Quick Bites:
- There is a growing need in modern IT environments for a centralized solution to efficiently configure and manage endpoints
- This blog provides an overview of Microsoft Endpoint Manager, a unified platform for managing all endpoints, integrating services like Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager
- Explaining access methods, dashboard features, and available services, the blog underscores the importance of streamlining IT administration tasks
- The conclusion highlights the simplicity and effectiveness of using Microsoft Endpoint Manager, emphasizing its integration benefits for IT administrators
Table of Contents
- What is Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
- How to access Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager dashboard
- Available services under Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Conclusion
What is Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a unified, integrated management platform for managing all your endpoints. Endpoint Manager combines services you may know and already be using, including Microsoft Intune, Configuration Manager, Desktop Analytics, Co-management, and Windows Autopilot.
Microsoft Endpoint Manager gives you easy access to device and client app management capabilities from the cloud. It enables secure productivity across all of your device types, including Windows, iOS, macOS, and Android. In Microsoft Endpoint Manager you can:
- Enroll and configure your devices
- Upload and distribute your apps
- Protect your organization’s data
- Cloud-enable computers enrolled with Configuration Manager
- Monitor and troubleshoot your deployments
How to access Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Microsoft Endpoint Manager has tighter integration with Azure Active Directory, and it can be accessed through Azure portal or through its own direct URL https://endpoint.microsoft.com/ On logging to the above URL with your Azure account, you can access the Microsoft Endpoint Manager services. All users created in Azure AD can access Endpoint Manager services if they have permission to avail the services.
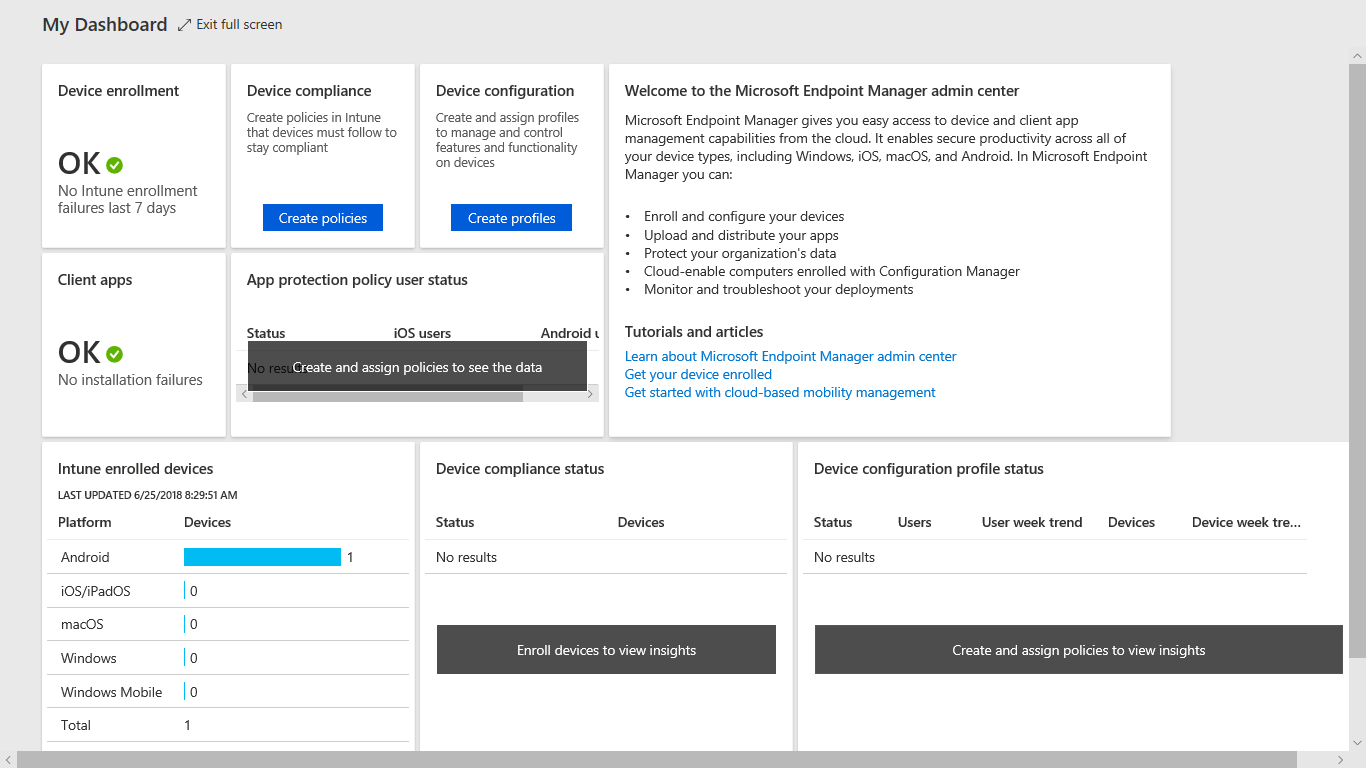
Microsoft Endpoint Manager dashboard
Dashboards provide a way for you to create a focused and organized view in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center. This is the starting point for using Intune to configure your devices by creating policies and managing devices by creating profiles. This dashboard provides overall data of Device Compliance Status and Device Configuration Profile Status of all enrolled devices under Intune. You have a detailed report on Intune enrolled devices under various platforms such as Android, iOS/iPad OS, Mac OS, Windows, and Windows mobile.
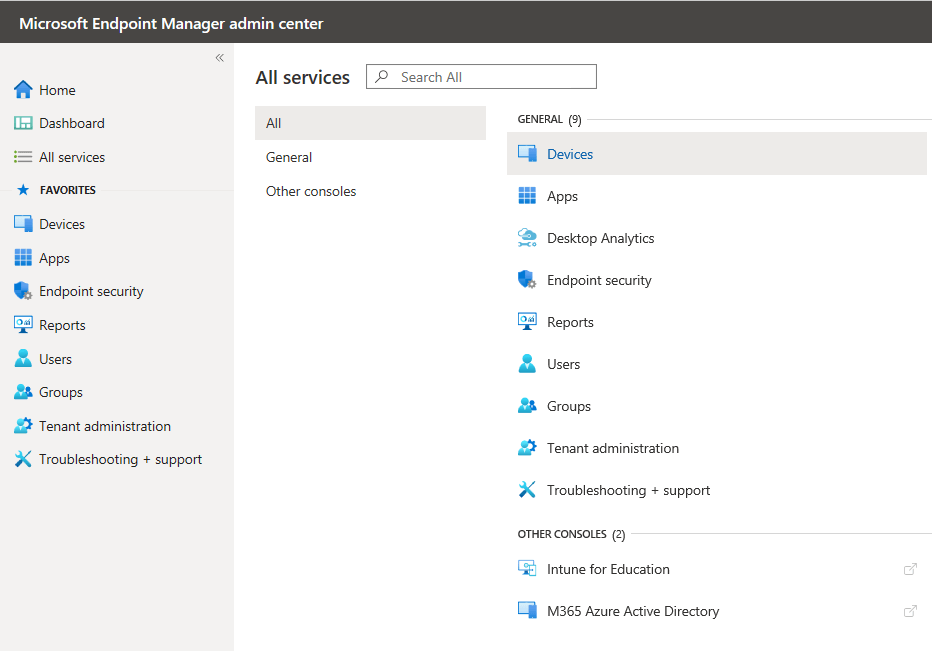
Available services under Microsoft Endpoint Manager
All Microsoft Endpoint Manager services are categorized under two groups General and Other consoles as shown in the picture below. You can also view all services under the All section.
Let us see an overview of major services one by one.
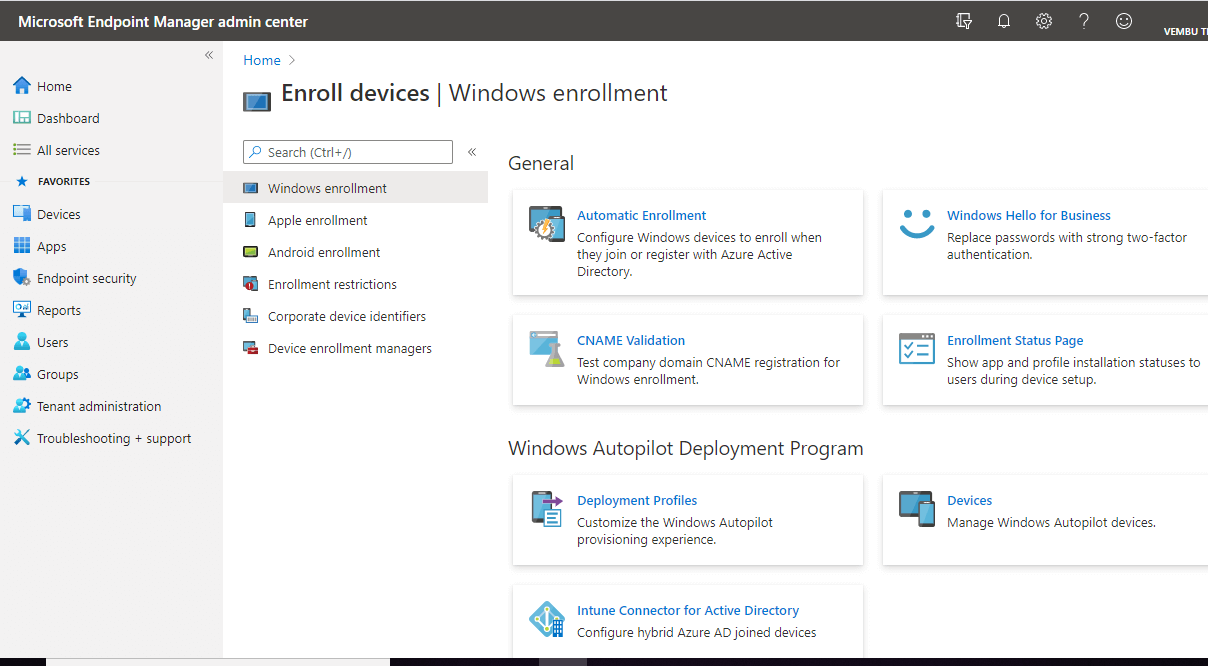
Devices – This blade allows you to enroll all your devices on these available platforms.
Windows device enrollment – you can enroll any windows devices using this blade. There are seven different ways a Windows 10 PC can be enrolled into Intune by users or admins. You can also use Windows Autopilot deployment program by creating deployment profiles as shown in the picture below
Apple device enrollment – Intune requires an Apple MDM Push certificate to manage Apple devices and supports multiple enrollment methods. You can use this blade to set up the MDM push certificate to begin the apple device enrollment process
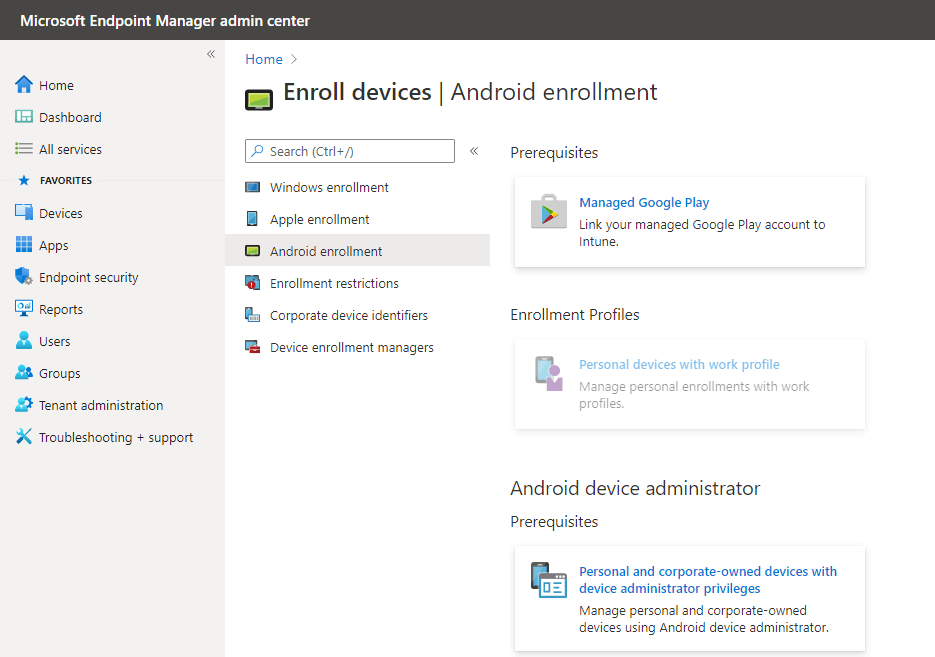
Android device enrollment – You can set up devices with one of these Android Enterprise solutions such as linking your managed Google play account into Intune. Android Enterprise supports the most up-to-date and secure management features for personal and company-owned devices. To enable these features in your organization, you must link your Managed Google Play account to Intune. To enroll Android devices with device administration privileges, enable the Android device administrator solution in the prerequisite section
Enrollment restrictions – A device must comply with the highest priority enrollment restrictions assigned to its user. You can drag a device restriction to change its priority. Default restrictions are the lowest priority for all users and govern userless enrollments. Default restrictions may be edited, but not deleted. You have two types of restrictions:
- Device type restrictions – Define which platforms, versions, and management types can enroll.
- Device limit restrictions – Define how many devices each user can enroll.
Device enrollment managers – In this blade you can add or remove device enrollment managers to allow certain users to enroll larger quantities of devices.
Apps – This blade allows you to control all devices apps on endpoints. You can control installation and app protection on Windows, iOS/iPadOS, Mac OS, and Android platforms.
You can create App protection policies, App configuration policies, iOS app provisioning profiles ( can use iOS app provisioning profiles to prevent your line-of-business apps from expiring ), S mode supplemental policies and Policies of office apps
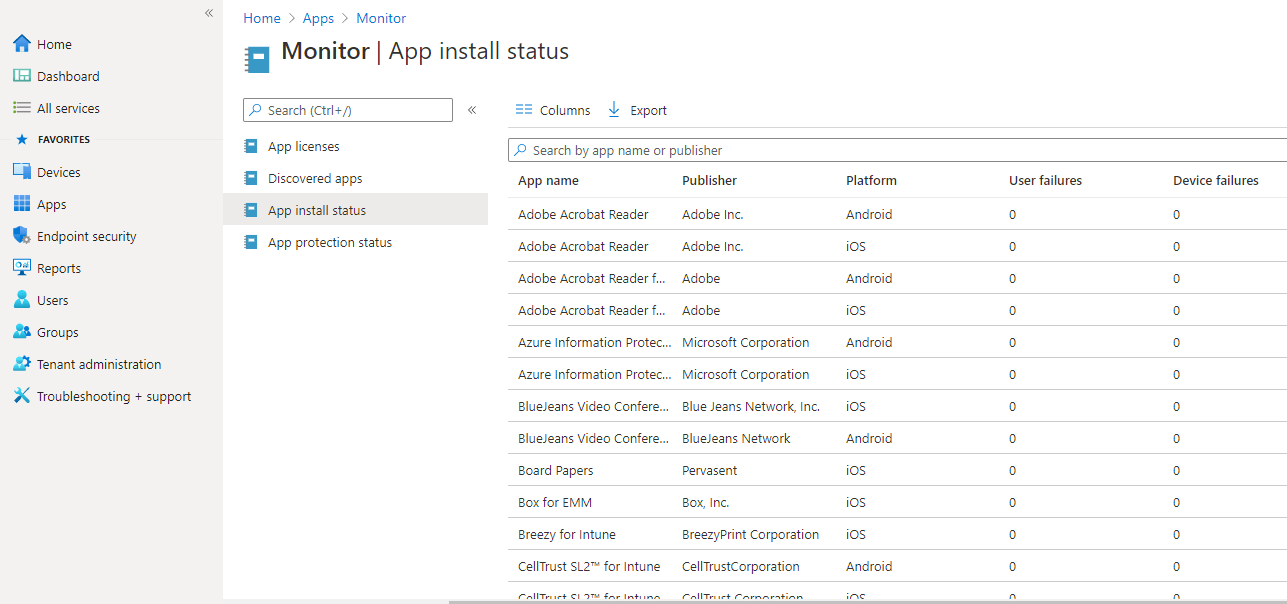
You can also monitor App licenses, Discovered Apps, App installation status, and App protection status.
Desktop Analytics – It is a cloud-based service that provides insight and intelligence for you to make more informed decisions about the update readiness of your Windows. It combines data from your organization with data aggregated from millions of devices connected to Microsoft cloud services.
Use Desktop Analytics with Configuration Manager to:
- Create an inventory of apps running in your organization.
- Assess app compatibility with the latest Windows 10 feature updates.
- Identify compatibility issues, and receive mitigation suggestions based on cloud-enabled data insights.
- Create pilot groups that represent the entire application and driver estate across a minimal set of devices.
- Deploy Windows 10 to pilot and production-managed devices using Configuration Manager.
- Minimize deployment risks by monitoring the health state of your devices during and after the deployment.
- Ensure your devices are still supported with security and feature updates status.
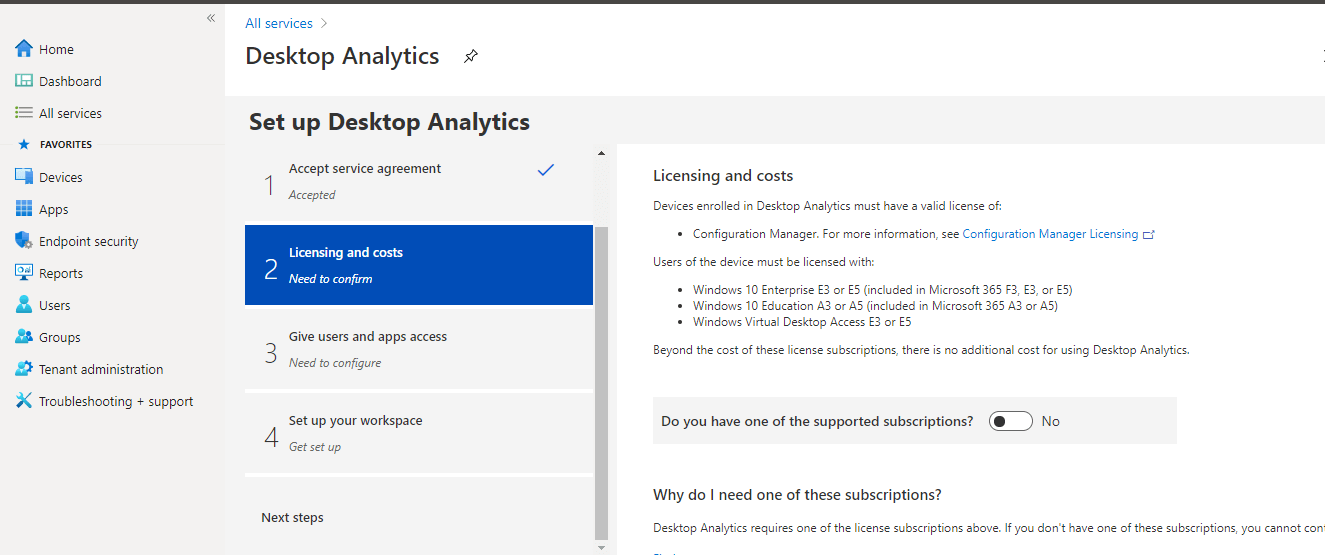
This setup involves four steps – Accept Service agreement, confirm licensing and costs, configure users and apps access, and finally set up your workspace.
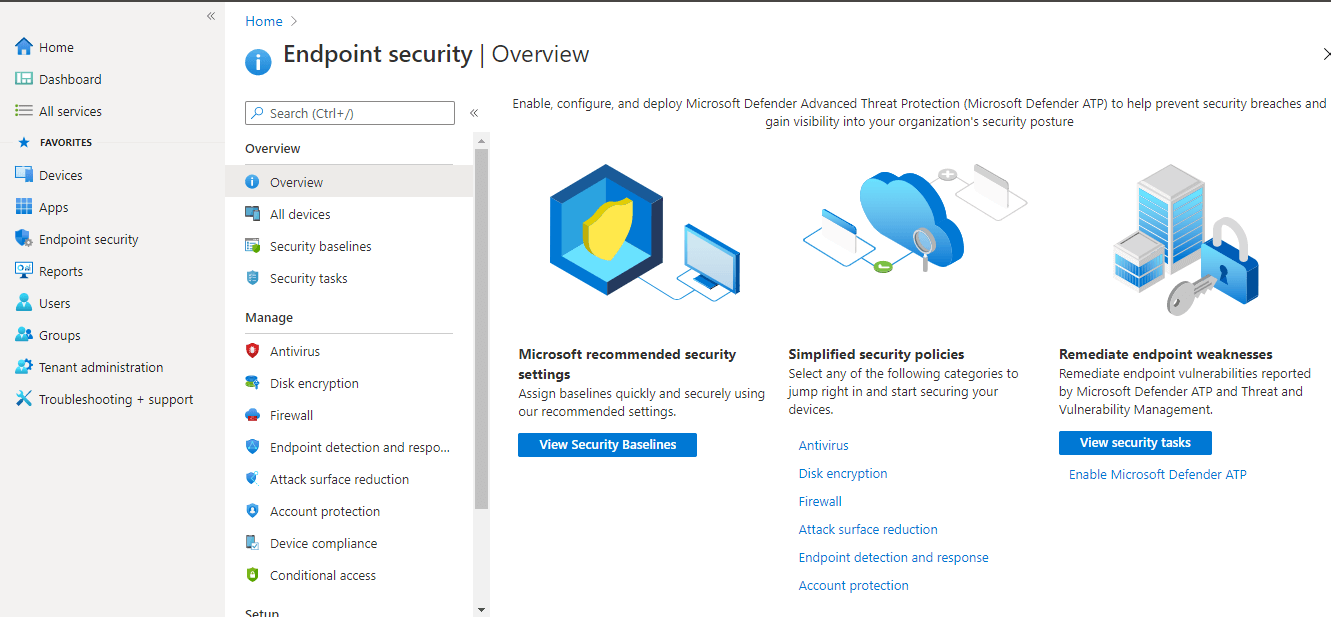
Endpoint Security – In this security management blade, you can protect and secure devices from one place. Here you can enable, configure, and deploy Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection (Microsoft Defender ATP) to help prevent security breaches and gain visibility into your organization’s security posture.
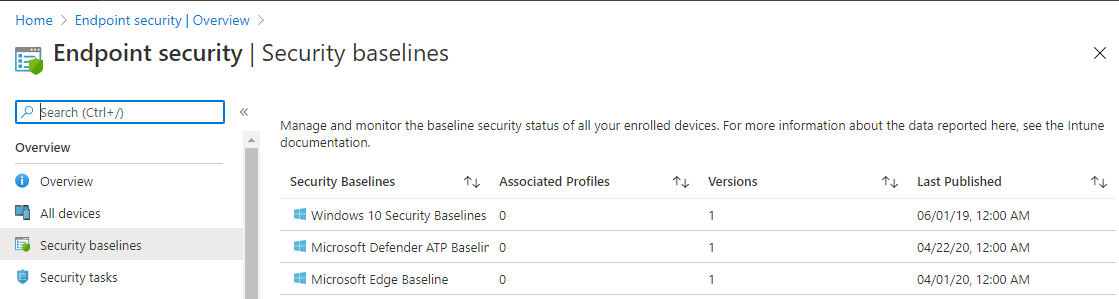
Microsoft recommended security setting using security baselines – Assign security baselines quickly and securely using Microsoft’s recommended settings. You can manage and monitor the baseline security status of all your enrolled devices. This includes three security baseline viz Windows 10 security baseline, Microsoft Defender ATP baseline, and Microsoft Edge baseline. On each baseline, you can create profiles to use on Windows devices.
Simplified security policies – In this blade, there are six categories to start securing your devices.
- Antivirus – Shows a summary of antivirus installed on the endpoint devices, and shows the report record of Windows 10 unhealthy endpoints.
- Disk encryption – Shows a summary of disk encrypted endpoints. You can create a policy to implement disk encryption on the endpoint devices which include mac os & windows 10 and later devices.
- Firewall – Shows summary of firewall enabled endpoints. You can create a policy to enable Firewall on Windows 10 and later endpoints
- Attack surface reduction – Your attack surface is the total number of places where an attacker could compromise your organization’s devices or networks. Reducing your attack surface means offering attackers fewer ways to perform attacks. Here you can create a policy to implement attack surface reduction on Windows 10 and later endpoints.
- Endpoint detection and response – provide advanced attack detections that are near real-time and actionable. Security analysts can prioritize alerts effectively, gain visibility into the full scope of a breach, and take response actions to remediate threats immediately. Here you can create a policy to enable endpoint detection and response on Windows 10 and Windows Server devices.
- Account protection – This is to protect your endpoints identity, user accounts on devices. You can create a policy to provide account protection on Windows 10 or later devices.
Remediate endpoint weaknesses.- Remediate endpoint vulnerabilities reported by Microsoft Defender ATP and Threat and Vulnerability Management. In this blade, you can enable Microsoft Defender ATP
Use Microsoft Defender ATP (Advanced Threat Protection) to gain visibility into your organization’s security posture and get recommendations to improve it. Connecting Microsoft Intune and Microsoft Defender ATP allows you to use ATP’s dynamically calculated machine risk scores in Intune compliance evaluation and Azure Active Directory conditional access enforcement.
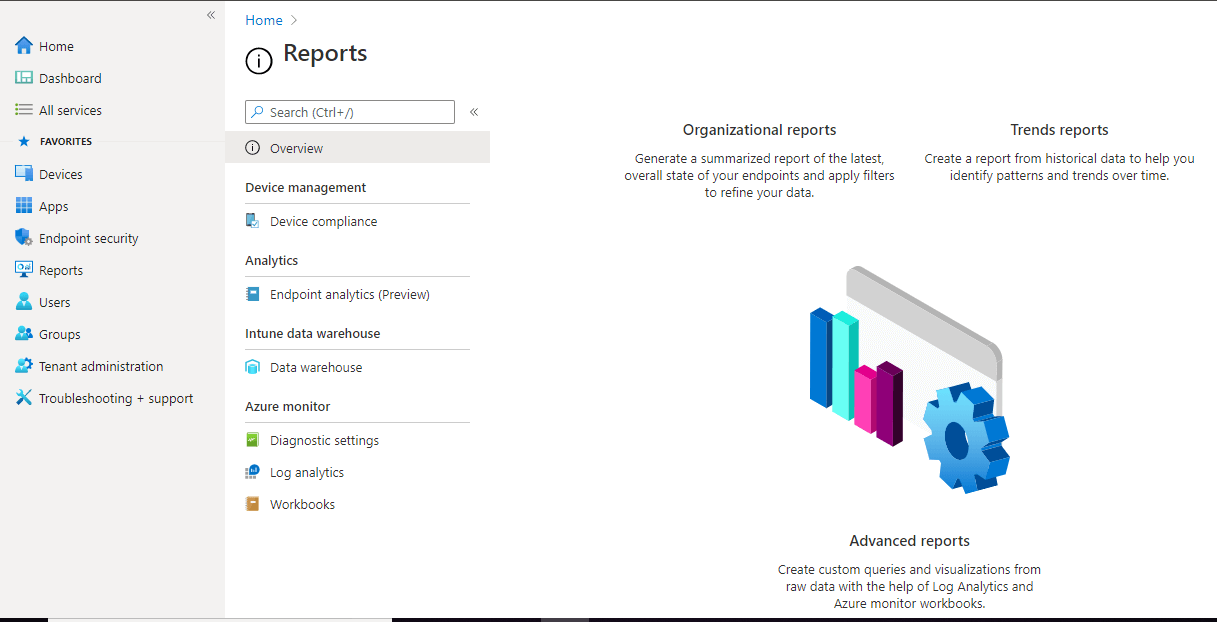
Reports – In this blade, you get to monitor the health and activity of your endpoints. Use Intune reporting to monitor endpoint compliance, health, and trends in your organization.
The report has three categories –
- Organizational reports – Generate a summarized report of the latest, overall state of your endpoints and apply filters to refine your data.
- Trends reports – Create a report from historical data to help you identify patterns and trends over time.
- Advanced reports – Create custom queries and visualizations from raw data with the help of Log Analytics and Azure monitor workbooks.
Users & Groups – These are Azure AD users and groups. From the Microsoft Endpoint Manager, you can use this blade to create and manage Azure AD users and groups directly.
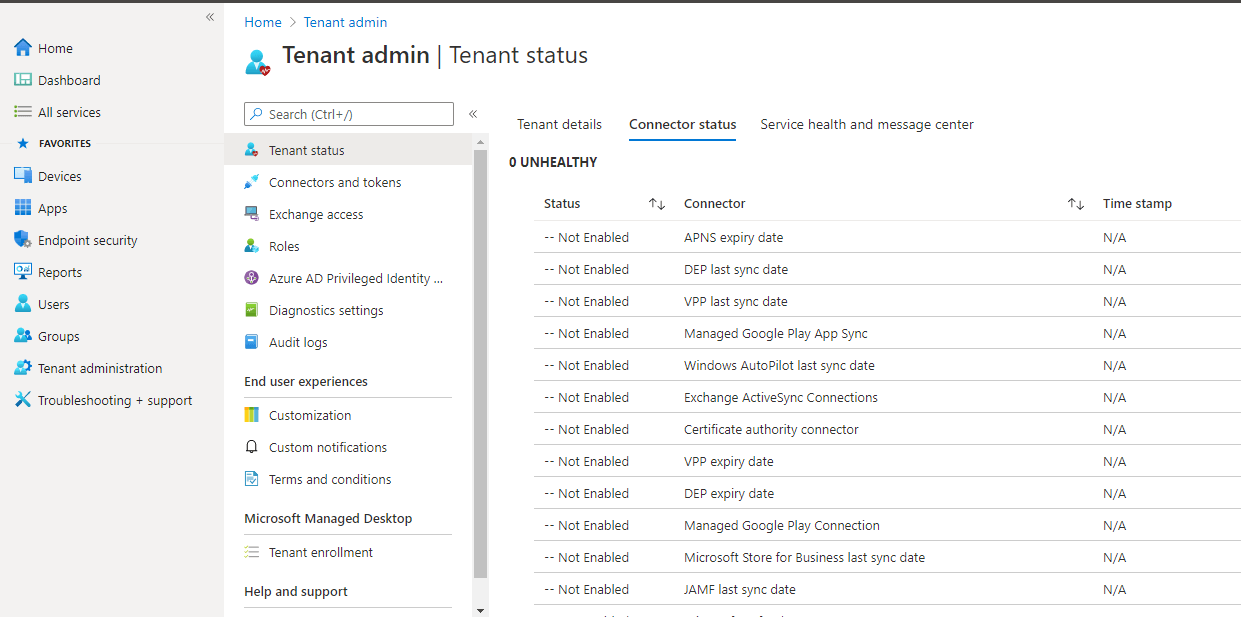
Tenant Administration – This blade provides overall tenant administration, such as the total number of licensed users, the total number of Intune users, and the total number of enrolled devices, etc… Also provides the tenant status as active or inactive. You can enable or disable the available connector to use with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Conclusion
Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a single, integrated endpoint management platform for managing all your endpoints and this Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center integrates ConfigMgr and Microsoft Intune together, for any IT administrator Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a boom to use one application for two essential services. Configuring and managing endpoints using Intune through Microsoft Endpoint Manager is simple and straightforward.
If you are looking for a robust and cost-effective Endpoints backup solution, try out BDRSuite for Endpoints today.
Related Posts:
Windows Admin Center Part 1 : Overview and Installation
Beginners’ Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V: Hyper-V VM Management with Windows Admin Center: Part 71
Managing Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct with Windows Admin Center
Microsoft 365 for Beginners – What is Microsoft Admin Center – Part 23
Microsoft 365 SharePoint Admin Center: An Overview
How to Setup Self-Service Password Reset (SSPR) in Microsoft 365 Admin Center
Microsoft OneDrive Admin Center: An Overview
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment