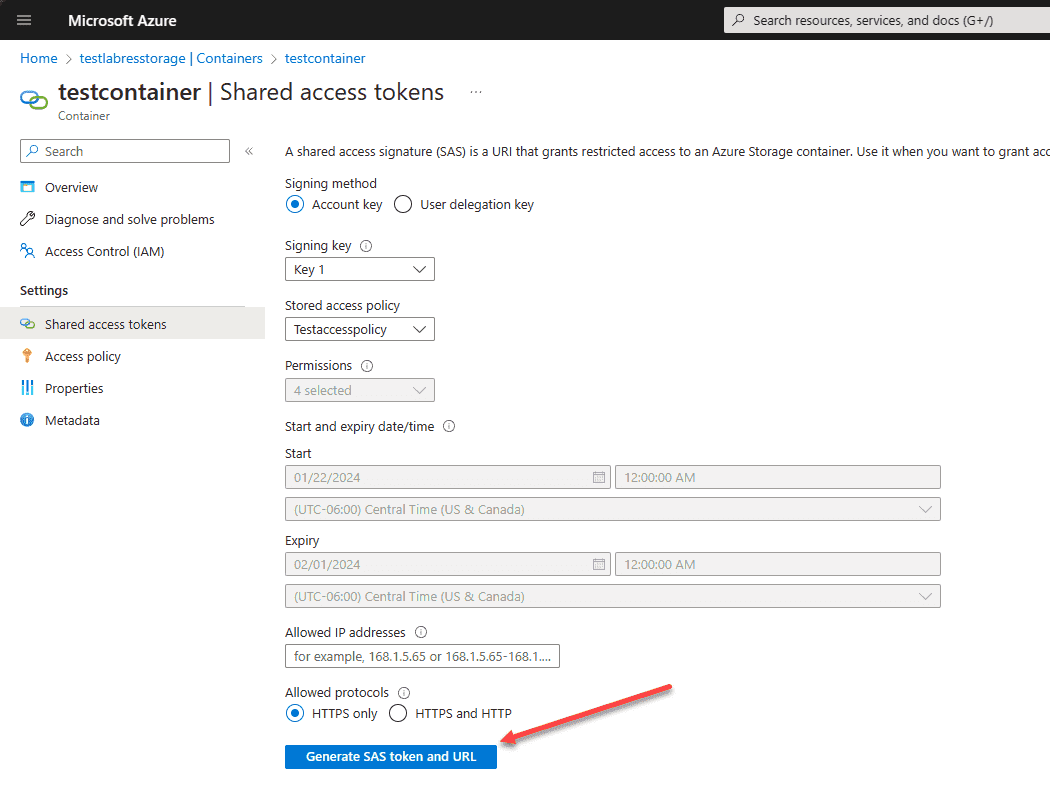
You will be presented with the Blob SAS token and Blob SAS URL.
Using Azure Storage Explorer
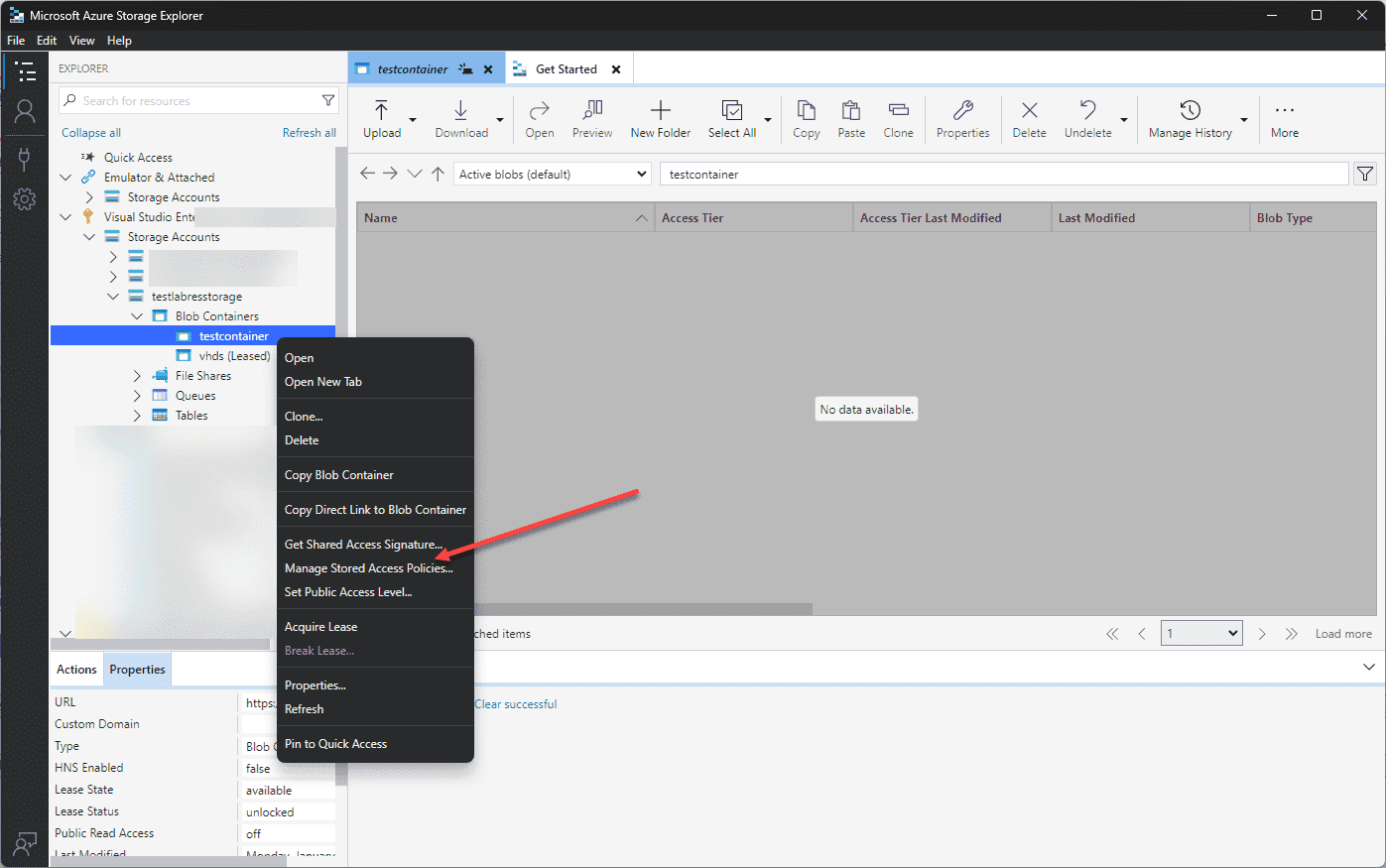
Azure Blob Storage is a key component of Azure’s storage services. Note how we can manage stored access policies on these containers. We can use the Azure Storage Explorer for managing access policies specifically for blob storage.
When you connect to your Azure storage environment and account, you can right-click on the container and choose Manage Stored Access Policies to launch the management of storage policies on the account container.
Then you will see the Access Policies screen that displays the access policies, including expiry time or permissions.
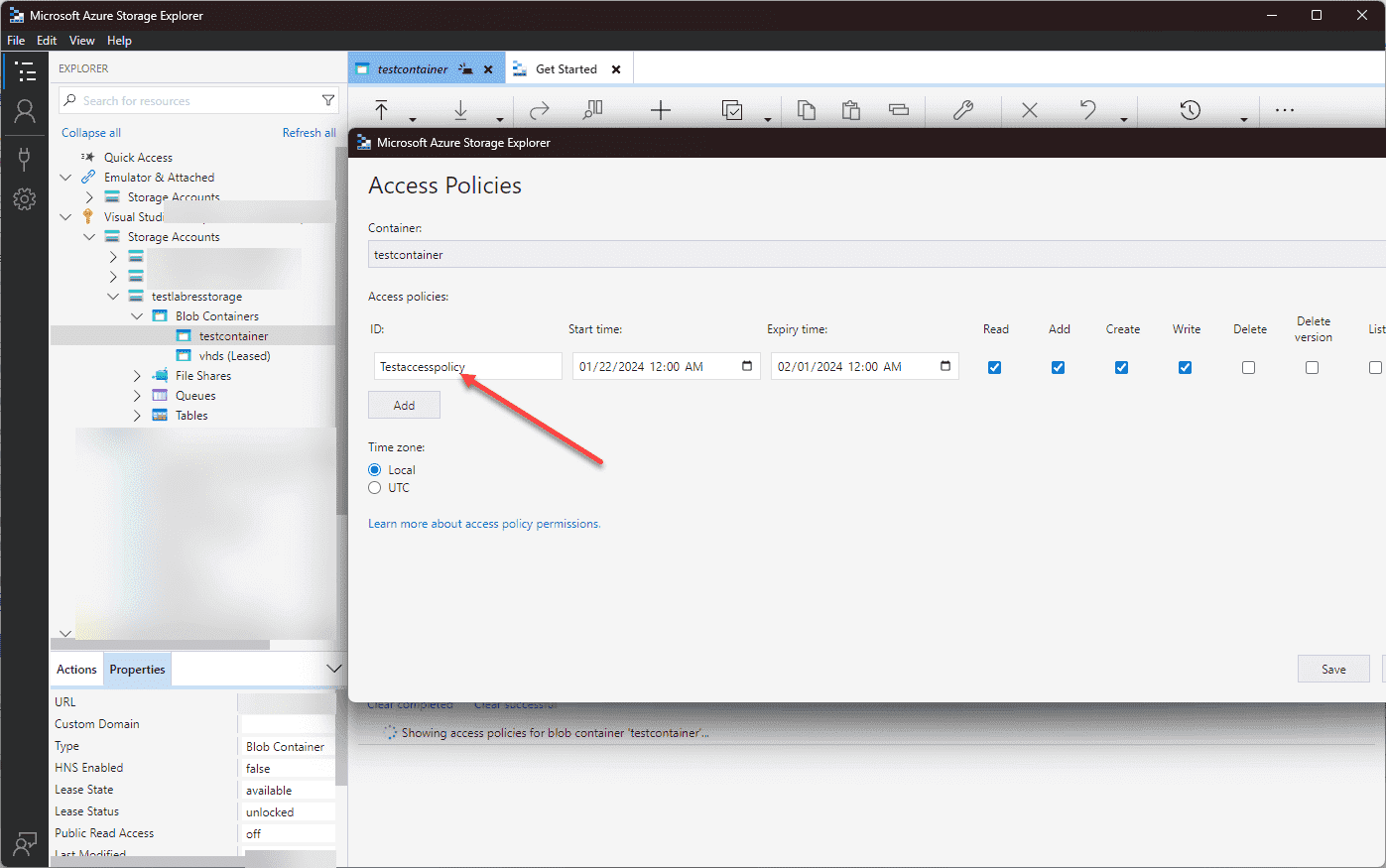
You can do the same for a file share, or other storage resource.
FAQs on Azure Storage Access Policies
How Do Stored Access Policies Enhance Security in Azure Storage?
Stored access policies provide a layer of security by allowing the management of access rights at a granular level. They enable administrators to control access to Azure Blob Storage and File Shares more effectively, allowing permissions to be adjusted without altering the primary access key.
What Is the Difference Between a Stored Access Policy and a Shared Access Signature?
While both are crucial for access management in Azure Storage, a stored access policy provides a centralized approach to manage permissions across multiple shared access signatures. In contrast, a shared access signature grants specific rights to a user for a limited time, creating a unique URL for secure access.
Can Azure Storage Explorer Be Used to Manage Access Policies?
Yes, Azure Storage Explorer is a practical tool for managing Azure Storage. It allows users to interact with Azure Blob Storage, file shares, and queues, and is instrumental in setting up and modifying access policies directly from a user-friendly interface.
How Does Azure File Sync Work with Access Policies?
Azure File Sync synchronizes files between different Azure File shares on your own servers that are housed on-premises. Access policies make sure that only users with proper access who are authorized can sync and modify files.
What Are the Best Practices for Setting Expiry Times on Access Policies?
The best practice is to set expiry times that align with the user’s need for access. For temporary access, short expiry times are recommended. It’s crucial to regularly review and adjust these settings to ensure they meet current requirements and enhance security.
How Can We Ensure Secure Access to Azure Storage?
Secure access can be ensured by implementing strong stored access policies, using shared access signatures judiciously, and regularly monitoring access patterns. Additionally, using tools like Azure Storage Explorer can aid in managing and reviewing access permissions effectively.
What Are the Common Scenarios for Using Stored Access Policies?
Stored access policies are commonly used in scenarios where there is a need to grant or revoke access dynamically, such as in temporary project collaborations, timed access for data analysis, or in scenarios where access needs to be regularly rotated for security reasons.
How Do Access Policies Interact with Virtual Networks in Azure?
Access policies in Azure can be configured to work alongside virtual networks, providing an additional layer of security. This setup allows for restricting access to storage resources only from specific virtual networks, enhancing control over who can access your data.
Wrapping up Stored Access Policies
Stored Access Policies are a great way to further secure your Shared Access Signature tokens. Using the stored access policies, you an effectively set the permissions for the storage resource as well as the expiry time or permissions for the resource. This can help bolster just in time administration and other security features. Be sure to be familiar with the Stored access policies in relation to your Storage account for the AZ-104 exam.
Related Posts:
Microsoft Azure Administrator: AZ-104: Create and Use Shared Access Signature SAS Tokens – Part 23



Leave A Comment