Disk Mount
Disk Mount
This feature is not applicable to Linux Server |
- There may be situations in which you may want to access your backup data instantly, without having to restore the entire backup. Disk Mount option will be helpful in such scenarios. You can auto-attach your backup data to the disk management and find your backup data available in the VembuVirtualDrive in various file formats such as IMG, VHD, VHDX, and VMDK.
- When the backup data is attached to disk management, the files will be created virtually by mounting the backup data. This restore type will be helpful in times of disk corruption. The restored virtual disk can be attached to any physical machine later.
Procedure
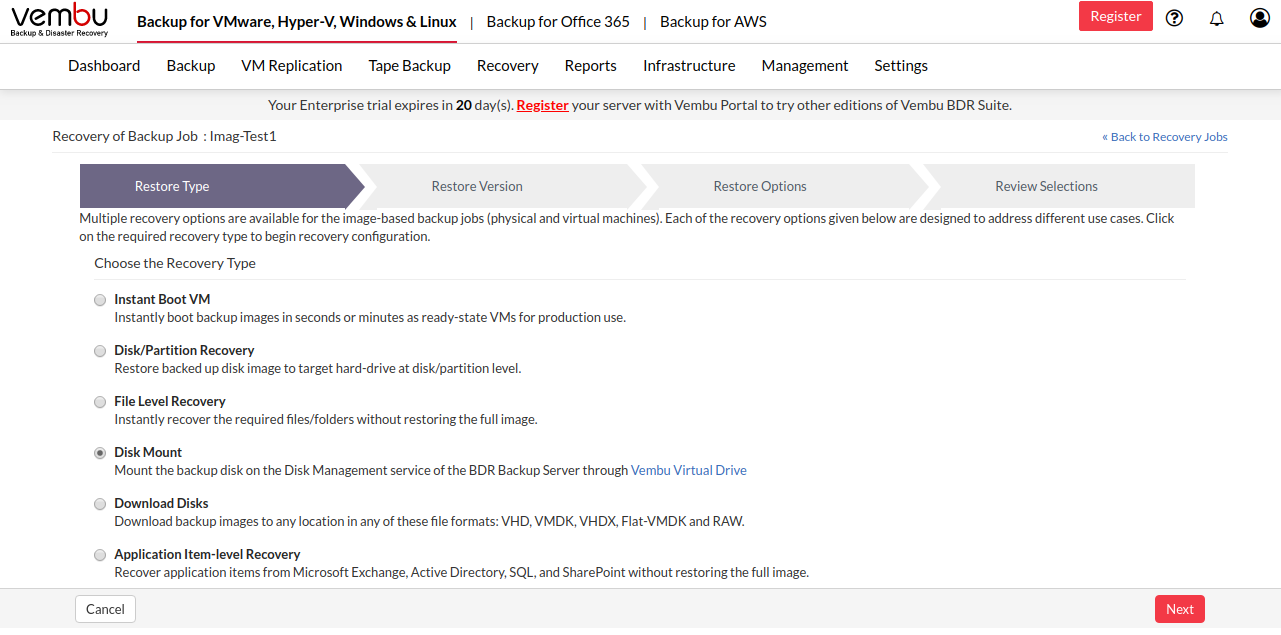
Step 1: Choose Restore Type
- Click the Recovery tab and select the restore icon near the Windows Image Backup that is to be restored. Select Disk Mount as the Restore type and click Next.
Step 2: Choose a Restore Point
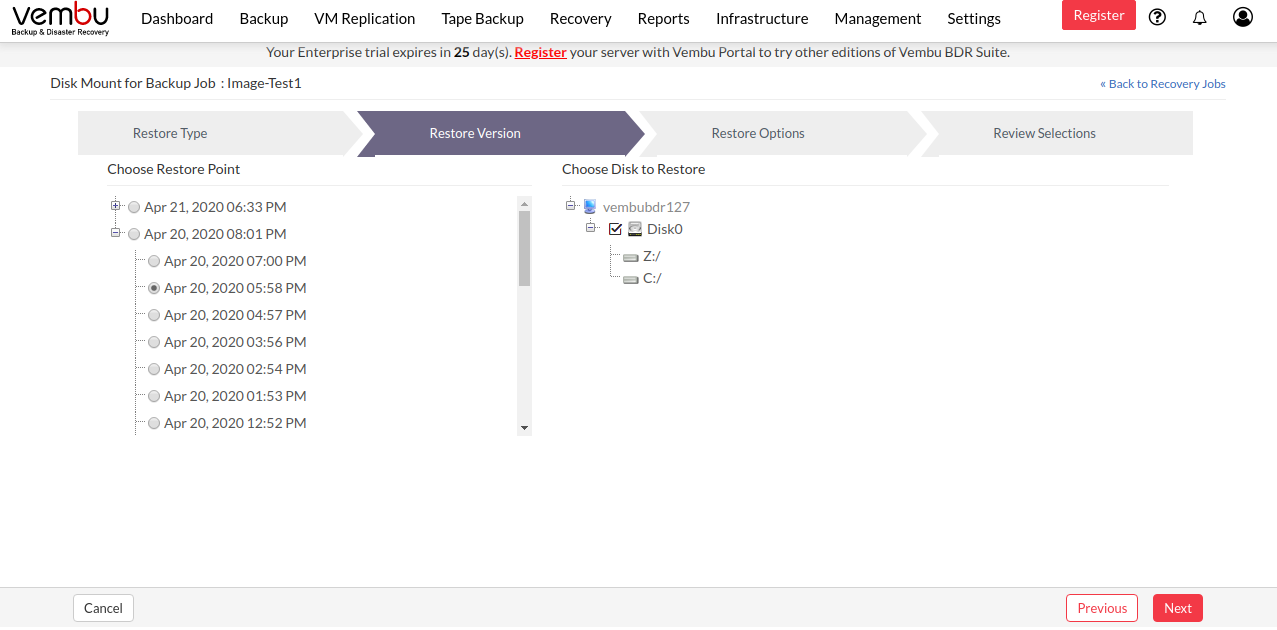
- Select the restore version for the restore process. The restore version is created based on the end time of the backup (i.e the date and time when the backup process scheduled is completed), this is named as Recovery points. The full backup and incremental backup time-stamps are listed with the latest backup version as a parent node and old backup version further sub-nodes. You can fall back to the required time-stamp whenever needed to recover the backed up data.
- If you have configured Additional full backups, then separate restore version time-stamp is created for each full backups with another tree structure.
- If the restore time-stamp version is denoted with symbols (d), (w), (m), (+P) at the end, indicates that the Daily Merge (d), Weekly Merge (w), Monthly Merge (m), and Persistent boot changes (+P) process has taken place on the version. Here (d), (w), (m) restore version specifies the merge process has done on the recovery point and Persistent boot changes (+P) specifies the Quick VM Recovery process has been done for that version.
- If you select Restore version time-stamp with (+P), you have to enable Include persistent boot changes in restore option to include the changes done during the previous boot restore process. If you don't enable the check-box, then the changes will not be included in the selected recovery process.
- You can select the full backup time-stamp for restore as well as the individual incremental time-stamp version for the restore process. On selecting the full backup recovery point, only the data of the full backup version is restored.
- Once done selecting the time-stamp version, click Next to configure the Restore data.
You can select only one time-stamp for the restore at a time |
Step 3: Choose the Disk to Restore
- Once you are done selecting the restore version, the next step is to select the Restore data. Select the disk that has to be mounted in the disk management for the restore process. Click Next to proceed to review your configurations.
You cannot mount more than one disk simultaneously. Choosing multiple disks for mount process will display the error message “User allowed to restore only one disk at a time". If you choose multiple disks, previous selection should be ignored |
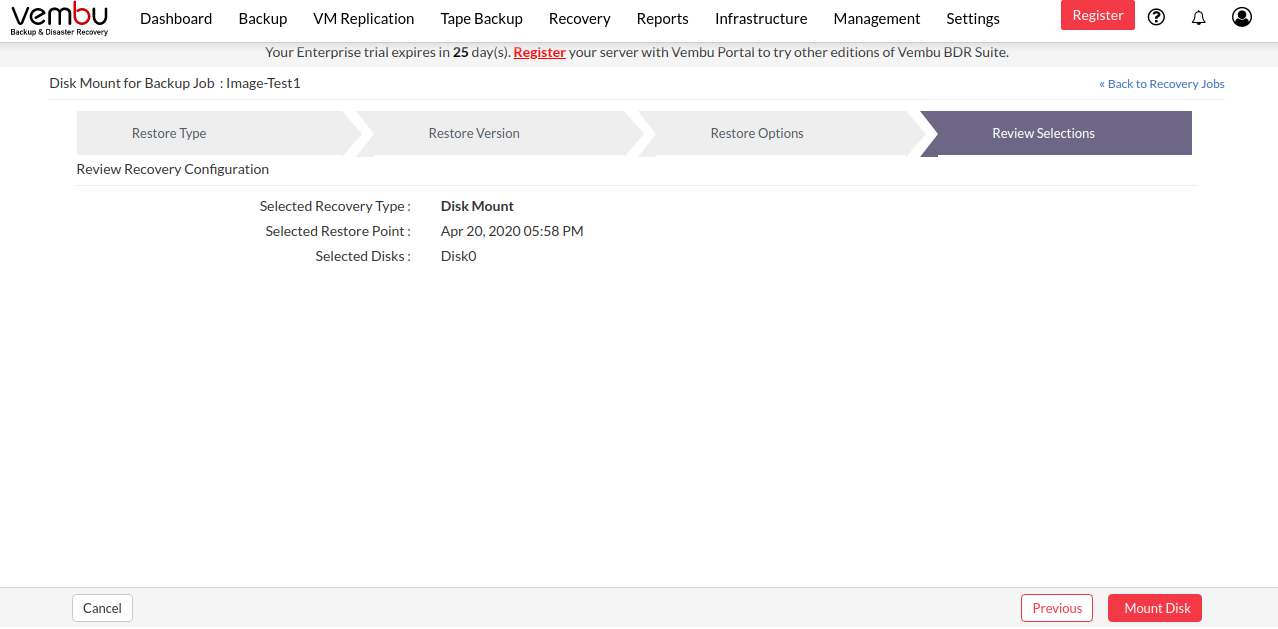
Step 4: Review Recovery Configuration
- The final step in this restore process is to review the configurations you have selected.
- Check the following:
- Restore type
- Restore version
- Selected Disk/Drives
- Verify all the details and click Restore Now. This will trigger the Disk Mount process.
Once done with the requirement, unmount the backup data. This will resume the backup job so that increments will run as per schedule |
- You will be redirected to the recovery page. In the Status tab click the arrow mark which will open the restore progress window.
- The following details will be available in the restore progress page:
- Backup Schedule: The backup schedule name mentioned by the user for indicating the backup during restore progress
- User Name
- Current File
- Total Files: The number of files present in the selected backup
- Transfer Rate: Speed of the restore process
- Bytes transferred: Rate at which the backup data is restored (Bytes, KB, MB, GB)
- Files Restored: Number of files restored during the process of recovery
- Time Left: Time remaining for the restore to complete

To enhance the restore performance, close the restore progress window and open it occasionally to check the restore progress |
- Open Disk Management. You can find the restored disk attached, indicated in blue.

