Introduction:
This document provides a comprehensive guide on how to import an AWS RDS MySQL database from an Amazon S3 backup. Restoring from backups is crucial for recovering data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or system failures. By following the steps outlined in this document, you can ensure the successful restoration of your RDS MySQL database. While importing an AWS MySQL DB, please ensure that the DB export in S3 is not encrypted.
Restoring AWS RDS MySQL Database from AWS S3
Step 1: Accessing the AWS Management Console
Log in to your AWS account using appropriate credentials.
Step 2: Navigating to the RDS Service
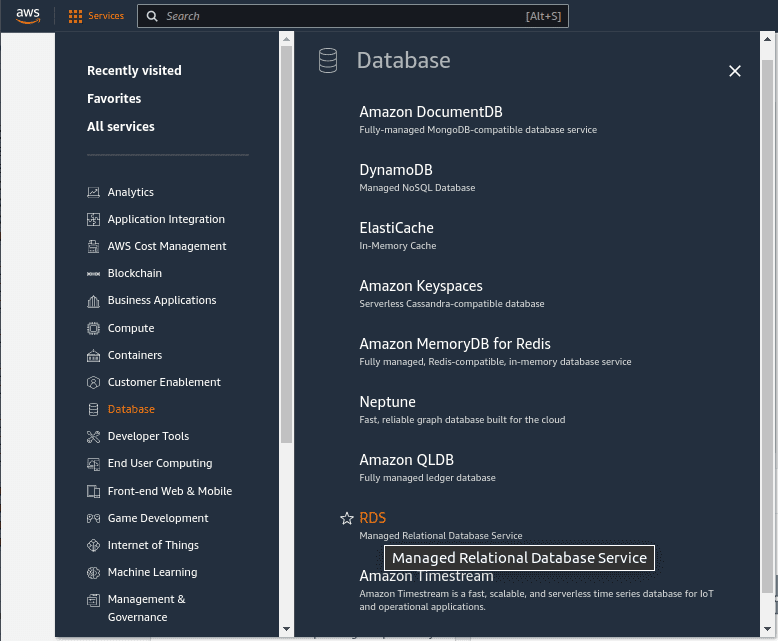
Once logged in, select the “Services” dropdown menu at the top of the console.
In the “Database” section, click on “RDS” to open the Amazon RDS service.
Step 3: Selecting the RDS MySQL Database
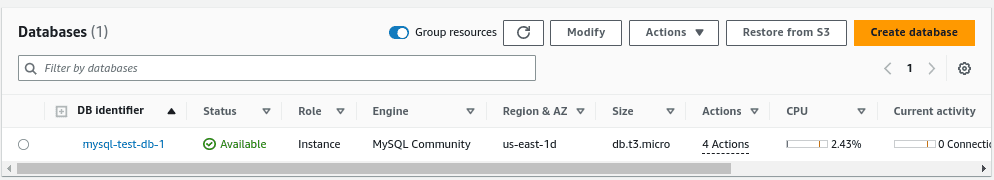
In the RDS service, choose the desired region from the top-right corner.
Locate and select the RDS MySQL database instance you want to back up.
In this tutorial, we will backup the MySQL database named mysql-test-db-1

Step 4: Initiating the restore process
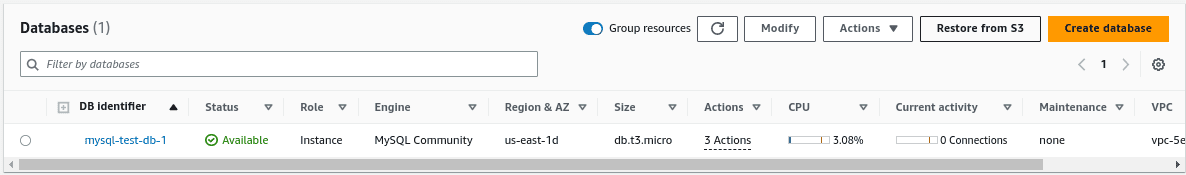
In the RDS console, select the database to restore and choose “Restore from S3” and provide all the required details to restore the DB.
Select the Storage bucket name and the directory in which the backup is exported.
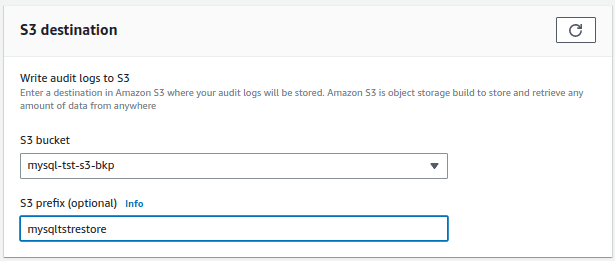
In the next screen, Enter the S3 destination bucket to write the audit logs.
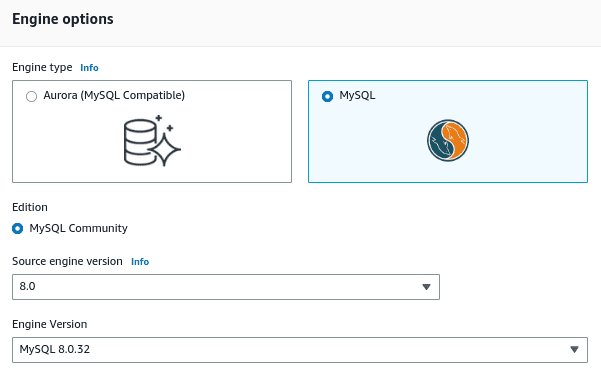
Select the engine version of the database to be restored. Here we choose the source and MySQL engine version 8.0.
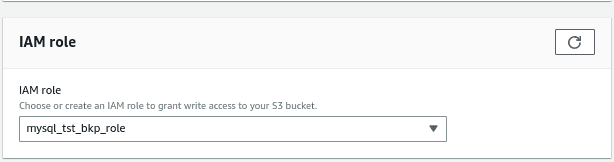
Select the IAM role that have permissions to restore the DB from the S3 bucket.
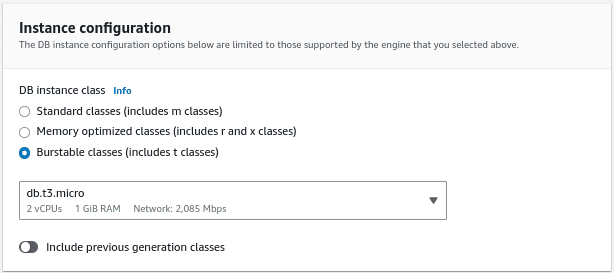
Select the instance configuration. Here we are choosing the db.t3.micro instance type.
Enter a DB identifier name
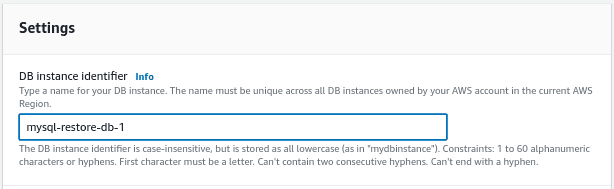
Enter the credentials to access the database
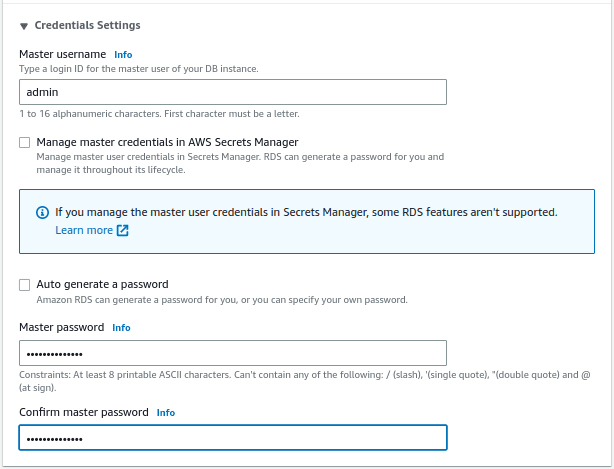
Select the storage capacity and storage type for the DB to be restored
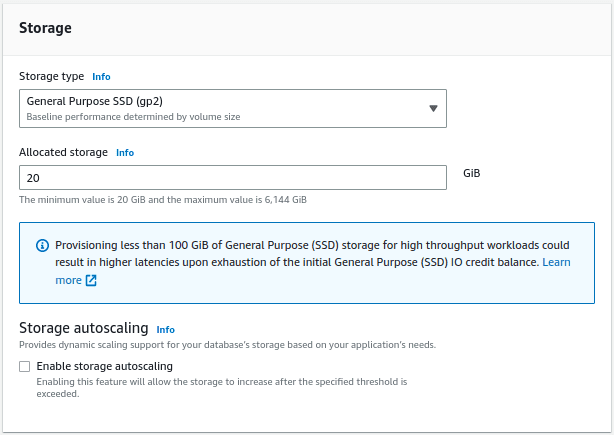
Choose the options for availability and durability. Here we are not creating a standby instance.
Choose the connectivity options like the VPC, Subnet and if public access required or not
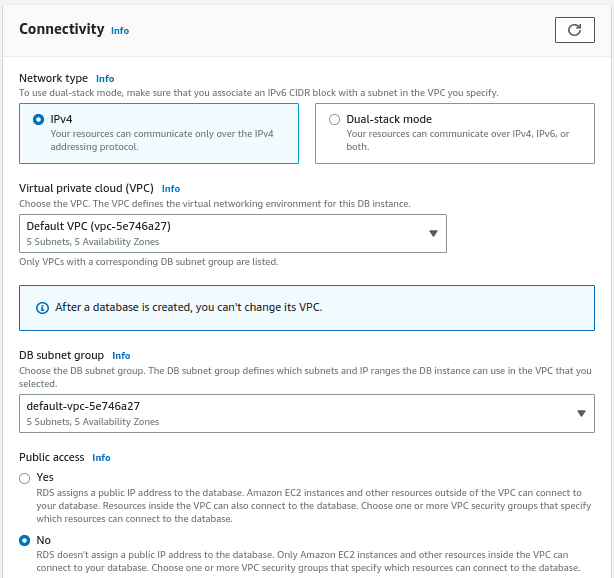
Select an existing VPC security group or create a new security group, database port, availability zone.
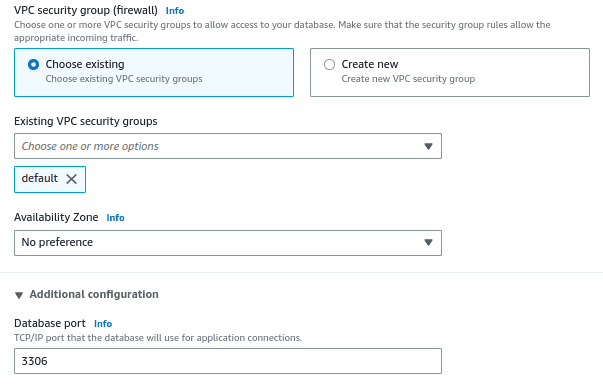
Select the database authentication method. Here we will use the password authentication method.
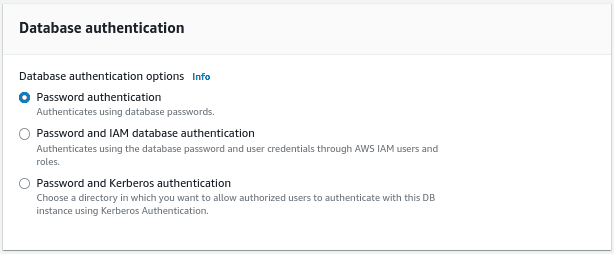
In the additional configuration section, give an initial database name and select the DB parameter groups. We are disabling automated backups for this tutorial.
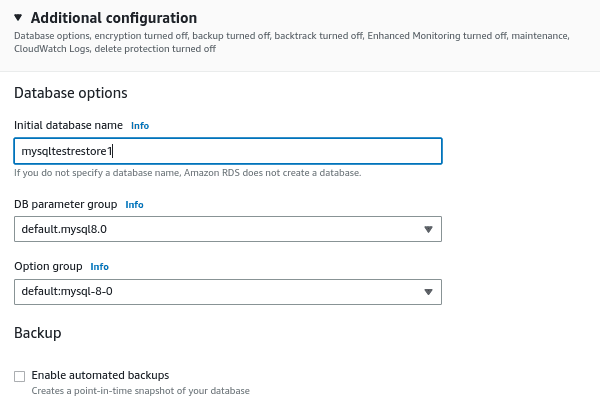
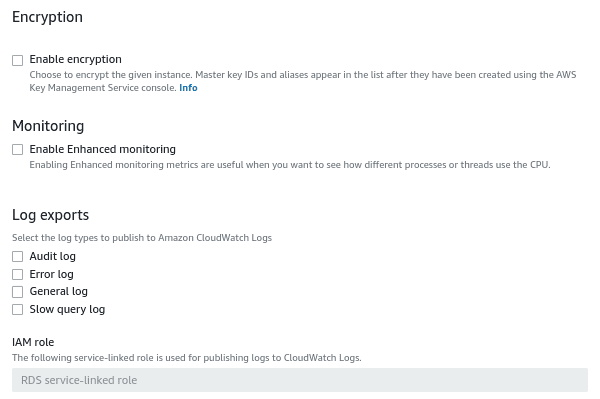
Select the encryption and monitoring options. Here we are disabling the options for this tutorial.
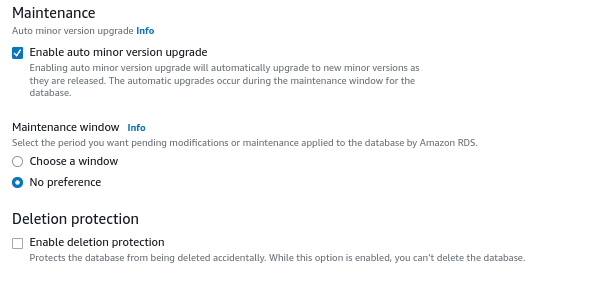
Select the options for maintenance. Select auto minor version upgrade and choose the maintenance window.
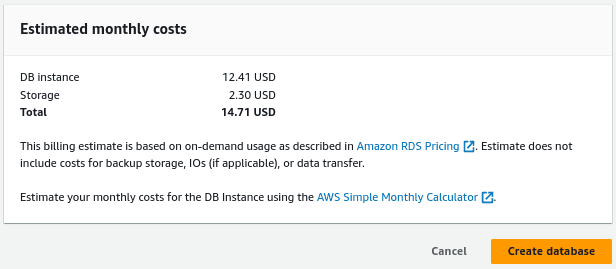
Review the estimated monthly costs and click on create database.
Permissions required for the IAM role to restore from S3
The role should have trust relationship for the service rds.amazonaws.com. The snippet of the policy is given below.
{
“Version”: “2012-10-17”,
“Statement”: [
{
“Sid”: “”,
“Effect”: “Allow”,
“Principal”: {
“Service”: [
“export.rds.amazonaws.com”,
“rds.amazonaws.com”
]
},
“Action”: “sts:AssumeRole”
}
]
}
Conclusion:
By following the detailed steps outlined in this document, you have successfully restored your AWS RDS MySQL database from Amazon S3. By leveraging AWS RDS and S3, you can confidently restore your MySQL databases, minimizing the impact of data loss and enabling quick recovery to keep your business operations running smoothly.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment