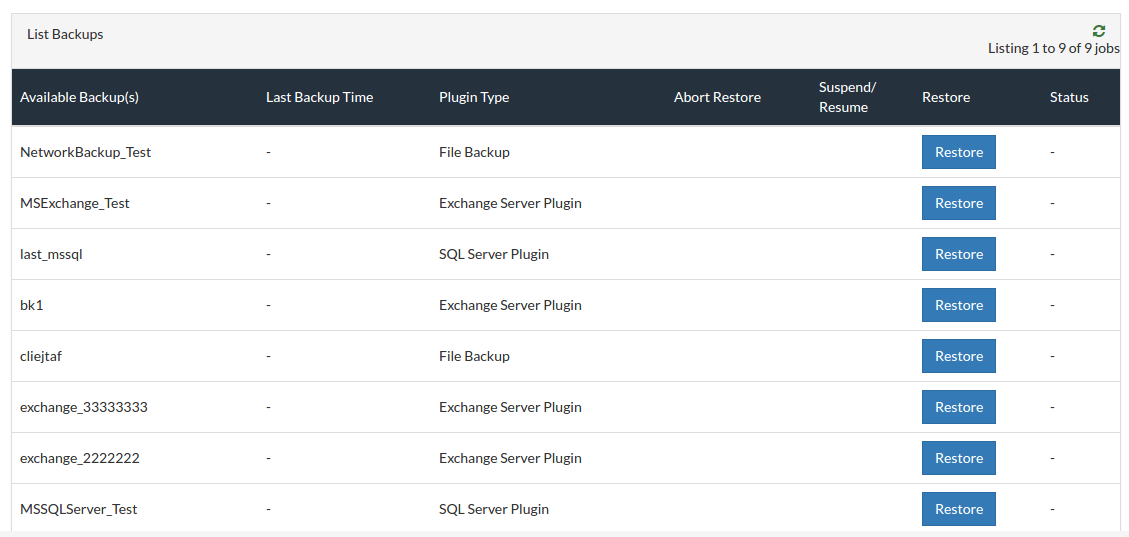
File Restore
Your files and folders can now be restored easily through Vembu NetworkBackup and does not require any help of administrators. More than one file can be restored at a time from the Vembu NetworkBackup client simultaneously.
Beginning the Restore Process
- From the Restore tab, click the Restore option that is available alongside the backup you want to restore. The plugin type will also be displayed near the backup name. Begin your restore process.
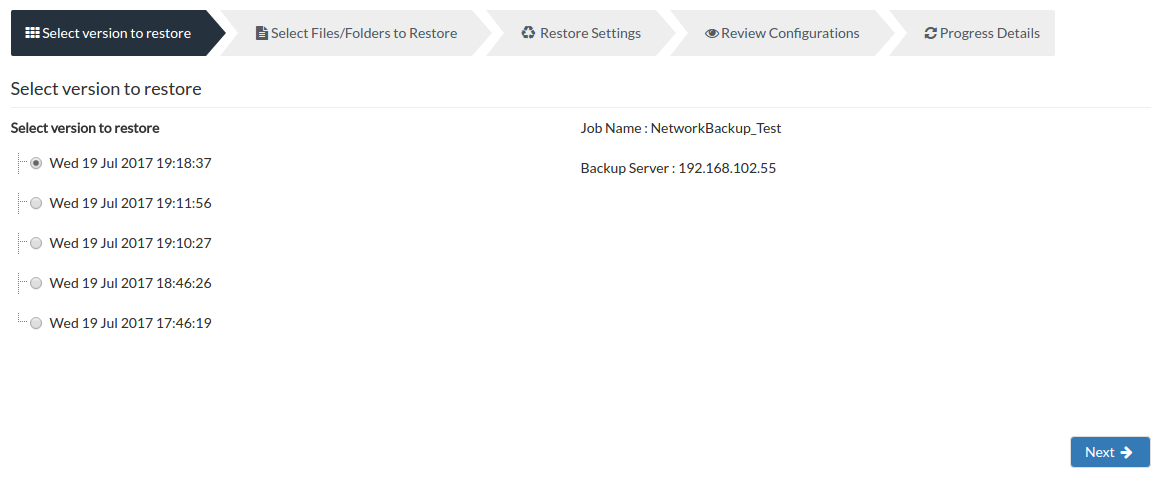
Step 1 - Select version to restore:
A tree listing various backup timestamps with the full backup as its parent node will be displayed. This list generated is based on incremental and retention configured. If additional full backup is configured, then there will be more than one parent node list based on the configuration.
