Read on
VMware for Beginners – vMotion and DRS: Part 11
VMware for Beginners – vSphere HA Configuration: Part 12(a)
VMware for Beginners – vSphere HA Configuration: Part 12(b)
VMware for Beginners – vSphere HA Configuration: Part 12(c)
Read More
In the last VMware for Beginners article, we discussed vSphere HA Configuration in three parts, and now that we have our vSphere HA enabled and working, we can configure vSphere Proactive HA.
What will we discuss in this vSphere Proactive HA:
- What is vSphere Proactive HA
- How does Proactive HA work
- How to configure Proactive HA
- What is the difference between Proactive HA and DRS
What is vSphere Proactive HA?
vSphere Proactive HA is a feature that provides enhanced high availability (HA) protection for virtual machines (VMs) by monitoring the health of the underlying physical servers and taking proactive measures to prevent potential failures.
Proactive HA monitors, the server hardware components such as memory, CPU, and storage, for potential issues that could lead to failure. It then uses this information to predict when a server could fail and takes proactive measures to avoid that failure.
For example, if Proactive HA detects that a physical server is running low on memory, it can automatically migrate VMs from one ESXi host to another ESXi host in the same Cluster with more available memory. This process allows the VMs to continue running without interruption, even if a server failure occurs.
Built on the core of vSphere HA, Proactive HA provides advanced monitoring and remediation capabilities to help prevent downtime and disruptions due to hardware failure.
In this blog post, we will discuss the features and benefits of Proactive HA, how it works, and how you can use it to keep your virtual infrastructure up and running.
How does Proactive HA work?
Proactive HA detects when an ESXi host is about to fail and then takes action to protect the VMs running on that host. It does this by using vSphere High Availability (HA) and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) to monitor the health of each ESXi host in a cluster.
Here’s how it works:
Proactive HA has 4 stages: Monitoring, Predictive Analysis, Remediation, and, Notification.
Monitoring: Proactive HA monitors hardware components of physical servers, such as memory, CPU, storage, and network. It also monitors environmental factors like temperature, power consumption, and other server health conditions.
Predictive Analysis: The monitoring data is analyzed by vSphere to predict potential hardware failures that might happen soon. For example, if memory usage runs high or the temperature rises above the acceptable limit, Proactive HA predicts that the server will soon encounter a problem.
Remediation: Once Proactive HA detects an impending hardware failure, it takes proactive measures to prevent it. For example, if a server is predicted to run out of memory, Proactive HA can automatically migrate VMs to other servers in the Cluster with more available memory. This ensures the VMs continue running without disruption, even if a server fails.
Notification: Proactive HA sends notifications to administrators when it detects an issue and takes action. The notification includes details of the problem and what action was taken, allowing administrators to respond if further action is necessary quickly.
Overall, Proactive HA provides additional protection for VMs in the vSphere HA and vSphere DRS by proactively identifying and mitigating potential issues before they cause downtime or data loss. It helps to increase the reliability of vSphere environments by detecting and addressing hardware issues early on.
How to configure Proactive HA
Select the Cluster that you want to enable Proactive HA, Configure tab, and in the vSphere Availability option for vSphere HA, you also have the option for Proactive HA, click Edit.
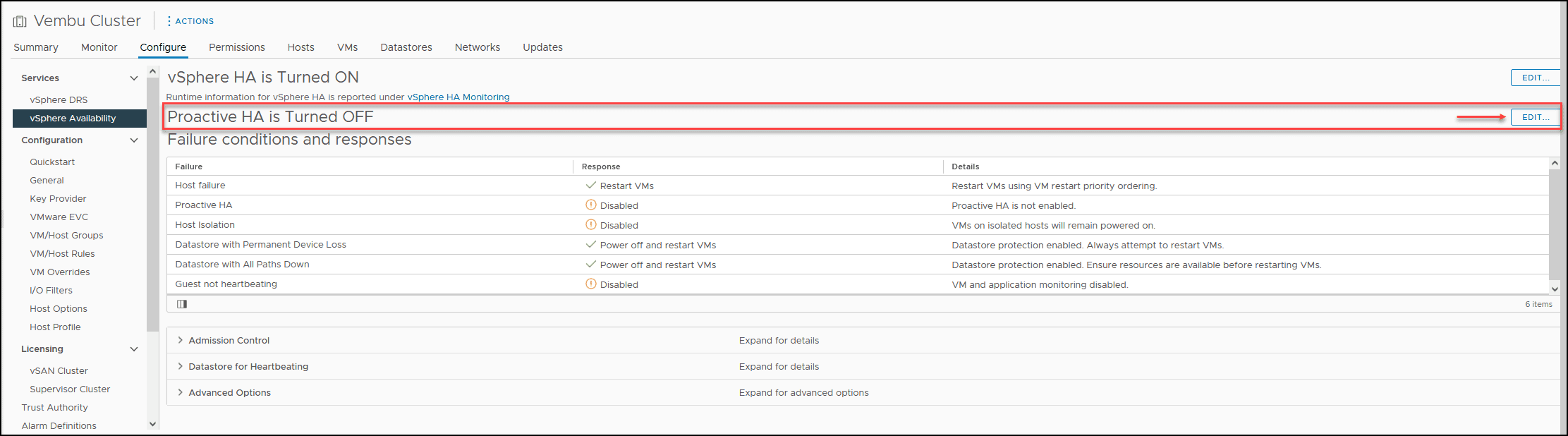
Then you enable Proactiva HA and select the Automation Level and Remediation option.
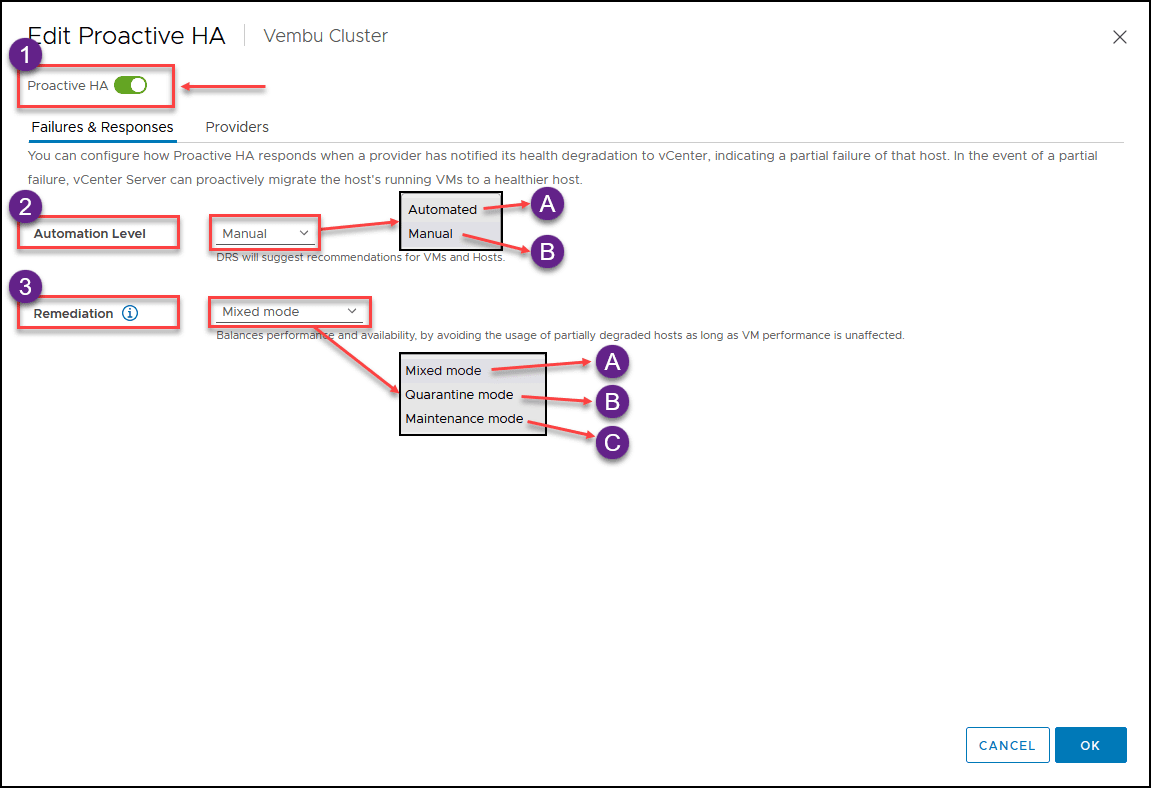
Let us explain both options:
- Automation Level Determine whether host quarantine, maintenance mode, and VM migrations are manual or automatic.
A. Manual: DRS will suggest recommendations for VMs and Hosts.
B. Automated: Virtual machines will be migrated to healthy hosts, and degraded hosts will be entered into quarantine or maintenance mode depending on the configured Proactive HA automation level - Remediation There are three types of Remediation in Proactive HA:
A .Quarantine Mode: Works for all types of failures. Balances performance and availability by avoiding the usage of partially degraded hosts, provided that virtual machine performance is unaffected.
B. Mixed Mode: Works for moderate and Maintenance mode for severe failures. Balances performance and availability by avoiding the usage of moderately degraded hosts, provided that virtual machine performance is unaffected. Ensures that virtual machines do not run on severely failed hosts.
C. Maintenance Mode: Works for all types of failures but ensures that virtual machines do not run on partially failed hosts
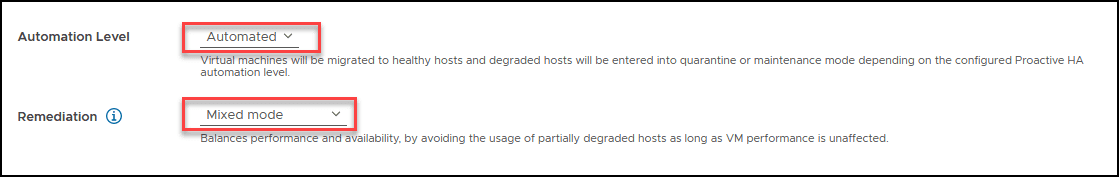
We will set the options to fully automatic: Automation Level to Automated and Remediation to Mixed Mode.
What is the difference between Proactive HA and DRS?
We have already discussed DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) here in the VMware for Beginners series, and readers may confuse about Proactive HA and DRS. They are not the same thing.
Proactive HA and DRS serve different purposes. But as discussed above, DRS must also be enabled to enable Proactive HA.
Proactive HA primarily focuses on identifying and mitigating potential hardware failures before they occur, such as predicting server component failures (like power could be a failure in a power supply, storage, disks, and network) and monitoring issues with server temperature. Proactive HA takes proactive actions to avoid this type of service disruption.
On the other hand, DRS is a feature that provides intelligent resource management for virtualized environments. DRS is designed to optimize resource utilization and balance workloads across ESXi hosts by automatically migrating VMs to hosts with more available resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage.
DRS helps to ensure that resources are used efficiently and workloads are evenly distributed, which can help to improve performance and reduce the risk of performance bottlenecks.
In summary, while Proactive HA and DRS are designed to improve the performance and reliability of virtualized environments, Proactive HA is focused on identifying and mitigating hardware failures before they occur, while DRS focuses on optimizing resource utilization and balancing workloads across ESXi hosts inside the Cluster.
Conclusion
Proactive HA is a valuable feature in VMware’s vSphere virtualization platform especially for cluster setup that provides enhanced high-availability protection for virtual machines by monitoring the health of the underlying physical servers and taking proactive measures to prevent potential failures.
Proactive HA helps to ensure that VMs continue running without disruption, even if a server failure occurs. Proactive HA can predict any hardware failures automatically in your VMware environment and takes remedial actions. This feature provides an additional layer of protection for your vSphere HA and vSphere DRS, helping to increase their reliability and minimize the risk of downtime or data loss.
vSphere Proactive HA is a powerful feature for VMware administrators to ensure their virtual machines remain highly available, even when faced with hardware outages.
In the upcoming VMware for Beginners series articles, we will discuss and learn about vSphere Fault Tolerance (FT).
Read more on our VMware for Beginners series:
VMware for Beginners – Overview of vSphere: Part 1
VMware for Beginners – vSphere Installation Requirements: Part 2
VMware for Beginners – How to Install vSphere: Part 3
VMware for Beginners – vSphere Networking: Part 4
VMware for Beginners – vSphere Datastores: Part 5
VMware for Beginners – vSphere Virtual Machines: Part 6
VMware for Beginners – How to Install vCenter: Part 7
VMware for Beginners – Datacenter and Clusters: Part 8
VMware for Beginners – How to Create and Configure iSCSI Datastores: Part 9(a)
VMware for Beginners – How to Create and Configure iSCSI Datastores : Part 9(b)
VMware for Beginners – How to Create NFS Datastores: Part 10(a)
VMware for Beginners – How to Create NFS Datastores: Part 10(b)
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.



Leave A Comment