Today’s hypervisor can do really amazing things from many different aspects, including compute and memory, storage, and networking. Microsoft Windows Server Hyper-V is no exception and can provide enterprise environments with a powerful solution to provide solutions to most business-critical use cases.
Windows Server Hyper-V can provide enterprises with a very versatile and fully featured solution from a networking perspective. In fact, Hyper-V includes some really great advanced virtual machine network settings right out of the box that can allow Hyper-V administrators the ability to control and secure network traffic. Many of these settings are configurable settings that many may not be fully taking advantage of from an administration standpoint.
Table of Contents
- Hyper-V advanced virtual machine network configuration
- Virtual Machine Queue (VMQ)
- IPsec Task Offloading
- SR-IOV
- DHCP Guard, Router Guard, Protected Network and Port Mirroring
- Concluding Thoughts
Let’s take a look at Hyper-V advanced virtual machine network configuration and the various use cases and functionality of these configurable settings bring to the table.
Hyper-V advanced virtual machine network configuration
While creating a Hyper-V virtual switch or virtual switches and connecting virtual machines to them is certainly an important and necessary task, it is by no means the only network configuration that can be taken advantage of in a Hyper-V environment. There are many advanced Hyper-V virtual machine networking settings that can be taken advantage of by Hyper-V administrators that serve to strengthen and broaden the control over the Hyper-V network for the administrator.
The advanced network configuration settings found in the settings of the Hyper-V virtual machine and Hyper-V in general include:
- Virtual machine queue
- IPsec Task offload
- SR-IOV
- DHCP Guard, Router Guard, Protected Network, and Port Mirroring
Let’s take a look at these different Hyper-V advanced network settings configuration and how they can be used and implemented in an organization’s Hyper-V infrastructure.
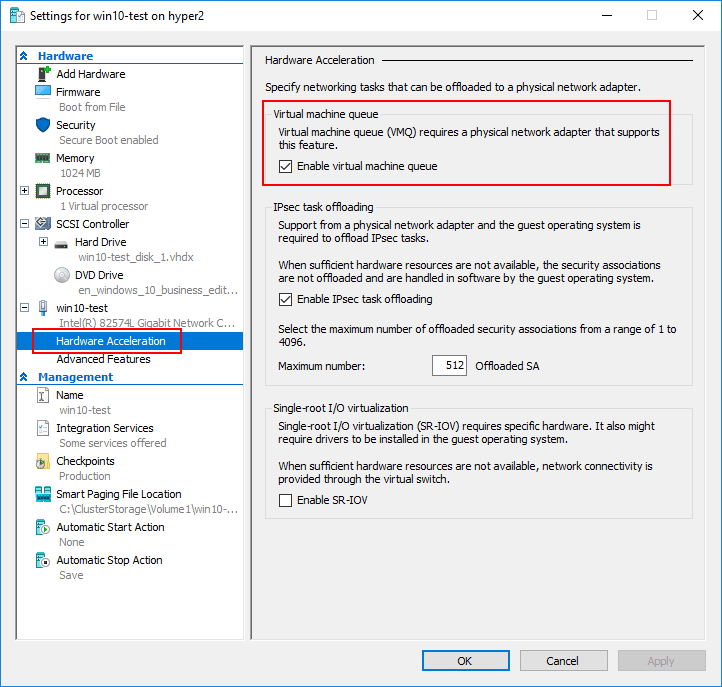
Virtual Machine Queue (VMQ)
What is Virtual Machine Queue or VMQ and how is it utilized?
Virtual Machine Queue or VMQ is a process that allows Hyper-V to improve network performance with virtual machines by expediting the transfer of network traffic from the physical adapter to the virtual machine. VMQ serves to decrease CPU utilization when network traffic utilization is elevated. When it is disabled, the CPU in the Hyper-V host has to utilize its own CPU power to process the multiple I/O streams to various virtual machines.