- Select the time-stamp from which you want to restore data and proceed to select files/folders. The IP address of the backup server and the name of the backup you are restoring will be available just in case you have selected another other backup for restore. The Restore version will be in the following format: Day/Date/Month/Year/Hours/Minutes/Seconds. Click Next to select the Files/Folders for restore.
Step 2 - Select Files/Folders:
- Your backed up files and folders will be available in a Tree format based on the chosen time-stamp. Select the required files/folders and click Next to proceed with the restore process.
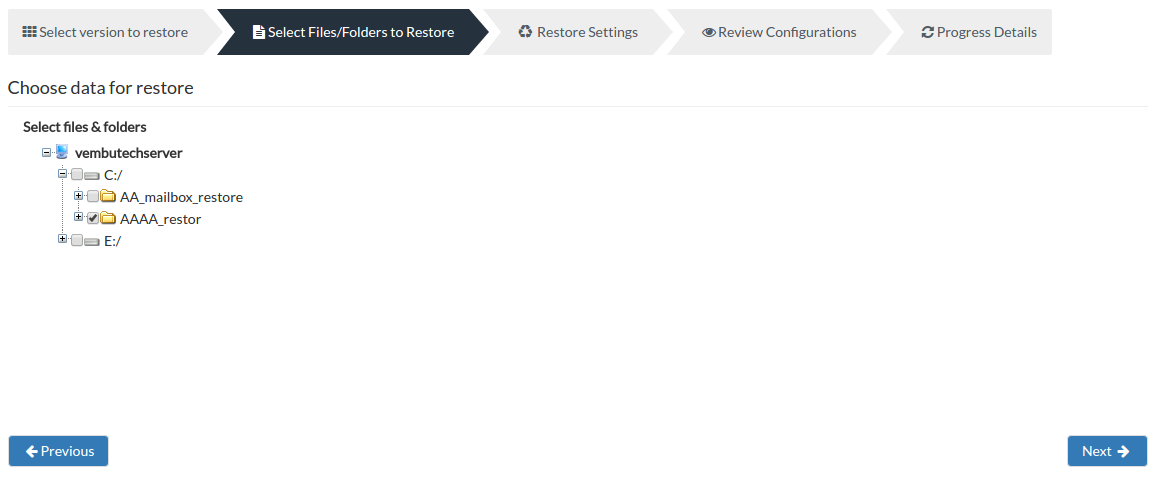
You can select files/folders in 3 ways. You can either:
- Select the root folder to proceed with restoring entire backed up data for the chosen time-stamp.
- Select specific files and folders alone based on requirement and proceed with the restore.
Step 3 - Restore Settings:
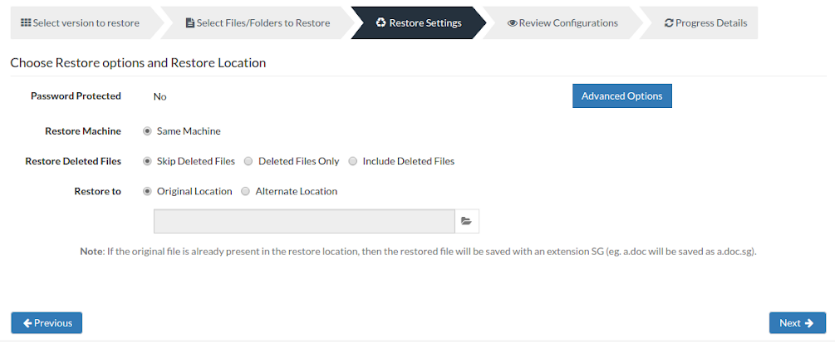
Password Protected - This option will display whether the backup is password protected. If encrypted, provide the respective password.
Restore Machine- This option will display the machine to which the restore is happening. In this case, the client machine is the restore machine.
Restore deleted files- You have 3 options to configure from:
- Skip deleted files (Restore backup data skipping deleted files) - Choosing this option will not restore the deleted files and skip them instead.
- Deleted files only (Restore deleted files alone) - This option will restore the files that are deleted alone and omit the other backed up data from the restore process.
- Include deleted files (Restore backup data along with deleted files) - This option will restore the backup data along with the deleted files.
Restore to(This gives two optional location to choose from):
- Original location- This option is available if the backup is restored to the same machine, where the backup data is restored to its original folder location.
- Alternate location- This option allows you to restore the backup to a different location, where backup data is restored in its original folder structure.
Note: If the source file is already present in restore location, then restored file will be saved with an extension ‘*.sg’. ( This can be changed using “Advanced Options”).
Advanced Options:
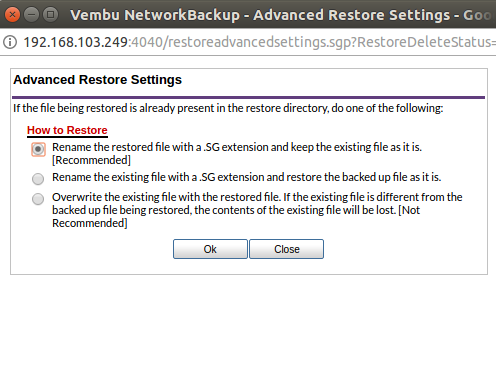
When backup data is restored, it is possible that source files are already present in restore location. In this case, Vembu NetworkBackup will retain the source file by default and restore files by renaming with a *.sg extension.
'Advanced Settings' allow alternate options to change this, they are:
- Rename the restored file with *.SG extension and keep existing files (This is the default option selected).
- Rename the existing file with *.SG extension and restore backup file as it is.
- Overwrite the existing file with restored file. (If the existing file is different from backed up file restored, the contents of source files will be lost. Choose this option if you are sure that current file can be overwritten).
Step 4: Review Configurations
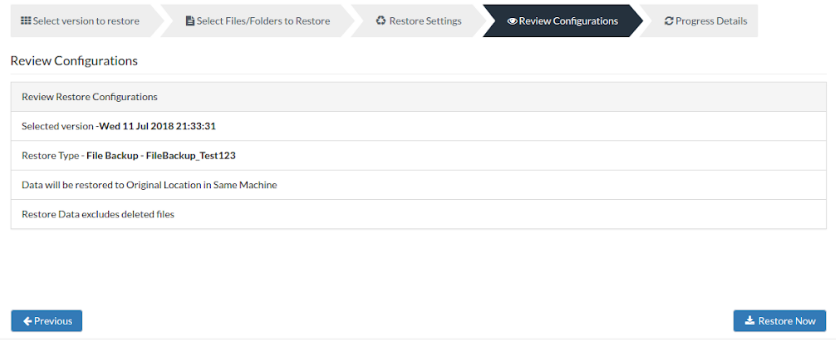
- You have reached the final step of the restore process wherein you have to review the configuration you have provided and click Restore Now option. This will trigger the restore process. Review restore progress and make sure it gets completed successfully.
- You can view the status of the Restore from the 'Status' option. Once you click the inverted arrow mark, the page displayed below will be available.
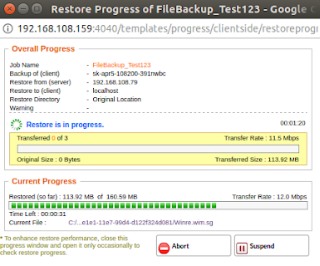
The following details will be available in the Restore Progress Page:
Job Name: Name of the backup job
Backup Of: Client Name
Restore from: From where the restore is happening, either from Client or Server
Restore to: To where the restore is happening.
Restore Directory: The location to where the restore is taking place.
Warnings (If any)
Transfer Rate: Speed at which the restore is occurring
Transferred Size: The amount of backup data that is transferred
Original Size: The actual size of the backup data
Time Left: Time remaining for the restore to complete.
Current Progress: The progress of the restore, it will depend on how much data is restored.
- You can abort your restore if not required from the Abort (-) option available in that window. You will get a pop up as shown below. Click OK to Abort your restore.
Note: To enhance your restore performance, close the progress window and open it only occasionally to check restore progress.
- You can suspend your restore if not required from the Suspend option available in that window. You will get a pop up as shown below. Click OK to Suspend your restore.