What is Azure AD Conditional Access?
Conditional access is nothing but policies that dictate how a user must authenticate to Microsoft 365 applications. Conditional access policies are powerful and are specific to Organisation and its requirements. It’s nothing but an if-then statement of Assignments and Access controls.
Table of Contents
- How Azure AD Conditional Access differs from Azure MFA & Microsoft 365 MFA?
- Azure AD Conditional Access Templates
- Prerequisites
- How to get Conditional Access in Azure AD?
- Conditional Access templates available in Azure AD and their details
- Conditional access classic policies
- Conclusion
Conditional Access is a part of Azure AD that helps organizations improve security and compliance. By creating Conditional Access policies, you can fine-tune your authentication process for the users.
How Azure AD Conditional Access differs from Azure MFA & Microsoft 365 MFA?
When you look at the overview of these services, all offer the same services which require an additional authentication mechanism while accessing any Microsoft 365 or Azure services.
Azure MFA for Microsoft 365 users is a free offering to Microsoft 365 customers and its main purpose is to protect the Microsoft 365 Services using basic step up authentication. Similarly, Azure MFA is also free now. In the case of Azure AD conditional Access, it supports many features besides MFA along with conditions it satisfies, and the combination of other factors that the policy defines. It’s important to note that Conditional Access is an Azure AD Premium Plan 1 feature, and verify your Azure AD tenant has this functionality before proceeding.
Azure AD Conditional Access Templates
Conditional Access templates are designed to provide a convenient method to deploy new policies aligned with Microsoft recommendations. These templates are designed to provide maximum protection aligned with commonly used policies across various customer types and locations.
Here in this blog, we are providing the details of the Azure AD conditional templates, and using one of the templates we are going to create a Conditional Access policy.
Creating a Conditional Access policy is subject to three critical elements namely Signal, Decision, and Enforcement.
- Signals are nothing but sources, on which the policy is applied. Examples of sources are Users, Groups, Devices, and Applications
- Decision can be to block access or grant access
- Enforcement is the action plan of the policy itself
Prerequisites
- A working Azure AD tenant with Azure AD Premium or trial license enabled. If needed, create one for free
- An account with Conditional Access Administrator privileges
