Table of Contents
- Hyper-V Manager
- Virtual Machine Manager
- Windows Server Hyper-V
- Hyper-V Server
- Client Hyper-V
- Hypervisor
- Guest Operating System
- Host Backup
- Guest Backup
- Checkpoint
- Production Checkpoint
Throughout my IT career, I have found that the key to learning a new skill is to learn the terminology that is associated with the particular product or technology that I am trying to learn.
After all, the associated terminology will have been used in the product’s documentation, and in supplementary materials produced by bloggers and other content publishers.
Like any other IT technology, Hyper-V has some specific terms that you will need to know. This article lists some of the more widely used Hyper-V specific terms.
1. Hyper-V Manager – The Hyper-V Manager is one of the two management tools that is included with Hyper-V (the other tool is PowerShell). The Hyper-V Manager is a graphical management tool, whereas PowerShell is a command line tool.

2. Virtual Machine Manager – Virtual Machine Manager is a supplementary tool for managing Hyper-V. Unlike Hyper-V Manager, Virtual Machine Manager provides a consolidated view of all of the Hyper-V host and virtual machine resources throughout your entire organization.
Virtual Machine Manager is licensed separately from Hyper-V. It is a part of the System Center suite and is often referred to as System Center Virtual Machine Manager. Microsoft documentation also commonly refers to Virtual Machine Manager as VMM.
3. Windows Server Hyper-V – There are three different ways that Hyper-V can be deployed. The most common deployment method involves installing Hyper-V as a role on Windows Server. When Hyper-V is deployed in this way, it is sometimes referred to as Windows Server Hyper-V.
4. Hyper-V Server – Hyper-V Server is the name given to the free, standalone version of Hyper-V. You can download and install Hyper-V Server without having to install or license Windows Server. The catch, however, is that you will still need to properly license any operating systems that you install on your virtual machines.
5. Client Hyper-V – Client Hyper-V refers to the version of Hyper-V that is included with client operating systems such as Windows 10. Client Hyper-V is nearly identical to Windows Server Hyper-V but is not supported for running production workloads. Client Hyper-V is used primarily for dev/test purposes.
6. Hypervisor – Hyper-V is what is known as a hypervisor, which is a platform for running virtual machines (which are sometimes called VMs). There are two main types of hypervisors, which are called Type 1 and Type 2.
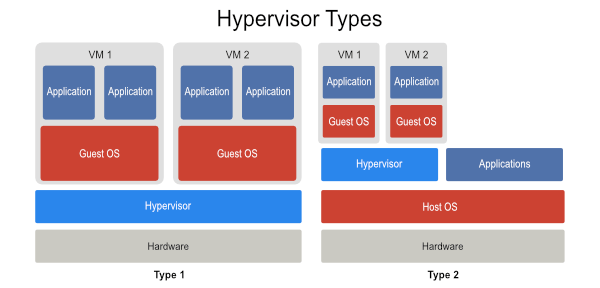
Older hypervisors are commonly Type 2, which means that the hypervisor runs on top of a host operating system. Type 2 hypervisors act as interpreters. They intercept commands from the virtual machine and then send it to the hardware for processing. Because of the dependency on a host operating system, Type 2 hypervisors tend to be slow.
Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor. Even though Hyper-V runs as a Windows Server role, it is still considered to be a bare metal, native hypervisor. The key difference between Hyper-V and a Type 2 hypervisor is that Hyper-V uses hardware-assisted virtualization. In other words, virtualization is supported at the CPU level by Intel VT or by AMD-V. This allows Hyper-V virtual machines to communicate directly with the server hardware, allowing virtual machines to perform far better than a Type 2 hypervisor would allow.
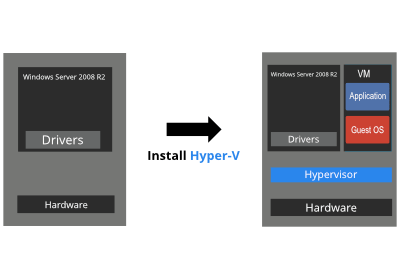
7. Guest Operating System – The guest operating system refers to the operating system that is running inside of a Hyper-V virtual machine. If for example, you were to create a virtual machine and install Windows 10 on it, then Windows 10 would be the guest operating system for that virtual machine.
8. Host Backup – A host backup is a backup that is created at the Hyper-V host level. The advantage to performing host backups is that you can backup Hyper-V and all of its virtual machines in a single backup job, as opposed to having to backup each virtual machine individually.
9. Guest Backup – A guest backup is a backup that is made of a specific virtual machine. Typically this means installing a backup agent into the virtual machine and backing up the VM in the same way that you might backup a physical server. Host backups are the preferred backup method for Hyper-V virtual machines, but guest backups are sometimes required. For example, guest clusters (a Windows failover cluster whose nodes are all virtual machines) commonly has to be backed up at the guest level.
10. Checkpoint – Checkpoints are a mechanism for reverting a virtual machine back to an earlier point in time without having to restore a backup. Checkpoints (which Microsoft previously referred to as snapshots) are based on a series of differencing disks. When an administrator creates a checkpoint of a Hyper-V virtual machine, all future I/O is redirected to a differencing disk, leaving the original virtual hard disk in the same state that it was in at the time that the checkpoint was created. If a rollback ever becomes necessary, Hyper-V removes the differencing disk and goes back to using the original virtual hard disk.
11. Production Checkpoint – Although checkpoints are convenient, they tend to cause problems for applications running on virtual machines. Production checkpoints are a newer type of checkpoint that uses the Volume Shadow Copy Services to maintain the integrity of applications running within the virtual machine.
As you can see, this article takes you back to the basics of Hyper-V through the most important terminologies. It is necessary to be strong at these basic technical terms to have a good start in your journey towards building knowledge on the Hyper-V Technology and its architecture.
Hyper-V Backup and Recovery: Protect your Hyper-V VMs with BDRSuite. Start 30-day Free Trial today!
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



I refer to the picture you used for explaining Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors. Should the “OS” immediate above Hardware in Type 2 be “Guest OS” or “Host OS”?
Thank you for pointing it out. We have made the necessary change in the image.