Note There have been known issues with certain network cards, such as Broadcom branded cards, where Virtual Machine Queue being enabled actually has the opposite effect. This seems to have been an issue with earlier versions of Hyper-V and have since been overcome with later Hyper-V releases and firmware updates from network card manufacturers.
Disabling or Enabling VMQ at the virtual switch level, can be accomplished with the Set-VMNetworkAdapter PowerShell cmdlet:
- Set-VMNetworkAdapter –ManagementOS -Name
-VmqWeight 0
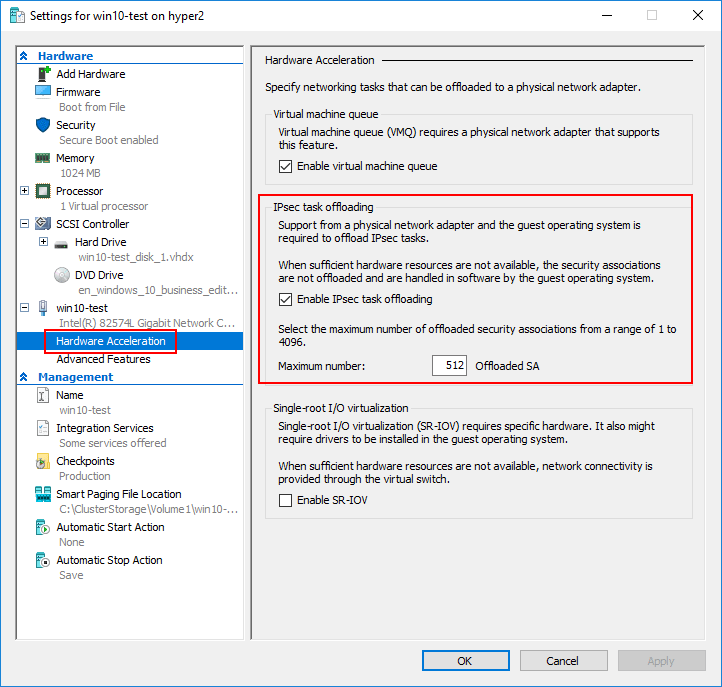
IPsec Task Offloading
Another mechanism to offload network processing to hardware is IPsec task offloading. When large IPsec packets are used on the network, the IPsec task offloading feature can lower CPU utilizing on the Hyper-V host. IPsec is very processor intensive due to authenticating and encrypting the contents of packets. This feature in Hyper-V allows offloading this process in virtual machines and not simply the Hyper-V host. This is beneficial from many different perspectives.
You can set the number of maximum number of security associations that can be offloaded to the physical adapter in PowerShell:
- Set-VMNetworkAdapter -IPsecOffloadMaximumSecurityAssociation
SR-IOV
Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V introduces Single-root I/O virtualization or SR-IOV.
What is SR-IOV?
Again this is network performance feature that allows network traffic the ability to completely bypass the software switch layer of Hyper-V and allows SR-IOV devices to be assigned directly to a virtual machine. This is accomplished by some slick remapping of resources to the virtual machine such as interrupts and DMA. This feature is extremely well-suited for virtual machines that heavily utilize the network. Hyper-V is able to pass network traffic directly from the virtual machine to the physical network card and in doing such, doesn’t manage the network traffic from the virtual machine to the physical network. This feature is compatible with many of the core Hyper-V features and virtual machine capabilities such as snapshotting, live migration, etc. Note that SR-IOV is not compatible with NIC teaming or extensible switch features.

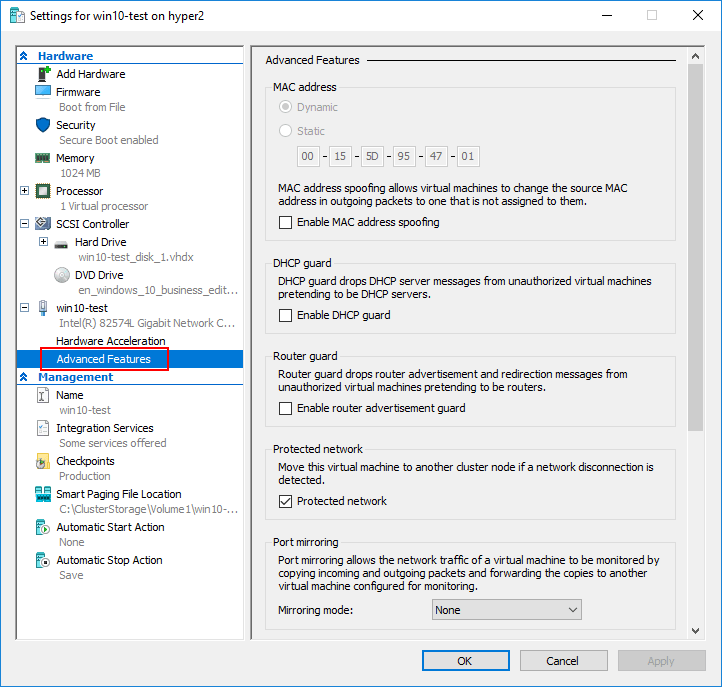
DHCP Guard, Router Guard, Protected Network and Port Mirroring
Under the Advanced Features of a Hyper-V virtual machine, there are a number of extremely powerful and interesting settings to take advantage of including DHCP Guard, Router Guard, Protected Network, and Port Mirroring. From a security and high availability standpoint, these settings provide some really great features for the Hyper-V administrator to control potential network issues as well as monitor network traffic.
The DHCP guard feature is a great way to ensure that a virtual machine is not enabled as a DHCP server accidentally or intentionally without authorization. When the DHCP guard feature is turned on, the Hyper-V host drops DHCP server messages from unauthorized virtual machines that are attempting to act as a DHCP server on the network.
With the Router guard feature, the Hyper-V host prevents virtual machines from advertising themselves on the network as a router and possibly causing routing loops or wreaking other havoc on the network.
Protected Network is a great feature for high availability. When set, this feature proactively moves the virtual machine to another cluster node if a network disconnection condition is detected on the virtual machine. This is enabled by default.
Port mirroring is a great way to either troubleshoot a network issue or perhaps perform security reconnaissance on the network. It typically mirrors traffic from one “port” to another “port” allowing a TAP device to be installed on the mirrored port to record all network traffic. With the Port mirroring virtual machine setting, Hyper-V administrators can mirror the network traffic of a virtual machine to another virtual machine that has monitoring utilities installed.
Concluding Thoughts
As shown, there are certainly many more options for the Hyper-V administrator to make use of and think about with Hyper-V networking than simply connecting a virtual machine to a virtual switch. All of these options serve a purpose and can be leveraged in various use cases depending on the support from a hardware perspective. Many of the features like VMQ, IPsec Task Offload, and SR-IOV can offload processing tasks to hardware for network operations which can lower CPU utilization on the Hyper-V host and improve network performance. Virtual machine queue is one of those features that you want to test extensively with your hardware configuration to make sure performance isn’t adversely affected instead of improved.
Additionally, features like DHCP Guard, Router Guard, Protected Network, and Port Mirroring provide even further capabilities that allow securing the network from rogue DHCP servers and routers. Protected network makes sure that virtual machines are moved to healthy hosts if the network becomes disconnected for a particular virtual machine on a particular host. Port mirroring allows monitoring the network traffic of a particular virtual machine by using another virtual machine setup for monitoring. By using these and other tools, Hyper-V administrators can ensure fine grained control over the network in terms of performance, security and high availability.
Related Posts:
Hyper-V Networking Configuration Best Practices
Hyper-V Network Switches: Choosing the Right One for Your Setup
Beginner’s Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V: Configuration of Hyper-V Networking Best Practices – Part 9
Hyper-V Network Virtualization Overview and Tools
Connecting Hyper-V Virtual Machines to the Physical Network
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment