Quick Bites:
- The blog discusses the importance of updating and patching Windows Hyper-V hosts and clusters for stability and security
- It highlights tools like Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Cluster Aware Updating (CAU), and PowerShell for managing updates effectively
- Administrators can control update timing, test patches, and automate cluster updates to ensure the smooth functioning of Hyper-V environments
- The article emphasizes the significance of applying updates in a scheduled and controlled manner to maintain the health of Hyper-V hosts and clusters
Keeping Windows Server systems updated with the latest patches is one of the key things that administrators can do to ensure their Windows Server environments are stable and secure. Patching is one of the necessary evils that administrators need to manage to keep Windows, Linux, and other environments healthy. Hyper-V hosts are part of the infrastructure that also needs to be kept updated.
Table of Contents
- Tools and Technologies Used to Update and Patch Microsoft Hyper-V
- Windows Server Update Services
- Hyper-V Cluster Aware Updating
- Cluster-Aware Updating PowerShell
- Concluding Thoughts
Microsoft Hyper-V is at its core simply a role that runs on Windows Server operating systems. As such they are not excluded from Windows Server patching schedules that should be maintained. Additionally, the guest Hyper-V integration Services may need to be updated as well. In this article we will cover –
- What is involved with maintaining and implementing Windows Server patches on Hyper-V hosts?
- What tools can administrators use to apply patches and ensure patches are applied properly in Hyper-V, including Hyper-V clusters?
Let’s begin with applying updates to Microsoft Hyper-V Hosts and Clusters.
Tools and Technologies Used to Update and Patch Microsoft Hyper-V
There are a few tools and technologies that are Microsoft specific that can be used to perform updates and patch in Microsoft Hyper-V. Some tools have been around for quite some time and are general Windows Update tools. There is also another Windows Server cluster specific technology that comes into play when updating Windows Server clusters. The technologies we will take a look at include:
- Windows Server Update Services
- PowerShell
- Cluster-Aware Updates
Now, let’s take these one by one and see how each comes into play when implementing Hyper-V updates, both on single hosts or Hyper-V clusters.
Windows Server Update Services
Most Windows Server administrators have at least some experience with Windows Server Update Services or WSUS. WSUS has long been a staple of the enterprise environment as a means to control Windows updates. It provides many benefits to administrators looking to control which updates are applied and when.
Why would administrators want to control updates?
While Microsoft has a pretty decent track record of supplying fairly stable updates, there are updates that get pulled back out from time to time because of an issue that was not caught before it was released. There is certainly merit in wanting to release updates first to a test or lab environment to check for any potential stability issues before releasing them to production. WSUS gives administrators the approval control on updates that are applied.
Scheduling when updates are applied can be a critical matter as well for production workloads. Application of Windows Updates typically requires a reboot depending on which updates are applied. Using WSUS allows administrators to have better control on when the updates are released to target production workloads and when they are applied. There are a few things for administrators to note about WSUS:
- Don’t run WSUS directly on the Hyper-V host
- Choose whether or not servers download the updates directly from Microsoft or from a local repository server on site
- There are no Hyper-V specific categories to be found in WSUS. The Windows Server category distributes all Windows Server patches including Hyper-V
WSUS can certainly be used as an effective means to keep Hyper-V hosts updated. Generally, administrators will want to assign Hyper-V hosts to their own OU for management and policy purposes. This allows Group Policy settings to be applied to the Hyper-V hosts for configuring Windows Update settings to utilize the internal WSUS server for updates.
Hyper-V Cluster Aware Updating
Starting with Windows Server 2012, Microsoft introduced a feature that greatly reduces the complexity of updated Failover Cluster based platforms such as Hyper-V. The new feature is known as Cluster Aware Updating or CAU and allows for an automated approach to applying updates in a Failover Cluster configuration. Cluster Aware Updating automatically drains the roles from a node, applies updates to the node, and then reboots it. After the host comes back up, roles are failed back to the node and then CAU continues with the next node in the Failover Cluster. If there are problems along the way, the process is stopped.
Enabling Cluster Aware Updating is a fairly straightforward process. We can enable this with the Cluster Aware Updating Administrative tool that is found in the Server Manager Console.
Below, we connect to the Hyper-V cluster name. The Hyper-V hosts are enumerated and the “last run status” and “last run time” is also shown if available. Below, the tool has never been ran so this information is not available.
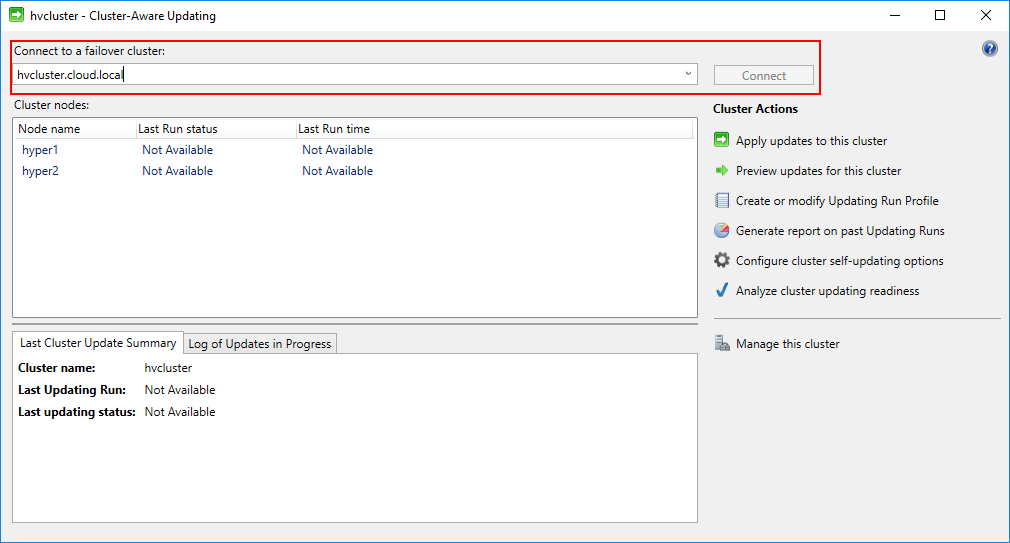
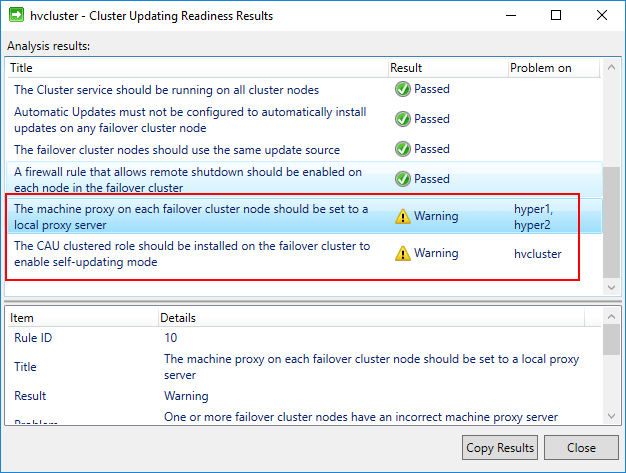
In the Cluster Actions there is an option to Analyze cluster updating readiness which determines the readiness of the Hyper-V cluster to have the cluster aware updating functionality enabled.
To actually enable the cluster self-updating option, click the Configure cluster self-updating options under the Cluster Actions pane. This launches the Configure Self-Updating Options Wizard.
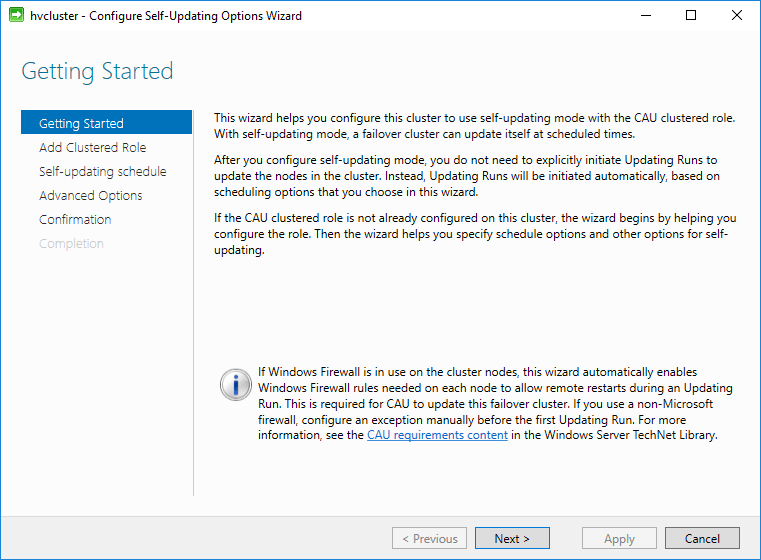
Next, choose the checkbox next to the Add the CAU clustered role, with self-updating mode enabled, to this cluster. You can also select the I have a prestaged computer object for the CAU clustered role, if a computer object has already been prestaged for this purpose. CAU uses a special computer object for the self-updating feature. We will see this below after the wizard has completed.
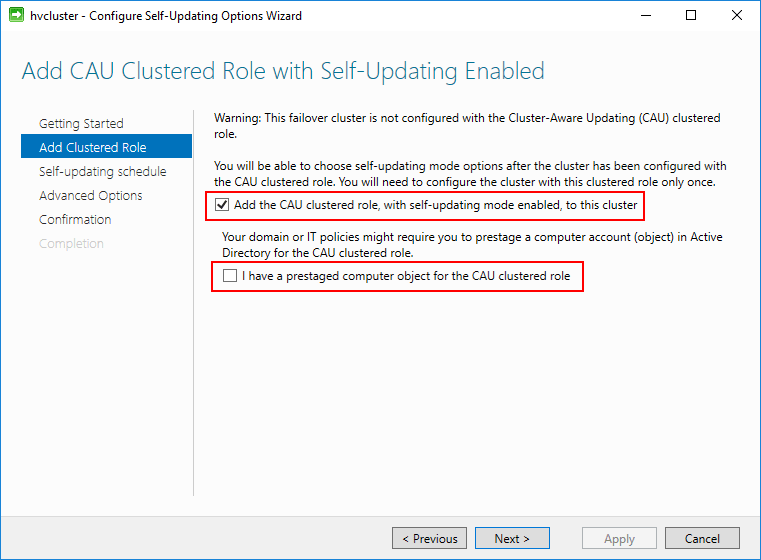
Next, we can configure the self-updating schedule. By default, the following options are selected. These can be changed as needed.
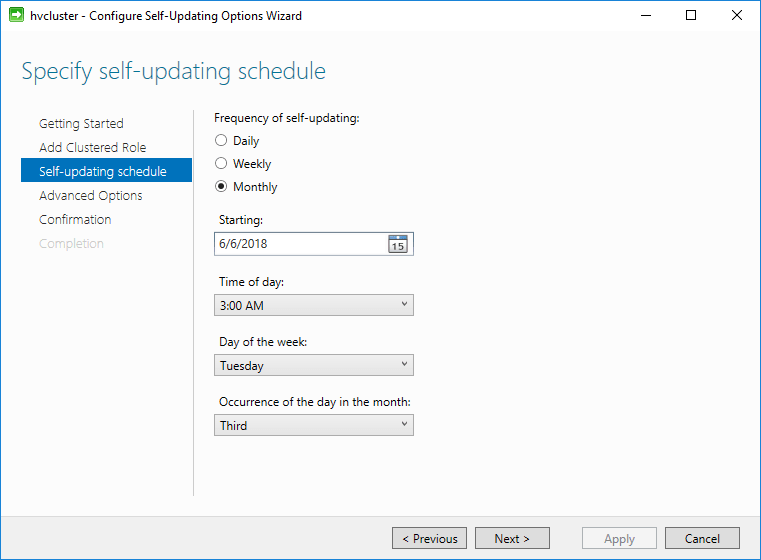
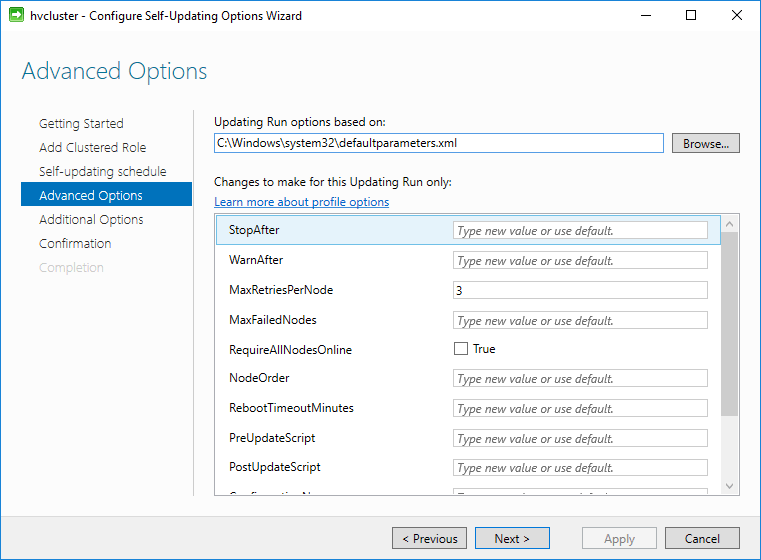
In the Advanced Options there are many configuration parameters that can be tweaked. For most, the defaults can be selected, but the configuration allows for highly customized settings that can be utilized for various environments.
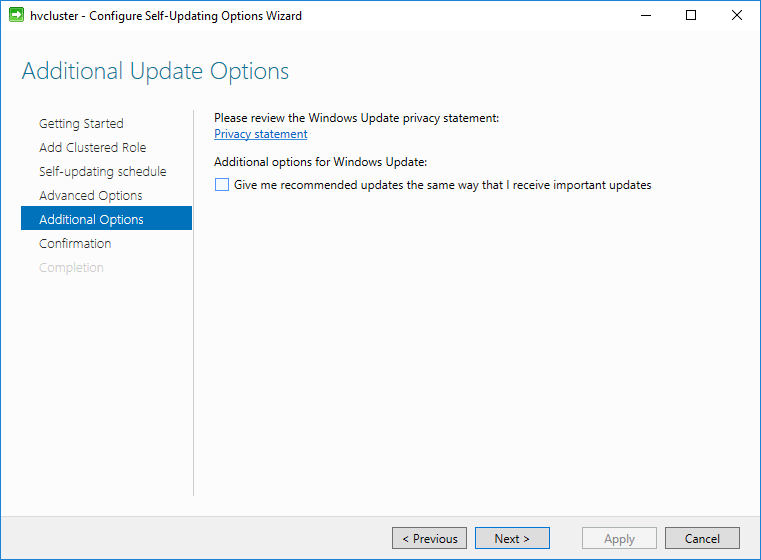
Additional update options can be selected such as the option to Give me recommended updates the same way that I receive important updates.
Finally, the wizard is ready to complete. Notice the PowerShell code that is displayed for the Command to run section. The wizard is simply running the PowerShell code for configuring the cluster aware updating option. This command could be ran manually outside of the wizard.
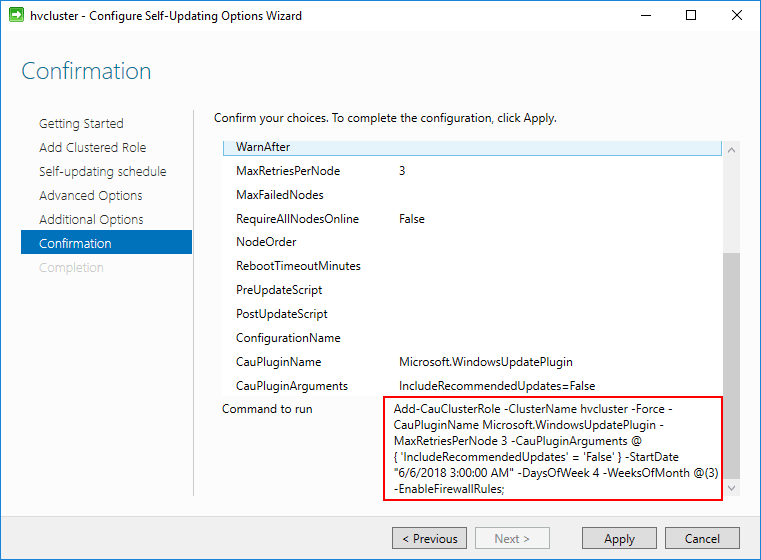
The Self-Updating Clustered Role is configured successfully on the Hyper-V cluster.
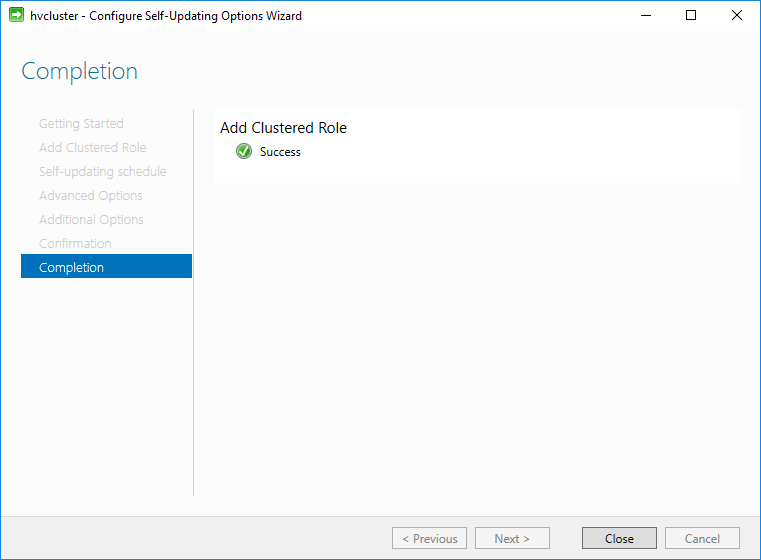
Below, we see the special computer object that has been created with the completion of the Cluster self-updating process.
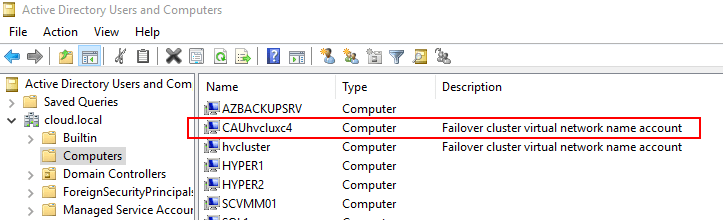
Another handy feature of the Cluster-Aware Updating management tool is the Preview Updates for this Cluster functionality. You can easily preview the available updates for each host in the Hyper-V cluster.
Using Cluster-Aware Updating in conjunction with Windows Server Update Services can provide a powerful means to apply updates effectively, safely, and consistently to Hyper-V clusters.
Cluster-Aware Updating PowerShell
As mentioned, PowerShell can be used to enable the Cluster-Aware updating options. Below is the snippet of PowerShell code needed to enable and configure the default options for a Hyper-V cluster.
Add-CauClusterRole -ClusterName hvcluster -Force -CauPluginName Microsoft.WindowsUpdatePlugin -‑MaxRetriesPerNode 3 ‑CauPluginArguments @{ ‘IncludeRecommendedUpdates’ = ‘True’ } ‑StartDate “6/6/2018 3:00:00 AM” ‑DaysOfWeek 4 ‑WeeksOfMonth @(2) ‑EnableFirewallRules;
Concluding Thoughts
Applying and administering updates is essential in a Windows Server environment. With Microsoft Hyper-V environments, this is crucial as well. Hyper-V hosts are simply Windows Server platforms with the Hyper-V role installed. As such, the updates and patches for Hyper-V are delivered as Windows Server updates. By utilizing available tools such as Windows Server Update Services and Cluster-Aware Updating configured on the Hyper-V cluster, administrators have a powerful set of tools that can deliver updates as needed and in a scheduled and controlled way to Hyper-V cluster hosts.
Discover the power of BDRSuite’s robust Hyper-V backup solutions with advanced features by trying our 30-days full-featured trial. Experience reliable data protection and seamless recovery firsthand!
Related Posts:
WSUS : Get Started with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) – Part 1
WSUS : Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) installation on Windows Server 2022 – Part 2
WSUS: Post-deployment WSUS configuration – Part 3
WSUS: Create Computer groups in WSUS – Part 4
WSUS: Configure GPOs and Prepare your WSUS Clients – Part 5
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment