Disk Rotation Backup Repository
Backup Disk rotation is one of the most popular strategies in which the backup data is stored to an external media device, such as a USB stick or external hard drive. Usually, two or more external media devices are used to set up the Backup Disk Rotation, and these external media used for disk rotation are swapped periodically based on the backup/data protection policy such as weekly or monthly.
Each external media device contains the full backup copy and the subsequent incremental backups. The disconnected media devices are generally kept in different physical locations so that they can also be used during data loss or DR scenarios.
Why Backup Disk Rotation?
The Backup Drives are rotated to,
Store a copy of business-critical backup data separately on different media that stays offline.
Setup offsite backup copies for Disaster Recovery.
Comply with the access control policy, where data has to be stored only on authorized devices.
Comply with legal & long-term data retention policy.
Steps to set up Disk Rotation Backup Repository
Step 1: To set up rotated drives for the backup storage, you need to first create a Disk Rotation repository using one of the external storage media connected to your backup server.
Step 2: Go to BDR Infrastructure > Backup Repository > Block Storage & click on Create New Block Storage Repository.
 Step 3: Provide a Name for your repository, select Disk Rotation as repository type & select a drive(1st drive) to use as a storage destination.
Step 3: Provide a Name for your repository, select Disk Rotation as repository type & select a drive(1st drive) to use as a storage destination.
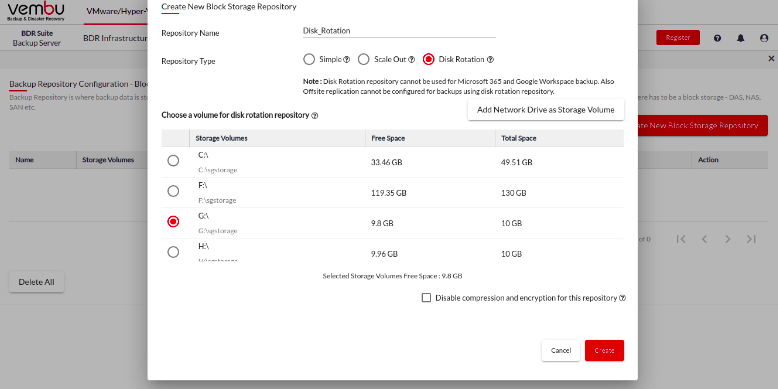
Note down the current drive letter of the drive when selecting it to create the Disk Rotation repository. In our case it is the ‘G:\’ drive, you have to connect the next rotating drive using the same drive letter.
Once the Disk Rotation repository is created, you can use it as a storage destination when creating backup jobs. A folder named ‘storage’ will be created in the drive selected for the rotation.
Working of Disk Rotation Repository
- The BDR Backup server will capture the UUID of the first external drive connected to the disk rotation repository and send the full backup data to it. For example, let us assume that the initial full backup data is sent to the G drive.
- During the successive backup schedule, BDRSuite Backup Server will continue to send the incremental data if the same drive is still connected.
- During the successive schedule, if the full backup or any of the incremental backup is missing, the BDRSuite Backup Server will send a new full backup again which is followed by the incremental backups.
- In between the backup schedules, if you want to send the backup to the new drive(swapping the drive), you have to disconnect the first drive and attach the new drive(2nd drive) using the same drive letter as the first one. In our case, the second drive has to be attached to the backup server machine as G:\ drive.
- During the successive schedule, the BDRSuite Backup Server detects the new drive and captures the UUID of the second external drive connected to the disk rotation repository. It then sends the full backup data to the new drive(2nd drive).
- The BDRSuite Backup Server will continue to send the incremental data to the new drive(2nd drive) until it is swapped with a new drive(3rd drive) or older drive which was used earlier. Make sure you are connecting the new drive using the same drive letter for the first time.
- If you are reusing the already used external drive, it may not need to be attached using the same drive letter. The BDRSuite Backup Server automatically identifies the drives used for disk rotation using its UUID.
- During each backup schedule, the BDRSuite Backup Server will check for the latest backup in the drive currently attached to the Disk Rotation repository. If the latest backup is found, the BDRSuite Backup Server will continue to send the incremental schedules to the currently attached drive. If it is not the latest backup schedule, then BDRSuite Backup Server will send a new full backup.
- If you are reusing a drive, say the 1st drive again, then BDRSuite Backup Server will send a new full backup as it does not contain the latest backup schedule.
- If there is no drive mounted on the drive letter used for Disk Rotation(G:\ drive). But the already used drives are attached to the machine with different drive letters, then the drive having the recent backup will be chosen and its drive letter will be updated in the Disk Rotation repository and the incremental backup is sent to that drive.
- If the Drive letter of the Disk Rotation is updated, you have to attach the new drive using the updated drive letter to use it for backup disk rotation
- If there is no drive mounted on the drive letter used for Disk Rotation, and no already used rotated drives are attached to the backup server machine then the backup schedule will be failed.
- If you have configured additional full backup, the full backup cleanup will happen at the disk level based on the retention policy
- During recovery, only the recovery points of the currently attached drive are available for selection. The recovery points of the other drives are not available for recovery.
|