- A test user (non-administrator) that allows you to verify policies work as expected before you impact real users
- A group that the non-administrator user is a member of
How to get Conditional Access in Azure AD?
Log in to the Azure AD portal with your Conditional Access Administrator privileges, choose the category Identity, and select Azure AD Conditional Access. You can also search the word “conditional access” in the search area to find. The below screenshot shows the main page of this Conditional Access service.
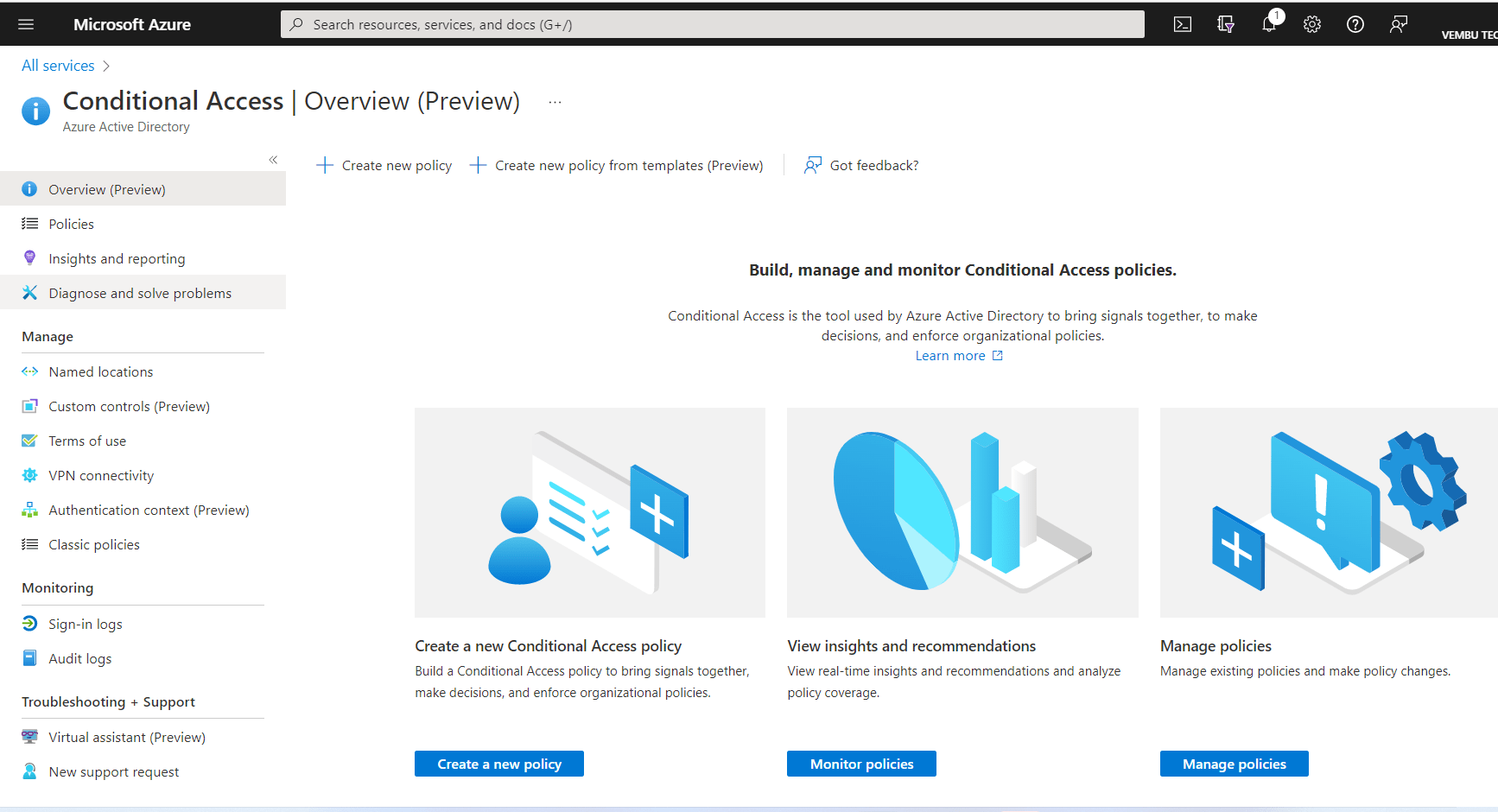
Here you can have two options:
- Creating a new custom policy
- Creating a new policy from templates
We are going to use a template to create a Conditional access policy.
Conditional Access templates available in Azure AD and their details
When you click on “Create a new policy from templates” you need to select a template category either Identities or Devices
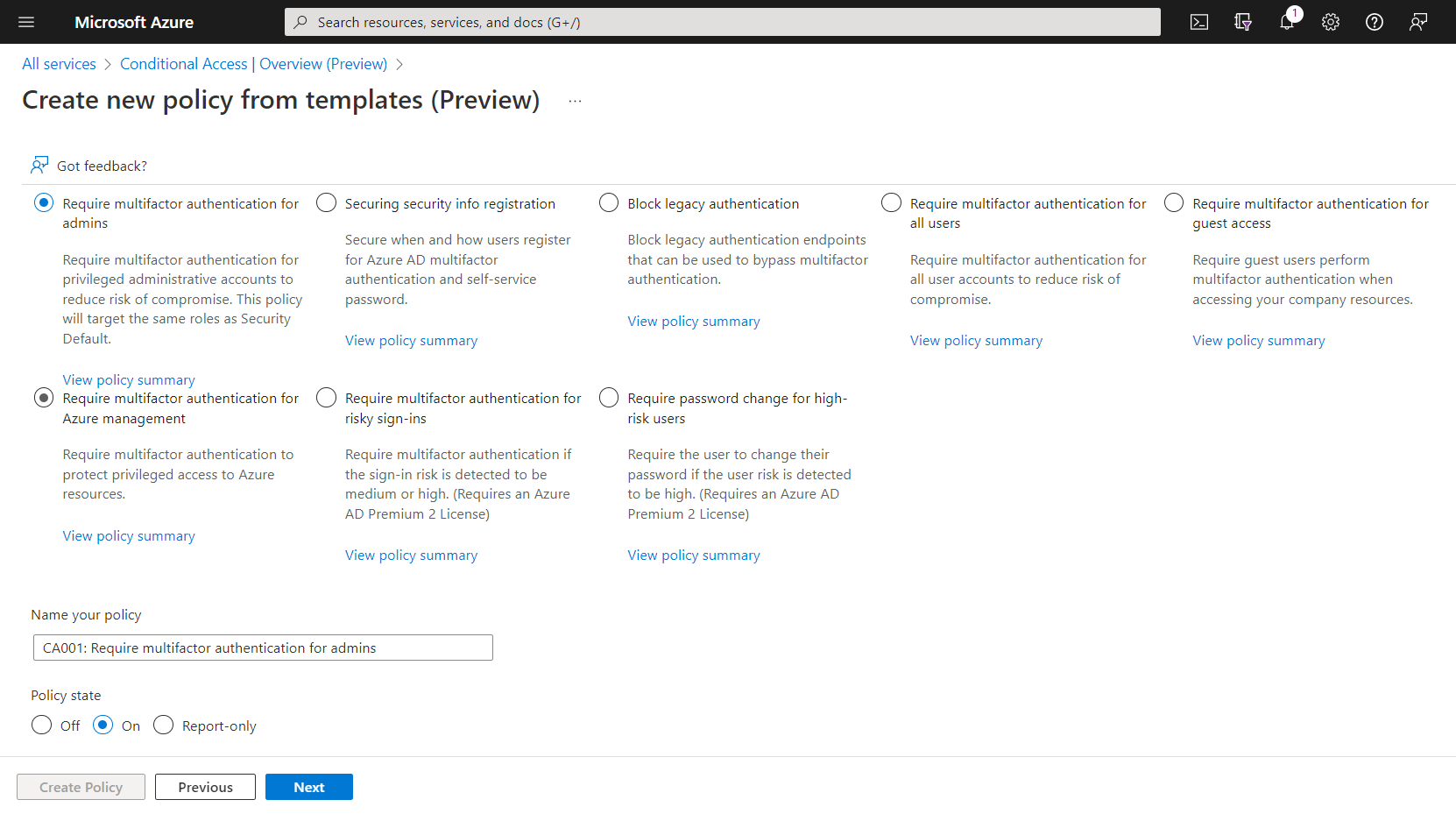
Under Identities category, below are the list of templates to choose:
- Require multifactor authentication for admins – Require multifactor authentication for privileged administrative accounts to reduce risk of compromise. This policy will target the same roles as Security Default
- Securing security info registration – Secure when and how users register for Azure AD multifactor authentication and self-service password
- Block legacy authentication – Block legacy authentication endpoints that can be used to bypass multifactor authentication
- Require multifactor authentication for all users – Require multifactor authentication for all user accounts to reduce risk of compromise
- Require multifactor authentication for guest access – Require guest users perform multifactor authentication when accessing your company resources
- Require multifactor authentication for Azure management – Require multifactor authentication to protect privileged access to Azure resources
- Require multifactor authentication for risky sign-ins – Require multifactor authentication if the sign-in risk is detected to be medium or high. (Requires an Azure AD Premium 2 License)
- Require password change for high-risk users – Require the user to change their password if the user risk is detected to be high. (Requires an Azure AD Premium 2 License)
The below screenshot shows these templates, and user has to select any of the template and choose Policy State to ON
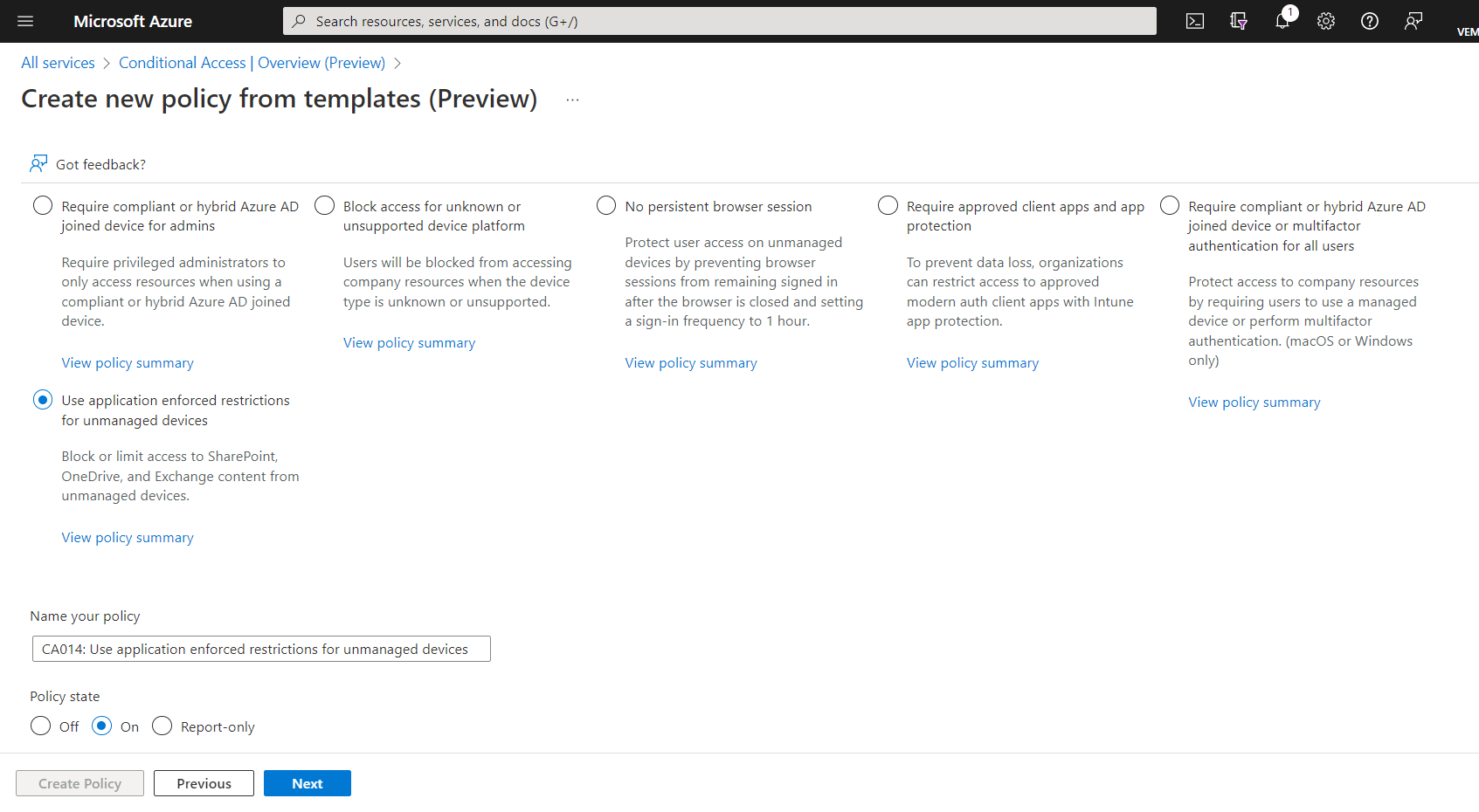
Under Devices category, below are the templates to choose
- Require compliant or hybrid Azure AD joined device for admins – Require privileged administrators to only access resources when using a compliant or hybrid Azure AD joined device.
- Block access for unknown or unsupported device platform – Users will be blocked from accessing company resources when the device type is unknown or unsupported
- No persistent browser session – Protect user access on unmanaged devices by preventing browser sessions from remaining signed in after the browser is closed and setting a sign-in frequency to 1 hour
- Require approved client apps and app protection – To prevent data loss, organizations can restrict access to approved modern auth client apps with Intune app protection
- Require compliant or hybrid Azure AD joined device or multifactor authentication for all users – Protect access to company resources by requiring users to use a managed device or perform multifactor authentication. (macOS or Windows only)
- Use application enforced restrictions for unmanaged devices – Block or limit access to SharePoint, OneDrive, and Exchange content from unmanaged devices
The below screenshot shows these templates, and user has to select any of the template and choose Policy State to ON
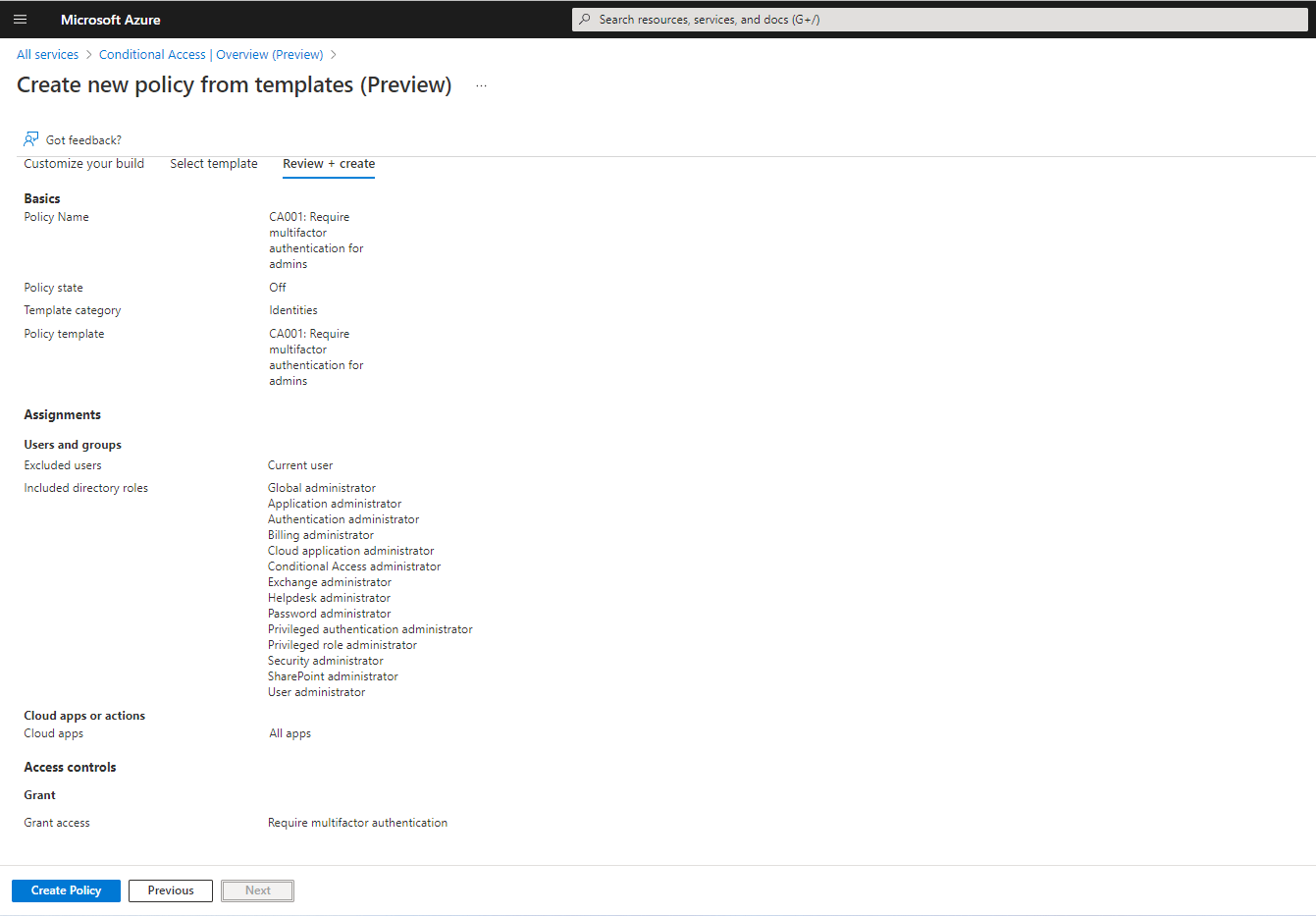
In this blog, we are choosing Identities Category, and choose the template “Require multifactor authentication for admins” You can set the policy state to OFF during creation, and later made to ON
Click Next to the final and review stage, there you click “Create policy” to proceed.
After a few minutes, your policy will be ready and is available under Policies, on clicking the policy name, you will get all the details of the policy as shown below, you can also enable the policy here.
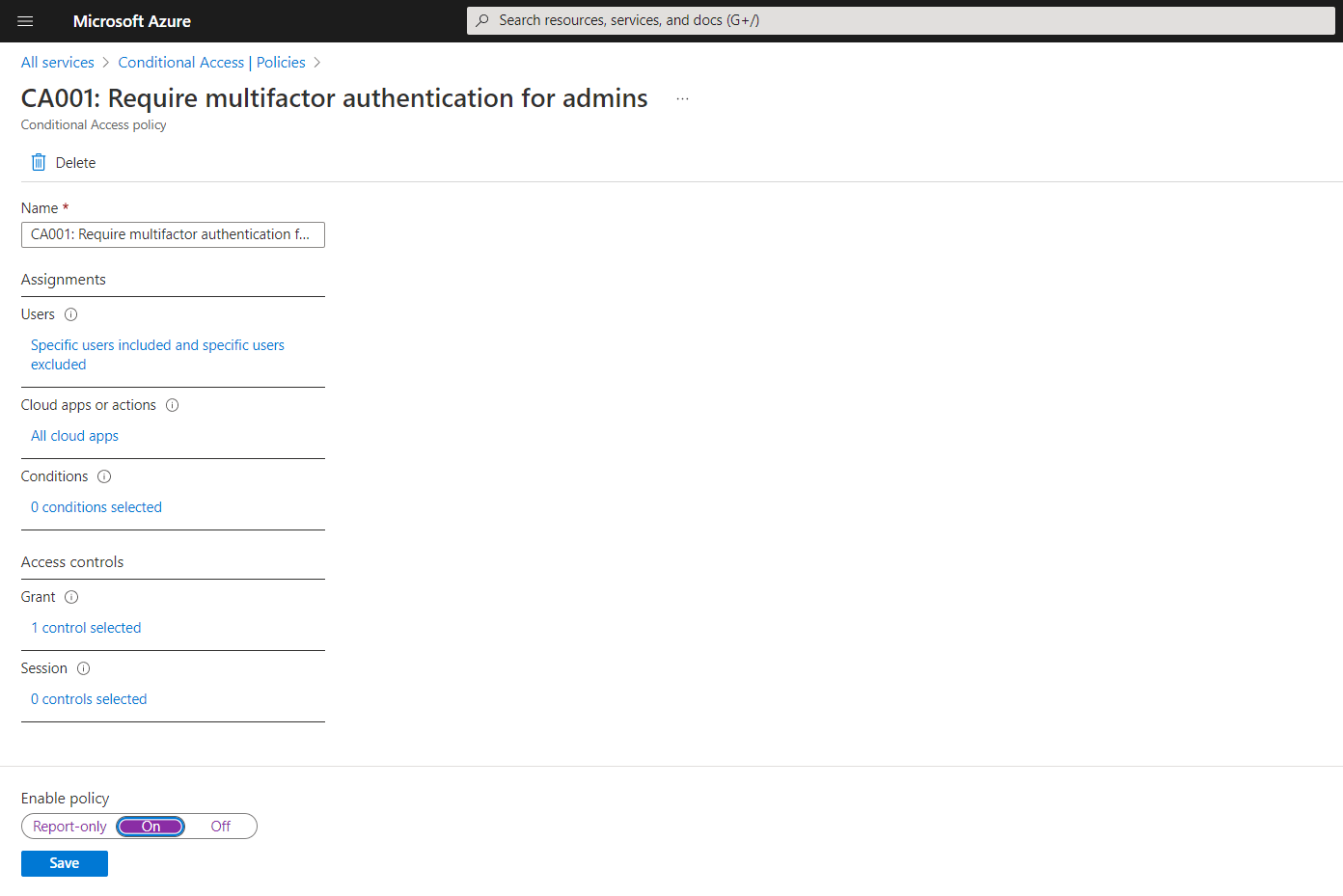
Conditional access classic policies
Conditional access classic policies are nothing but older policies, which are created under the legacy portals such as,
- The Azure classic portal
- The Intune classic portal and
- The Intune App Protection portal
On the Conditional Access page, you can access your classic policies by clicking Classic policies under the Manage section, as shown in the below image.
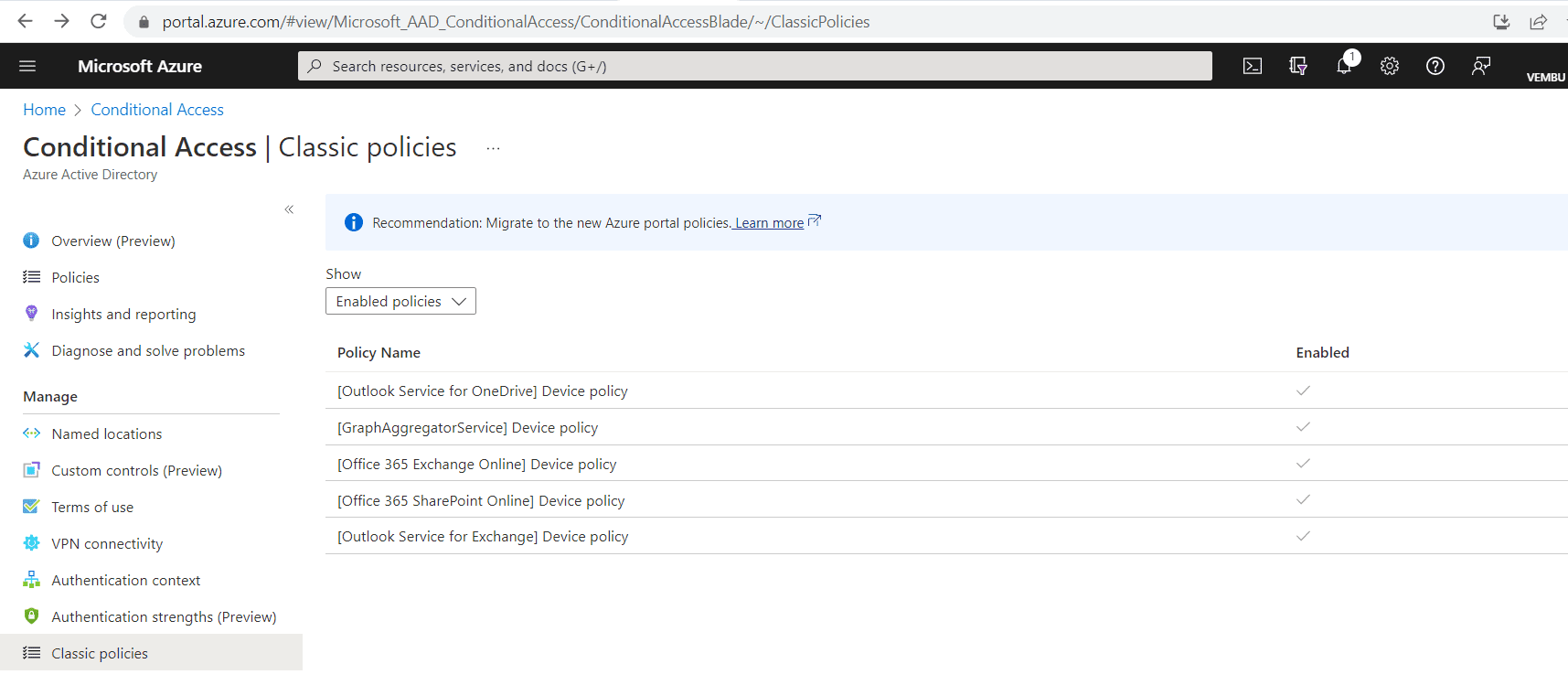
The details view of a classic policy allows you to document the settings, modify the included or excluded groups, and disable the policy. You can also use the classic policies for migration to current conditional access policies after disabling it. According to Microsoft documentation, a few important migration considerations are listed out when you use classic policies. They are:
- The classic policies continue to work side by side with the new policies until the user disables or delete them.
- While classic policies are tied to a specific cloud app, users can select as many cloud apps as they need to, in a new policy.
- Controls of a classic policy and a new policy for a cloud app require all controls (AND) to be fulfilled.
- In a new policy, users can combine multiple conditions based on the classic policies output depending on the user requirement.
Conclusion
Azure Active Directory (AD) Conditional Access provides added security by allowing access to the applications across cloud and on-premises only from trusted and compliant devices. Since it is a policy-based approach, users can configure a Conditional Access policy with the required conditions to apply the access controls in a few steps. Conditional Access provides you with great configuration flexibility. However, great flexibility also means users should carefully review each configuration policy before releasing it to avoid undesirable results.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment