Windows Image Backup
Before you begin configuring the backup job, keep in mind that you have to balance the load equally in the source and target because if backups are triggered simultaneously, it will cause the backup job to run slower, the reason being the disk will be accessed at the same time by different jobs.
There are five steps in Windows Image backup configuration. The section below explains the working of each functionality along with the guidelines.
- Choose drive(s)
- Guest Processing
- Schedule
- Settings
- Review
Read this section for more - Step 1 - Windows Image Backup
We recommend including boot partition (System Reserved) in the backup so that the backed up image is bootable during the restore.
Guest Processing
Read this section for more - Step 2 - Windows Image Backup
Application-Aware Image Processing
- This feature provides data consistency for the applications (MS Exchange Server, MS SQL Server, MS SharePoint Server, MS Active Directory) that reside in the machine.
- Refer our documentation for further explanation on the steps involved while you configure Guest Processing.
- In a Windows environment, Vembu BDR backup server connects to the guest machine and performs the guest processing if application-aware is enabled.
- Since agent push process is taking place, Guest OS credentials will not be required.
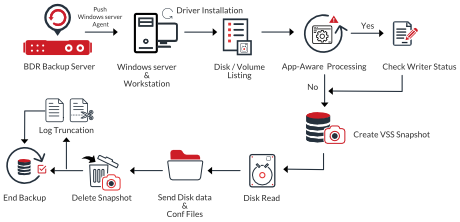
How Application -Aware Works
- Vembu BDR backup server checks if the Appwareguestool.exe file is already present in C:\Windows.
- If the .exe file is already present, the file will be removed and pushed again. The tool installation will happen, this is the pre-read and write process.
- This process ensures the writer stability. From the C:\ Windows location, Appawarestatus.txt file will be read to check if the status is stable or not. The log truncation takes place after this.
- Regarding the sizing, no special guidelines are required. Ensure free space in each drive for VSS Snapshot.
- No ports are necessary to be open between the Vembu BDR backup server and the Guest machine.
- A user account for application-aware image processing should have administrator privileges in the guest machine.
Configuring Backup Schedule
- When you trigger a backup job for the first time, a full backup will be performed. The backup data is read as a whole (irrespective of changed files) and is stored in your storage repository. The data will be compressed and when a new full backup is triggered, a completely new backup chain will be formed.
- We have three options for scheduling your backup, they are - Run Every, Run Daily, Run Weekly. Schedule frequency begins from 15 minutes, select this option only for your critical VMs as RPO will be less than 15 minutes.
- Read more on configuring backup here - Step 3 - Configuring Backup Schedule
We recommend you to use separate storage for backup jobs. Do not combine your backup data with production data.
Retention
- If you have configured retention policies, the previous full backup can be purged if they match the retention settings. Note that the incremental backup will be generated based on the changes that happen in the initial full backup and depend on them. Once the full backup schedule is completed, the incremental backups will start. They will be stored in the storage repository as an SGCF file (Chunk).
- The backup data is stored in the storage repository in a compressed format. The backup data is compressed so that the amount of data transferred across the LAN is reduced. The compression takes place at the block level using the AES-256 bit algorithm. By default, compression will be enabled.
We do not recommend you to disable compression.
- If your aim is to store space more efficiently, you can opt for the Forever Incremental process. In this process, only one full backup will be created (FBM) and from there on, incrementals alone will happen.
- Since there is only one full backup created in the storage repository, you save a lot of space. Based on the previous incremental file the next incremental file will be created thereby maintaining the backup chain.
We do not recommend you to use this method if you make changes too frequently as the merge process takes time.
Encryption Best Practices
- Encryption protects your data from unauthorized users and intruders. Using the AES-256 bit encryption algorithm, your backup data will be encrypted both at rest and on the fly. Without the encryption key, access to the backup data will be blocked. This ensures your backup files are secure.
- By default, your backups will be encrypted using the system-generated password even if Encryption is disabled. You can opt to a custom password for extended data protection and you will be required to provide it during recovery. Opting to the custom password will disable integrity check from being performed automatically.
You must configure encryption if -
- Your backup data can be easily accessed by intruders
- If you are configuring offsite copy
- If your organization's policy includes configuring encryption
We do not recommend using the same name for Password and its hint to avoid security issues.
You can configure encryption in two ways -
- When you configure the backup schedule
- From the Settings tab - Data Encryption.
Do not configure encryption if your backup jobs must run fast.
We recommend you to re-verify your backup schedule and drives that are configured for the backup job, they cannot be edited.
Windows Image Backup Anatomy
- An sbc file will be created and sent to the backup server with details regarding the backup job. The server sends an ACK that it is ready for data transfer. When the backup is triggered, the configured drives will be listed for backup.
- Using the Voltracker.sys, the individual drives will be listed for backup. To track this listing we use the Bitmap.dat file.
- For Windows, the VSS utility will take a snapshot of the selected drives. The drives will be frozen up to 300 milliseconds.
- Data transfer will begin and the data will be sent as 512 KB blocks to the backup server. After receiving the backup data, Vembu BDR backup server will send an ack back to the client stating that all the files are received and the connection is closed. The connection is closed in the client side as well.
- Once the connection is closed, the following tasks will take place -
- Blocks will be stored as chunks in the backup server
- DB Updation process will begin
- Reports will be generated
- You can check the log files for detailed information.
The working of Windows Image backup is explained with the help of an architecture diagram below -