Direct Storage Access (SAN)
- Direct SAN transport mode will be selected if VMs disk are connected to the ESXi hosts, and their disks are located on a VMFS SAN LUNs. Data will be directly read from the SAN storage, this mode will be the fastest if your VMs are kept connected to ESXi host through a shared storage.
- SAN transport mode performs best when deployed in a physical environment for backup. It performs the best and worst in some cases. The performance is great in a thick disk but does not perform well in a thin disk.
- The data is directly read from the NFS datastore that is connected to the Vembu BDR backup server. The data is transported over a LAN connection if the SAN accessibility is open.
Prerequisite -
Vembu BDR backup server must run in a physical machine with access provided to FibreChannel or iSCSI SAN which contains the virtual disks that is to be accessed. A VM in SAN Storage or iSCSI SAN storage in the same ESXi server and the presence of VDDK libraries in an appropriate location.
Guidelines -
- During SAN restore CBT must be disabled
- Writing to redo logs are not supported
- Will work only in a physical machine and with SAN storage or Fiber Channel or iSCSI SAN Storage
We recommend you to attach the SAN and iSCSI storage properly.
We recommend you to set the temp directory path correctly.
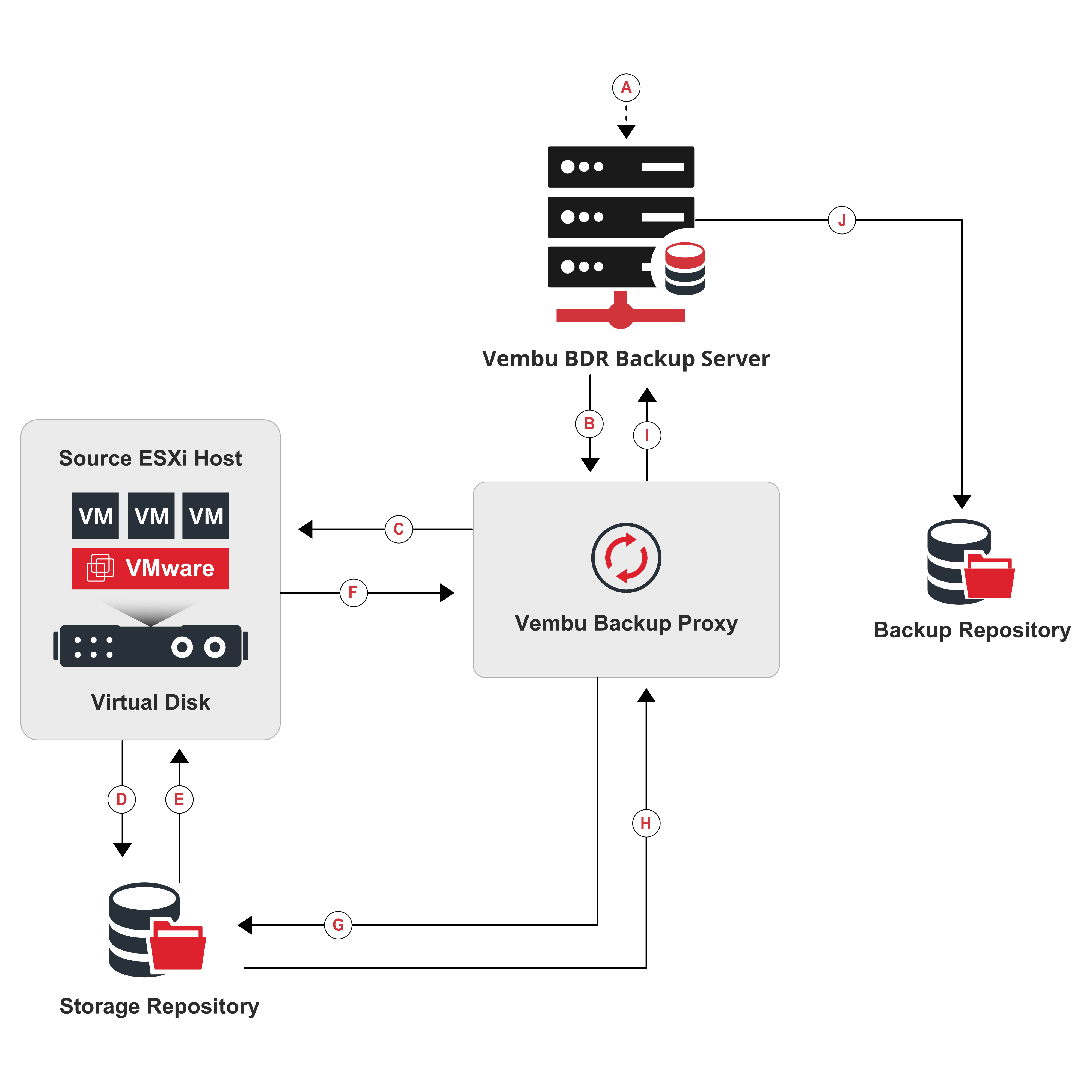
Working -
- The backup job is triggered from the Vembu BDR backup server and a initiation is sent to the Vembu backup proxy that the backup process is taking place.
- The Vembu backup proxy then request the ESXi host to fetch and locate the details of the VM from the datastore. Vembu BDR backup server also sends an acknowledgment to the vSphere host to take a snapshot.
- The ESX(i) host fetches the details of the VM (meta data) and sends it back to the backup proxy. The backup proxy sends this meta data to the Vembu BDR backup server.
- The backup server backups the data directly from the source and sends it to the backup repository.
