In this post, we will look at the difference between Hyper-V 2016 server and Hyper-V role that can be installed inside of Windows Server 2016 installation. Also, we will discuss the advantages & disadvantages of both, their use cases and licensing model.
Microsoft Hyper-V Versions Comparison
First, we will take a look at – Hyper-V 2016 Server.
Hyper-V 2016 Licensing:
The Microsoft Hyper-V 2016 platform is a free version of the hypervisor offered by Microsoft.
For those more familiar with the VMware, you can think about Hyper-V 2016 as the pseudo equivalent of the free version of the ESXi hypervisor.
The free version of Hyper-V 2016 is available for download publicly here:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-hyper-v-server-2016
Hyper-V 2016 Installation:
When looking at the architecture of Hyper-V 2016, it is essentially Windows Server 2016 Core with the Hyper-V role already installed. So, once installed, this is basically a Windows Server Core with the minimal set of features needed for it to function as a hypervisor. Also, it has no GUI (graphical user interface); you need to manage using the command-line interface (CLI).
As opposed to installing Windows Server 2016 and then configuring roles, you are already up and running with a hypervisor once the Hyper-V 2016 installation finishes.
As opposed to Hyper-V 2016, when you install Windows Server 2016 you still have to install the Hyper-V role. Some may think that Windows Server 2016 with the Hyper-V role installed would be considered a type 2 hypervisor.
What is a type 2 hypervisor as opposed to a type 1 hypervisor?
A type 2 hypervisor is a hypervisor that runs as an application on top of an existing operating system. In contrast, a type 1 hypervisor is known as a bare-metal hypervisor that runs directly on top of the physical server hardware.
In what we described – installing the Windows Server 2016 operating system and then installing the Hyper-V role, would this not be type 2?
Microsoft does something very interesting here when you install the Hyper-V role. Once the role is installed, Hyper-V is instantiated first before Windows Server 2016. In fact, once the role is installed, Windows Server 2016 runs on top of the hypervisor. This qualifies Hyper-V as a type 1 hypervisor.
Use cases of the free version of Hyper-V 2016
One caveat with the Hyper-V 2016 platform is that you don’t get any Windows guest licensing included with the product since it is free. So, it is better suited for running Linux workloads that don’t incur guest OS licensing fees. Additionally, it can make sense for running VDI workloads as well.
Advantages of Hyper-V 2016 Free
- The obvious one (It’s free)
- Lightweight – Server 2016 Core with Hyper-V role
- Minimal configuration required – After install Hypervisor is functional (basically)
Disadvantages of Hyper-V 2016 Free
- Doesn’t include guest operating system licenses
- This can add up if you desire to host many VMs
Hyper-V Role on Windows Server 2016
Installing Windows Server 2016 and then installing the Hyper-V role:
Windows Server 2016 offers the ability to install the Hyper-V role.
As mentioned in the comparison with the free Hyper-V 2016 install, the installation of Hyper-V via the Windows Server 2016 installation requires adding the Hyper-V role into the Windows Server 2016 installation via the Add Roles/Features functionality.
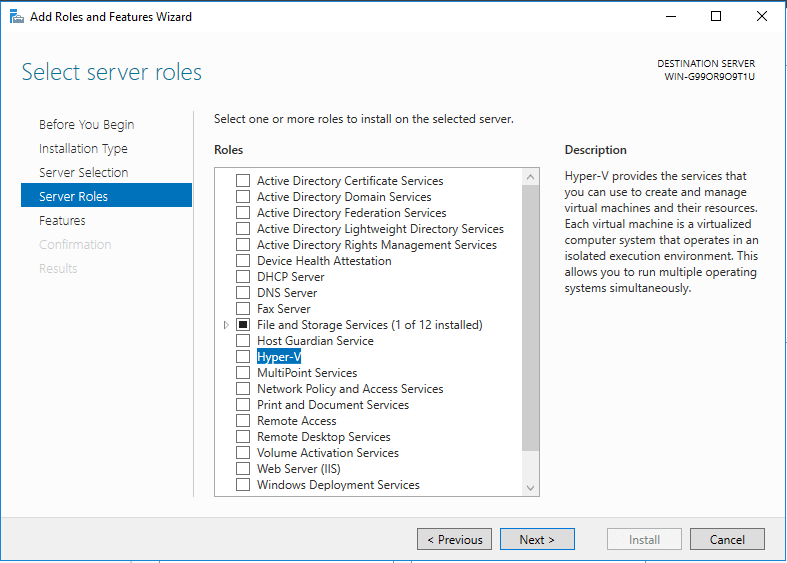
After adding the server role, the server reboots and Hyper-V is instantiated first, then booting the Windows Server 2016 operating system.
One thing not to confuse with the Hyper-V 2016 free installation is Windows Server 2016 Server Core. You can install the full Windows Server 2016 operating system as Server Core (GUI-less) and then install the Hyper-V role. This is not the same (licensing wise) as Hyper-V 2016 Server.

After the Hyper-V role installation, there isn’t really a noticeable change in the appearance of the server booting, however, after the reboot, you now have access to the Hyper-V management tools to manage the configuration of the server role.
Licensing:
The Windows Server 2016 installation of the Hyper-V Role offers advantages when it comes to licensing as well as features (especially with Datacenter).
Initially, you need to license your Windows Server 2016 choosing either Standard or Datacenter Edition. Standard Edition includes licenses for two Windows-based Hyper-V VMs and Datacenter Edition for unlimited Windows-based Hyper-V VMs.
The breakdown of guest operating system licensing received is as follows:
Windows Server 2016 Standard edition – Suitable for small environments
- Windows Server OSes and Containers with Hyper-V isolation – 2 instances
- Unlimited containers without Hyper-V isolation
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter edition: – Suitable for Enterprise datacenters
- Unlimited Windows Server OSes and Containers with Hyper-V isolation
- Unlimited containers without Hyper-V isolation
- Storage Spaces Direct with storage replicas
- Shielded Virtual Machines
- Software-Defined Networking stack
Aside from the unlimited guest OSes and containers that are available with Hyper-V isolation, the Windows Server 2016 Datacenter edition with the Hyper-V role provides all the enterprise features and functionality that enterprise data centers will no doubt want to take advantage of for most of their production workloads.
Storage Spaces Direct:
Storage Spaces Direct is Microsoft’s solution that competes with such SDS solutions as VMware vSAN. It allows using industry-standard servers with DAS storage to create software-defined storage arrays between nodes. Similar to VMware vSAN it contains features such as caching, storage tiers, and erasure coding for fault tolerance.
Shielded Virtual Machines:
Shielded Virtual Machines are encrypted virtual machines with BitLocker encryption to provide encrypted protection at rest on disk as well as when virtual machine data is moving across the network during a Live Migration.
Networking Stack:
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter edition provides access to the software-defined networking stack that allows virtualizing network resources and abstracting the network layer into the hypervisor. This brings about tremendous security and mobility advantages for production workloads.
Windows Server 2016 with Hyper-V Role – Advantages:
- Provides a much more powerful solution than Hyper-V 2016 (more features, etc)
- Provides built-in OS and container licensing for running with Hyper-V isolation
- Datacenter edition provides access to Storage Spaces Direct, Shielded Virtual Machines, and Networking Stack
Windows Server 2016 with Hyper-V Role – Disadvantages:
- Much more expensive than Hyper-V 2016, especially Datacenter Edition
- More involved installation and configuration
- May be overkill for some customers who only need to run Linux or VDI workloads
Windows Server 2016 with Hyper-V Role – Use Cases:
Heavy lifting enterprise environments that are looking for dense virtual machine provisioning of Windows Server operating systems, customers will benefit by purchasing the Standard or most likely Datacenter licensing for Windows Server 2016 as Datacenter includes unlimited OS and container licensing running with Hyper-V isolation.
Conclusion
Irrespective of which edition of Hyper-V you choose to use in your environment, backing up your virtual machines is important.
Vembu BDR Suite is a comprehensive backup & DR solution to protect data across virtual (VMware, Hyper-V), physical (Windows, Linux, Mac), cloud (AWS, Azure) workloads and SaaS Applications (Office 365, G Suite).
Vembu supports agentless backup for Hyper-V VMs running on the Standalone host, Cluster, CSV, and SMB share. Learn more about Vembu Hyper-V Backup here.
Download a 30-day free trial of our latest version Vembu BDR Suite v4.1.0 and experience modern data protection for your environment.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment