One of the tremendous advantages of virtualization platforms like Microsoft Windows Server Hyper-V is the ability to make the production virtual machine workloads highly available. High availability is essential for business-critical applications as it provides a mechanism to withstand hardware failures without these drastically impacting the virtualized resources that are being served out.
Windows Server Hyper-V clustering is built on top of Windows Server Failover Clustering, so it provides all of the inherent benefits that Failover Clustering brings to the table. However, with the Hyper-V role, there are a few things that need to be considered when enabling high availability on a virtual machine.
Table of Contents
- Hyper-V High Availability Requirements
- Choosing the Right Tool for Hyper-V Virtual Machine High Availability
- Creating a Hyper-V Virtual Machine using Hyper-V Manager and Enabling High Availability
- Concluding Thoughts
What are the requirements to ensure that the Hyper-V virtual machines are highly available?
Is high availability enabled on a virtual machine by default?
Does it matter how the virtual machine is created?
Let’s take a look at how to make Hyper-V virtual machines highly available.
Hyper-V High Availability Requirements
With Windows Server Failover Clustering, Hyper-V is a role that is protected inherently with the benefits of the failover cluster. Virtual machines, of course, are the “resource” that needs to be protected in the Hyper-V environment.
Windows Failover clustering provides high availability to the Hyper-V role by allowing the mechanism for all Hyper-V hosts in the cluster, the ability to run a virtual machine if that virtual machine’s current host fails.
While this still leads to a short amount of downtime for the virtual machine due to the virtual machine needing to be restarted on a different Hyper-V host, this is a much shorter disruption than having a virtual machine down until the failed Hyper-V host is brought back online.
Below are three of the main requirements for properly configured virtual machine high availability:
Use Hyper-V hosts with identical hardware – While Windows Server Failover Clustering may technically allow forming Failover Clusters with dissimilar hardware configurations, don’t do it. You introduce variables and problems by straying from identical hardware and supported configurations.
Same Virtual Machine Networking – Hopefully, this requirement is satisfied by default with a properly configured Hyper-V cluster networking. However, it goes without saying, if a virtual machine is highly available on multiple hosts, those hosts have to be able to present the same networking to the virtual machine, regardless of which host the virtual machine is running on. This includes all layer 2 VLAN configuration, etc. Network wise, nothing could be worse for high availability than the virtual machine properly failing over to another host and only to have the virtual machine in a disconnected network state due to the lack of the virtual machine network requirements existing on the healthy, failover host.
Shared Storage – Even if the compute and memory resources are in a clustered configuration via Windows Server Failover Clustering, you still need to have shared storage between the Hyper-V failover cluster nodes. When a virtual machine that lives on a failover cluster.
Choosing the Right Tool for Hyper-V Virtual Machine High Availability
For those that are not using System Center Virtual Machine Manager, managing Windows Server Hyper-V clusters can be a mixture of using many different tools. Generally speaking, the two main tools that are utilized are the Hyper-V Manager utility and the Failover Cluster Manager. When thinking about high availability and ensuring that Hyper-V virtual machines are configured correctly for high availability, the tool used to create the virtual machine changes the process of how high availability is enabled on the Hyper-V virtual machine.
A bit of background on Windows Server Hyper-V and how virtual machines are considered “highly available”.
Simply creating a cluster of Hyper-V hosts using Windows Failover Clustering does not automatically make virtual machines that exist on one or more Hyper-V hosts highly available. Why is this?
Virtual machines that are enabled with high availability are treated as clustered roles. So, they have to be enabled as such. This high availability mechanism is available through the Failover Cluster Manager. If a virtual machine is created on a Hyper-V host that is a member of a Failover Cluster using the Hyper-V manager, it is not automatically configured as highly available. This must be done using the Failover Cluster Manager GUI utility or by using PowerShell.
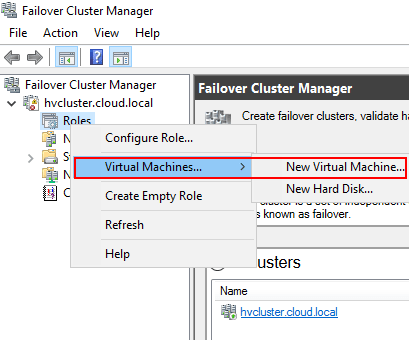
Creating a Hyper-V Virtual Machine using Hyper-V Manager and Enabling High Availability
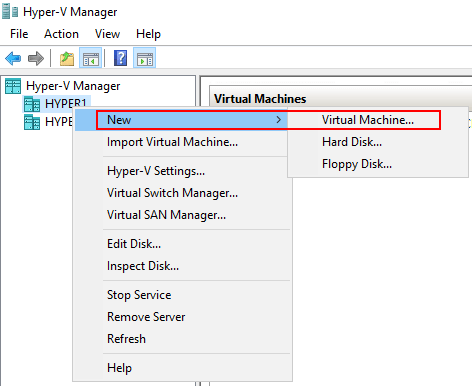
To show the process of enabling high availability on a Hyper-V virtual machine, let’s create a virtual machine using the Hyper-V manager to demonstrate this scenario.
Note, below, as you can see, there are HYPER1 and HYPER2 displayed in the Hyper-V Manager console. Both of these servers are part of a Hyper-V Failover Cluster. However, if we create the virtual machine using Hyper-V manager, it creates the virtual machine as a “local” resource on the particular Hyper-V host selected and not as a clustered resource.
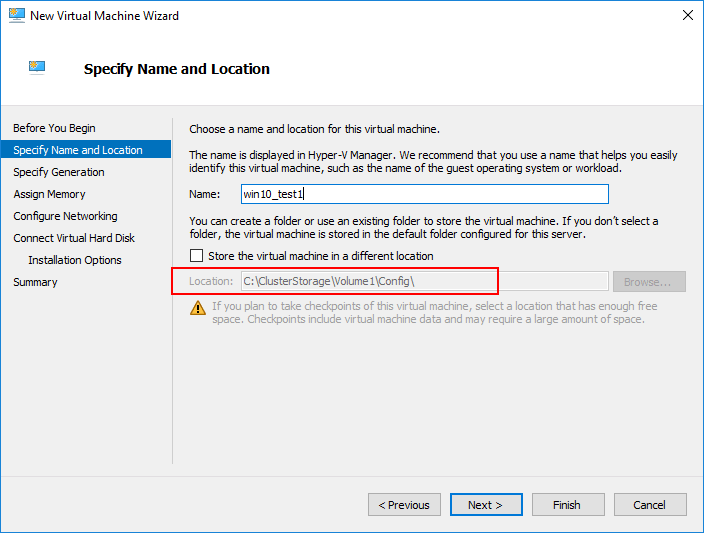
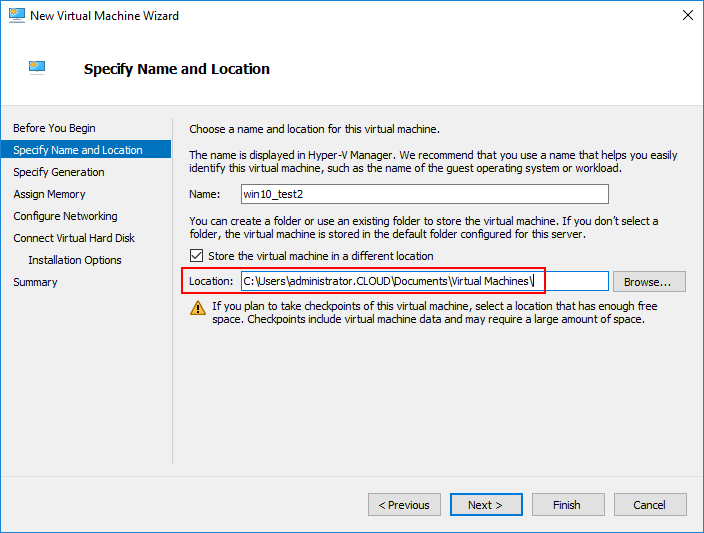
Below, in the new Virtual Machine Wizard, we are creating a new virtual machine in the Hyper-V Manager. Note that the storage used is ClusterStorage which means we are utilizing storage that is shared between the Hyper-V hosts.
Now that we have created a new virtual machine using the Hyper-V Manager, we can use the Failover Cluster Manager to enable high availability on the newly created virtual machine. To do that launch the Failover Cluster Manager, right click the roles container, and select the Configure Role option. This will launch the High Availability Wizard.
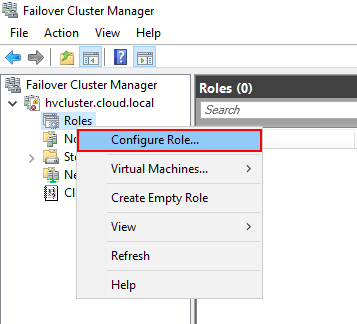
Once the High Availability Wizard launches, you are ready to begin configuring the virtual machine for high availability.
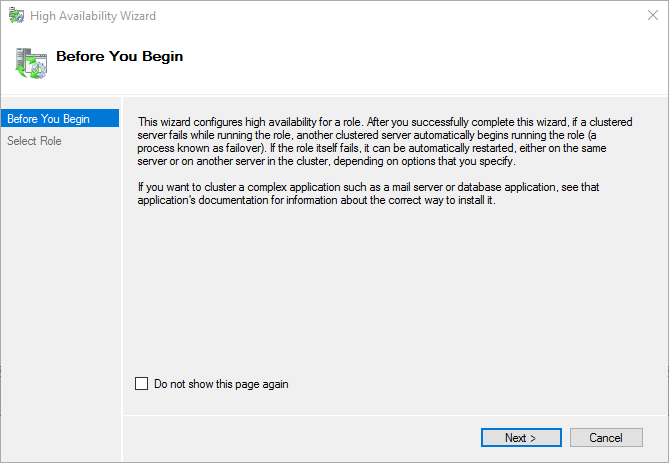
On the High Availability Wizard Select Role screen, choose the Virtual Machine option.
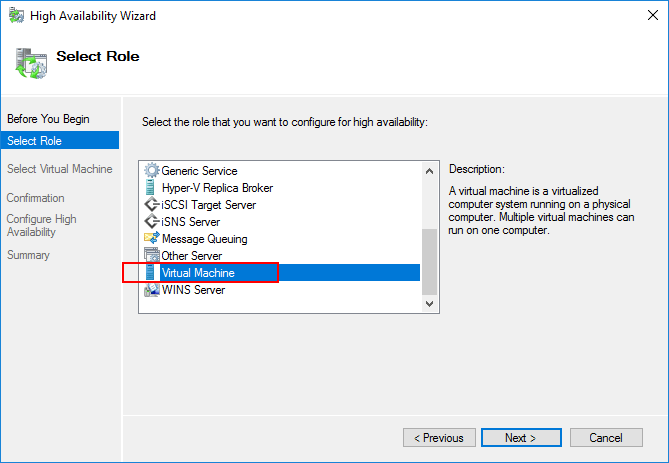
Any virtual machine that do not currently have high availability enabled on them will be listed in the Select Virtual Machine screen. Place a check by the box next to the virtual machine(s) you want to enable for high availability. The host server will also be shown.
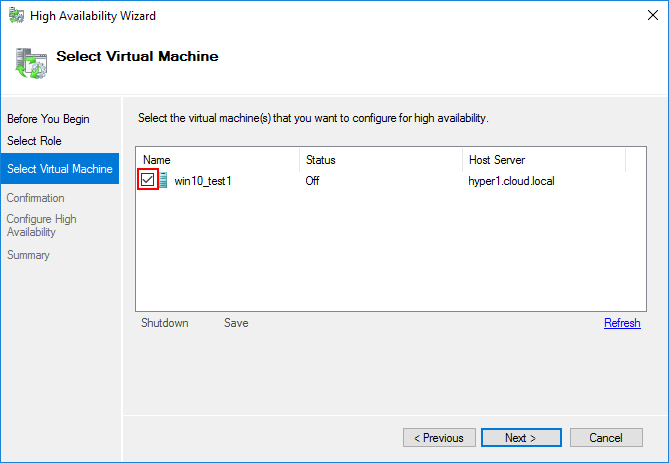
Next, confirm the virtual machines that were selected in the previous step. Once the confirmation is made, Hyper-V will begin enabling high availability on the virtual machines.
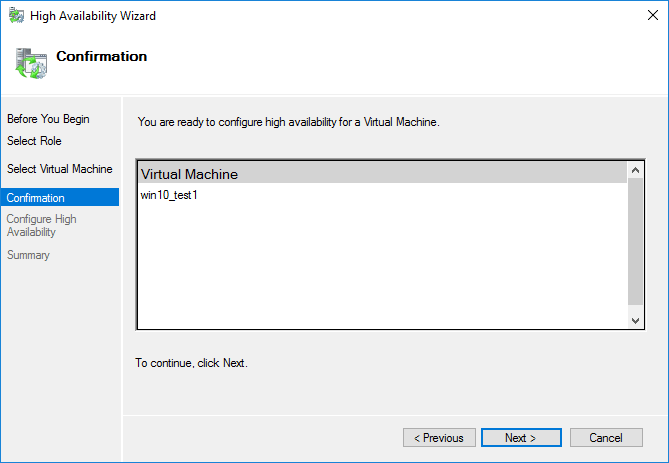
On the summary screen, you will see the results of the operation. Note the View Report button. Clicking here allows viewing an HTML report that is generated showing both the steps of the high availability operation as well as any warning or errors that may have been encountered.
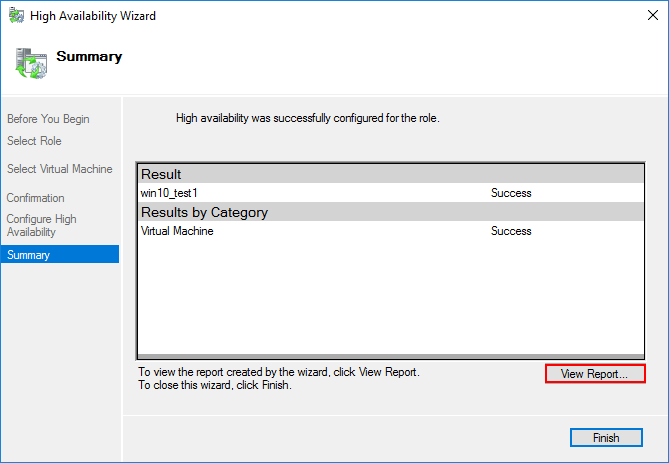
Below, you will see an example of the report that is generated on the high availability operation. Note the important steps of the configuration process. The storage is checked, the clustered role is created for the virtual machine and any dependencies are verified.

To show the difference in the report with a virtual machine created using the Hyper-V manager with local, non-shared storage, note the virtual machine is created on local storage attached to a Hyper-V host.
The results of the report are different. We now see the warnings displayed for the virtual machine. The report shows the storage is not shared across the cluster and details how to move the virtual machine storage, so it satisfies these requirements for high availability.

To move the virtual machine to storage that satisfies the storage high availability requirements, you can utilize the storage Live Migration capabilities of Hyper-V. In the Failover Cluster Manager, right-click the virtual machine and choose Move >> Virtual Machine Storage.
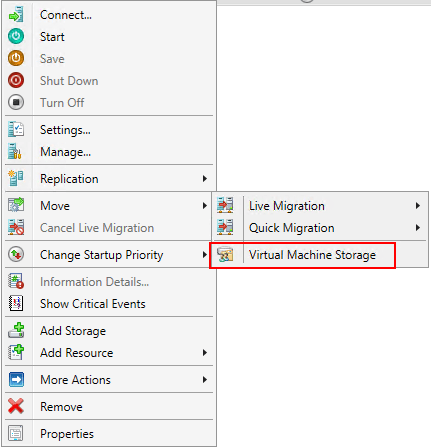
Use the Move Virtual Machine Storage to properly migrate virtual machine storage to cluster aware shared storage to satisfy the requirement for shared storage.
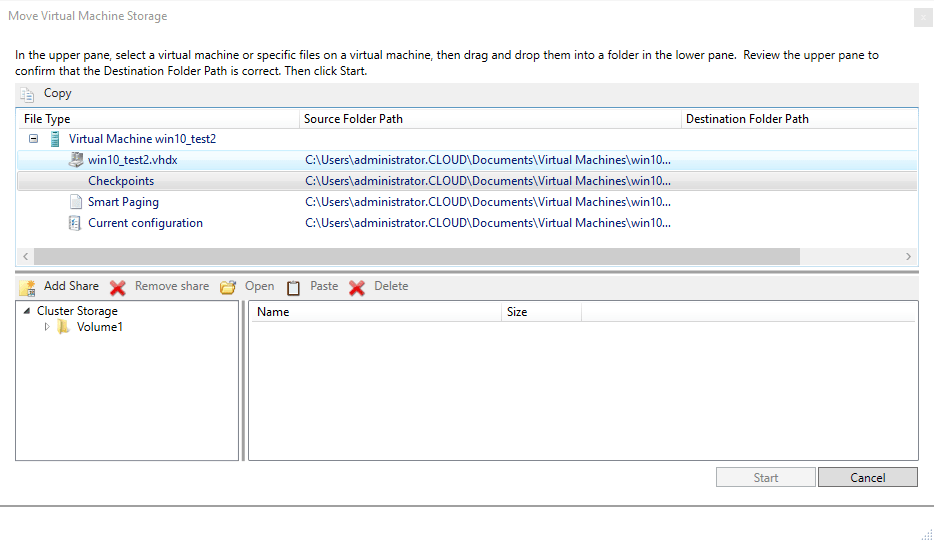
Moving Virtual Machine storage in Hyper-V
Concluding Thoughts
High availability is crucial in any virtualization platform. Windows Server Hyper-V has a unique mechanism for ensuring virtual machines are highly available and configured as such. Requirements for virtual machine high availability include hardware configuration similarity between hosts, shared storage, and duplicate network configuration across the cluster hosts. Additionally, it is important to understand the difference in behavior when creating highly available virtual machines in Hyper-V as different tools have different results when it comes to the HA configuration.
By using the Failover Cluster Manager to create a virtual machine, the HA aspect of the virtual machine is baked into the new virtual machine wizard. If you utilize the Hyper-V manager, you need to make sure to enable high availability on the virtual machine after the fact. Even if you use shared storage for the virtual machine, HA is not configured by default as shown. By understanding the tools and desired end result for high availability, Hyper-V administrators can ensure HA for their production workloads.
Read More:
How to Configure a vSphere High Availability Cluster
Windows Server Redundancy Mechanisms for High Availability
Beginners’ Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V: Hyper-V High Availability – Part 25
High Availability and Disaster Recovery considerations in Cloud
Microsoft Azure High Availability: Overview and Key Features
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment