When you create a virtual machine in VMware, one of the settings you need to configure is disk mode. VMware disk mode refers to the mode in which a virtual disk in a VMware virtual machine operates. There are three disk mode types including dependent disk, independent-persistent disk, and independent-nonpersistent disk. All three of them differentiate in the way they operate and how they interact with other virtual disks and snapshots.
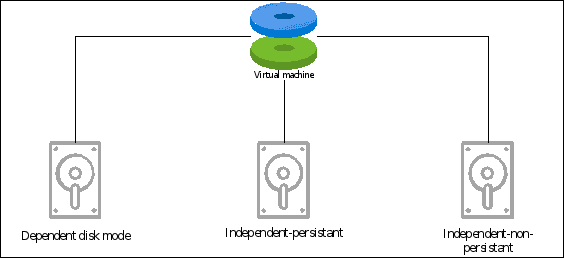
Table of Contents
- Dependent disk mode (OOBE)
- Independent – persistent disk mode
- Independent-nonpersistent disk mode
- How to configure or change the disk mode of a virtual machine?
- Wrap up
If you configure one type and decide later to change it, you can do it by reconfiguring the settings of your virtual machine. In this article, we will explain the different disk modes, and their use cases and explain the process of configuring them in VMware.
Dependent disk mode (OOBE)
This is the default disk mode your virtual machine will be assigned upon creation. The dependent disk is associated with the parent disk and can’t be used independently. When you create a virtual machine snapshot, the snapshot will include this disk in it.
When you revert the virtual machine to the snapshot, the dependent disk will reflect the state of the parent disk when the snapshot was taken. Dependent disks might not be the ideal solution for environments that require high levels of I/O performance.
If you delete a snapshot, the dependent disk will be merged with the parent disk.
Independent – persistent disk mode
Independent persistent disks are standalone disks that are not part of the snapshot chain. When you create a snapshot, it will capture the VM state. However, the independent disk will not be included in the snapshot. That means any changes made to the independent disk after the snapshot was taken will be retained, even if you decide to revert the machine to the snapshot.
If you delete a snapshot, the independent disk will not be affected.
Independent-nonpersistent disk mode
If you need the flexibility to test Windows updates or configuration changes without committing to them permanently, and easily revert back to a working state by simply rebooting your virtual machine, then this disk mode may be the ideal choice for you. Independent – non-persistent disk mode is a better alternative to snapshots.
Basically, upon every reboot, your system goes to its original state.
How to configure or change the disk mode of a virtual machine?
There are two methods for changing the disk mode of a virtual machine: one during the initial creation of the VM and the other after the VM has already been created.
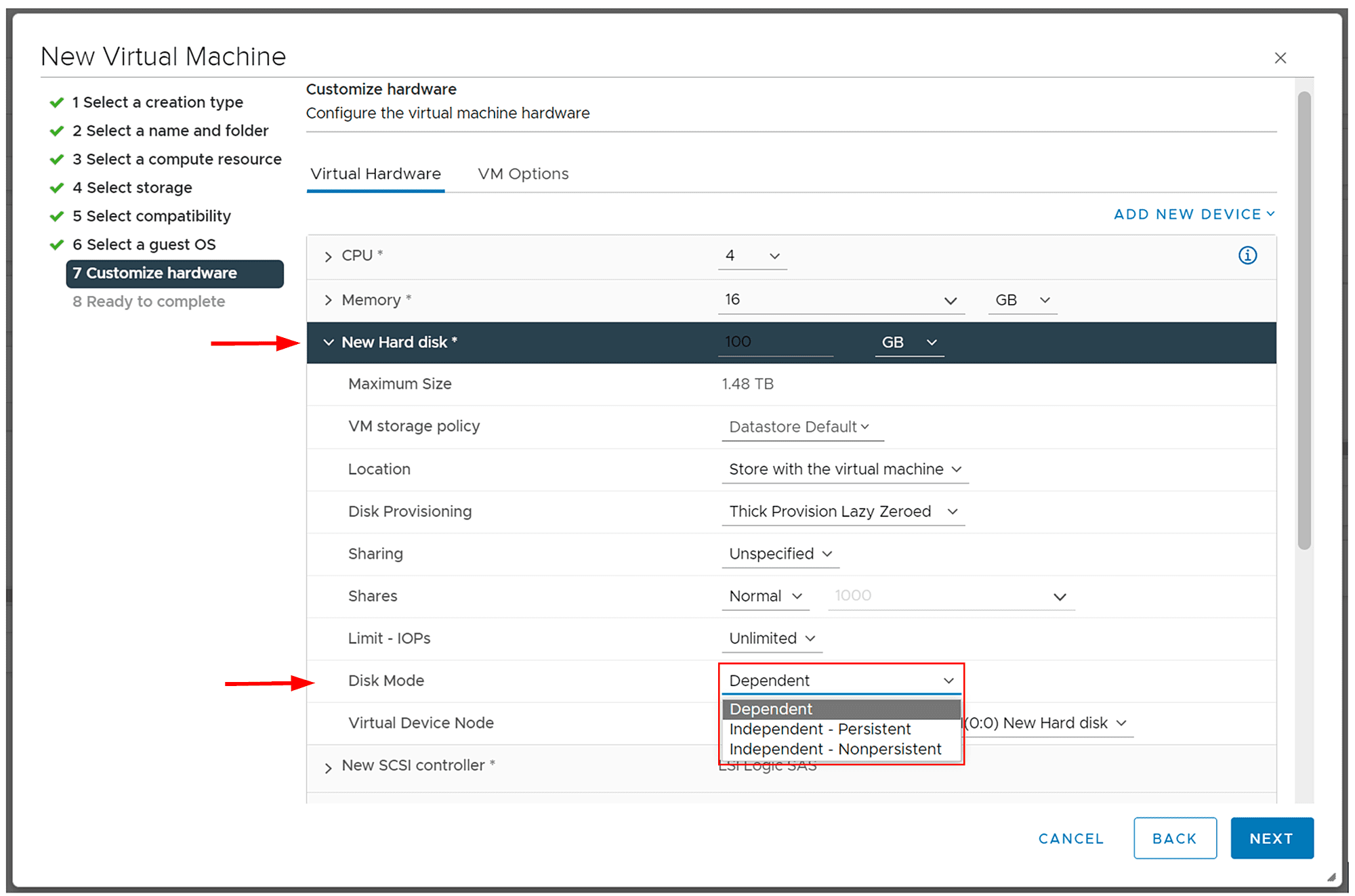
When you create a new virtual machine, you will have the opportunity to choose disk mode. Once you get to the point where you need to customize hardware specification (Customize Hardware), you need to expand the New Hard disk and then under Disk Mode change it to the one that fits your needs.
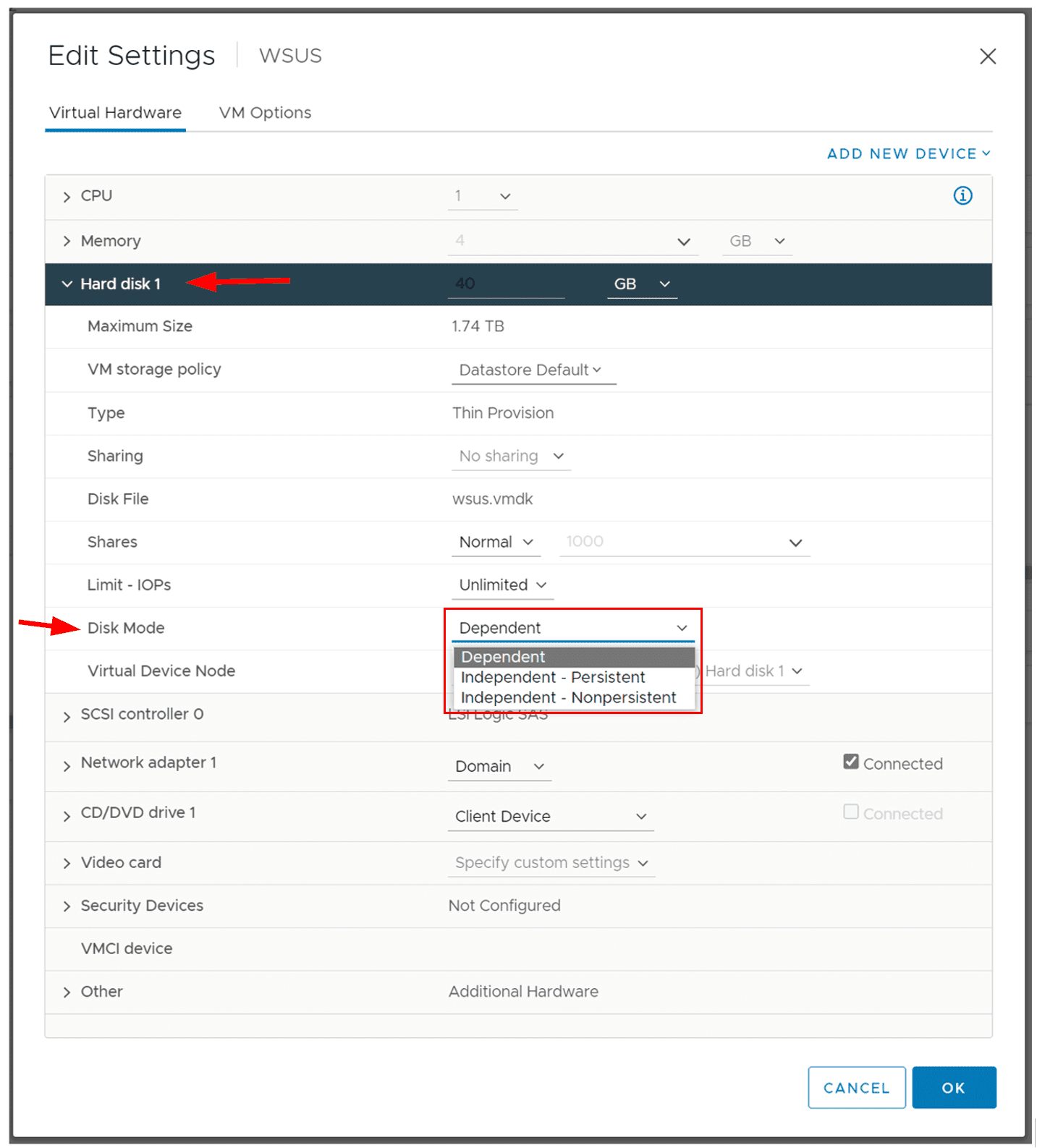
If you need to change the disk mode of a virtual machine that is already created and running, you can do so with just a few simple steps. You need to navigate to your virtual machine, right-click on the virtual machine, and then select Edit settings. Expand the Hard disk 1 and then under Disk Mode change it to the one that fits your needs.
Wrap up
VMware support three disk modes including dependent, independent-persistent, and independent-nonpersistent mode. All three of them differentiate in the way they operate and how they interact with other virtual disks and snapshots.
Each of them can be configured upon creating a virtual machine or afterward. This article covers the differences between these three modes and explains how you can configure them in your environments.
Related Posts:
The different types of vSphere virtual disks
VMware Virtual Disk Thick vs Thin Provisioning – Complete Comparison
The different types of vSphere virtual disks
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment