Hyper-V is a very flexible and capable hypervisor that offers many options for virtual machine compatibility and capabilities. In addition, Hyper-V enables admins to choose between two generations of virtual machines with pros and cons. Hyper-V administrators must select the generation of virtual machines that make sense in their environments based on the requirements needed. Let’s look at choosing a Hyper-V virtual machine type for beginners and see which option is best for which use case.
Choosing a Hyper-V Virtual Machine type for beginners
There are many options available when creating a new Hyper-V virtual machine. However, one of the first options you have when creating a new VM is the virtual machine “Generation type.” There are two choices on this screen, Generation 1 and Generation 2. As noted, a message at the bottom states, “Once a virtual machine has been created, you cannot change its generation.” So, it is essential to understand the differences between these virtual machine types.
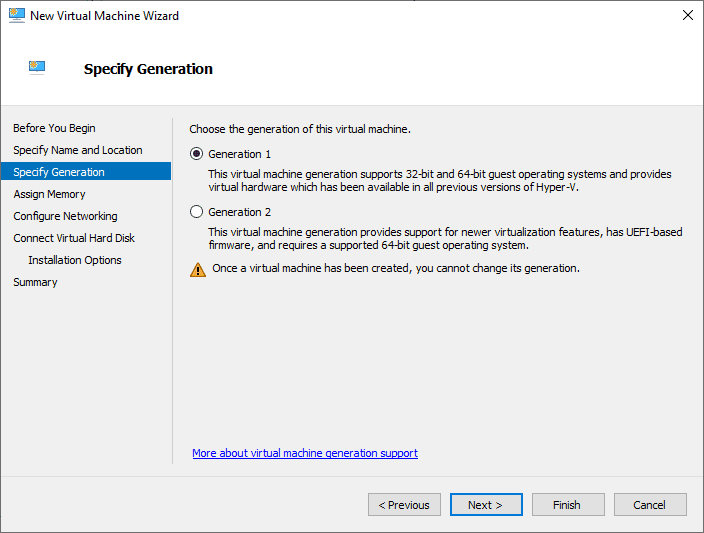
Hyper-V Generation 1 virtual machines
The Hyper-V Generation 1 virtual machine generates a VM most compatible with all versions of Hyper-V. The earliest versions of Hyper-V support Hyper-V generation 1 VMs. Generation 1 virtual machines are configured to resemble traditional computers with BIOS-based systems, supporting 32 and 64-bit versions of Windows and a handful of Linux distributions.
The Hyper-V Generation 1 virtual machine can also run the oldest operating systems, including DOS, OS/2, and other legacy OSes requiring BIOS firmware for the boot process. In addition to the BIOS-based firmware, generation 1 VMs use virtual hardware similar to traditional hardware in physical computers. These virtual hardware components include virtualized IDE, SCSI, and conventional network adapters.
Advantages of using Generation 1 virtual machines
There are advantages to using Generation 1 virtual machines in Hyper-V if you require the most flexibility for your Hyper-V VMs. The Generation 1 virtual machines can run on the broadest range of hardware, including legacy servers and the newest servers to run your virtual machines.
Also, it is important to note that Microsoft Azure now supports both Generation 1 and Generation 2 virtual machines. Previously, if you wanted to migrate VMs to Azure, you must ensure your virtual machine was running as a Generation 1 VM. However, it is important to note that you need to look at the specific VM series you want to run in Azure and see which Generation of virtual machines it supports. You can see the currently supported VM series as it relates to Hyper-V virtual machine generations here: Azure support for generation 2 VMs – Azure Virtual Machines | Microsoft Learn.
Limitations of Generation 1 Virtual Machines
There are some limitations of the Generation 1 virtual machine to note. These include that Generation 1 VMs do not have all the latest security mechanisms built into the architecture. For example, one of the significant security mechanisms you won’t find in Generation 1 Hyper-V virtual machines is Secure Boot and Shielded VMs.
Generation 1 virtual machines also have limited support for UEFI-based firmware. Without the ability to run UEFI firmware, the Generation 1 virtual machine can’t take advantage of the latest performance and functionality features found in the latest UEFI firmware.
Hyper-V Generation 2 virtual machine
Generation 2 virtual machines are the newest generation with modern versions of Hyper-V and provide the most capabilities and features between the two Generation types. The Generation 2 virtual machines also have the largest configuration maximums if you need very wide and large virtual machines in an environment with many resources.
Advantages of using Generation 2 virtual machines
Generation 2 virtual machines can support up to 64 virtual processors and 1 TB of virtual memory. Generation 2 virtual machines are optimized to run modern operating systems with the features and capabilities these afford. Running the latest Windows operating systems as well as Linux OSes benefits from the Generation 2 platform.
Limitations of Generation 2 Virtual Machines
There are a few limitations of Generation 2 VMs to note. These limitations include compatibility. Hyper-V Generation 2 virtual machines are only compatible with Hyper-V versions from Windows Server 2012 R2 and newer. In addition, if you need to run older versions of Hyper-V or older guest virtual machines that need to run operating systems based on DOS or OS/2, these require the BIOS firmware included with Generation 1 VMs.
Like the Generation 1 virtual machines, if you plan to migrate your VM to Azure, you must ensure the VM series you are targeting supports Generation 2 virtual machines. Remember that you cannot change the generation type once the virtual machine has been created.
Which Hyper-V virtual machine type should you choose?
Selecting the generation of a Hyper-V virtual machine is an integral part of creating new virtual machines in your Hyper-V infrastructure. As we have mentioned, both Generation 1 and Generation 2 virtual machines have their pros and cons when compared.
To summarize:
- Generation 1 VMs are an excellent choice when you need to run legacy virtual machines or are inter-operating with legacy Hyper-V infrastructure
- Generation 1 VMs offer the best compatibility between Hyper-V versions and are compatible with all Hyper-V versions from the oldest to the newest
- Generation 2 VMs offer the latest functionality and capabilities as well as much larger configuration maximums
- Run Generation 2 VMs if you require the latest security features such as UEFI, Secure Boot, and Shielded VMs
- Microsoft Azure now supports both Generation 1 and 2. However, you need to choose the generation based on the VM series in Azure, as Generation 1 and 2 VMs work with specific Azure VM series.
Wrapping up
Microsoft Hyper-V provides excellent functionality and capabilities for enterprise organizations and offers two virtual machine generation types to fill most use cases. Choosing the correct virtual machine generation type is essential since you cannot change the VM generation once you have created a virtual machine as one or the other.
Be sure to plan your deployments carefully and ensure you have thought through the requirements and needs for each workload. For most, choosing the latest Generation 2 virtual machine may be the direction to go since it offers the most capabilities and features. However, there are certainly use cases that still require the Generation 1 virtual machine type.
Read More:
Beginners’ Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V: What is Virtual Ethernet Adapter: Part 69
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment